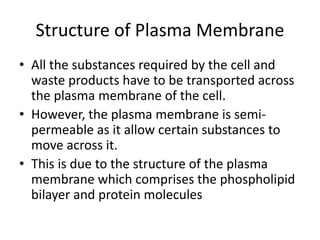
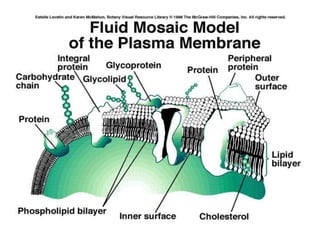
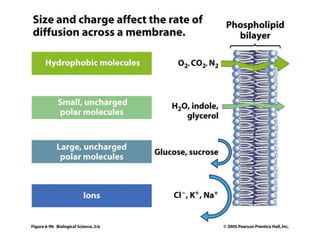
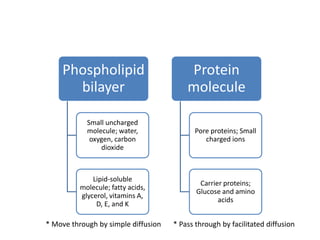
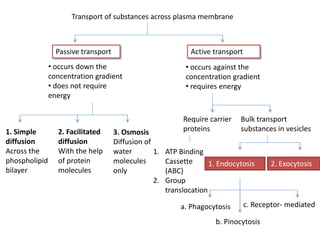
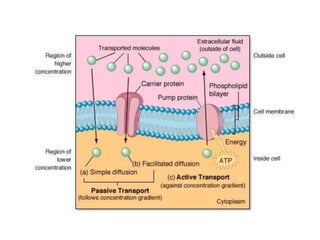
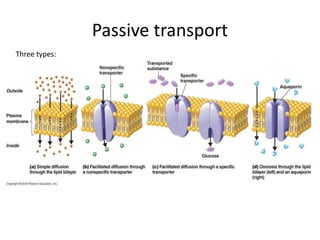
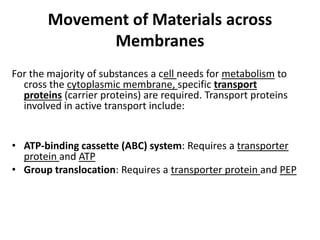
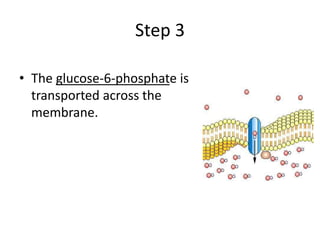
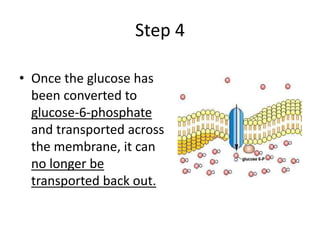
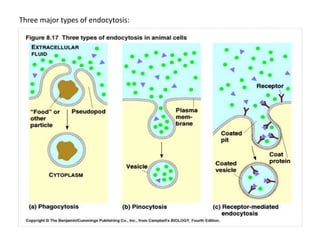
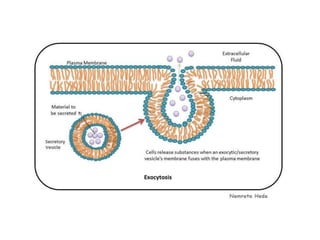
The document summarizes the structure and functions of the plasma membrane in transporting substances into and out of cells. It discusses that the plasma membrane is semi-permeable and allows movement of substances through passive transport mechanisms like simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis as well as active transport powered by ATP. Active transport and bulk transport use vesicles and carrier proteins to move substances against their concentration gradient.