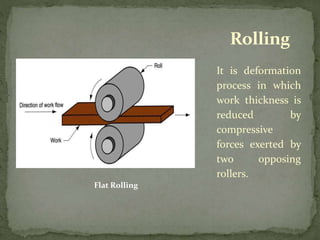
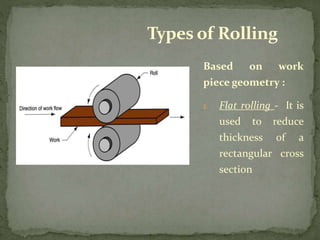
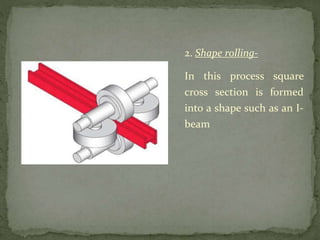
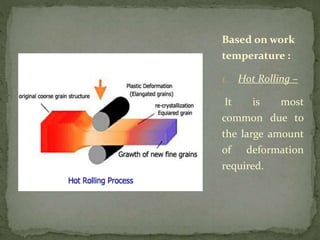
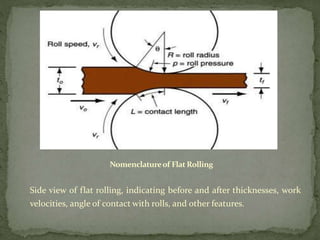
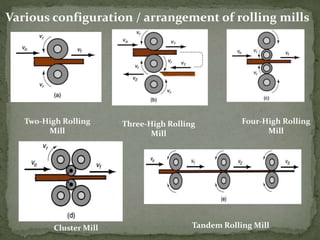
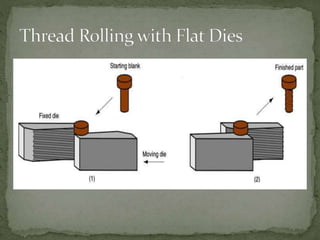
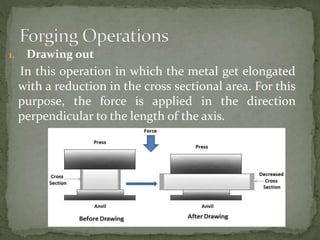
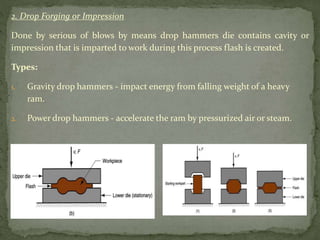
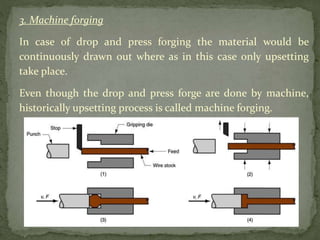
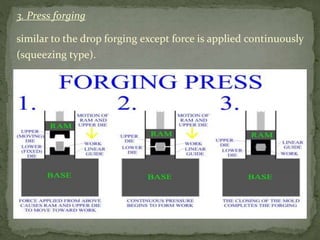
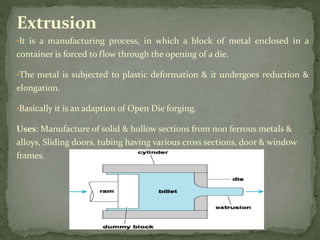
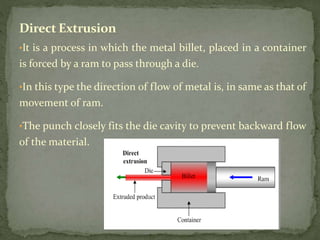
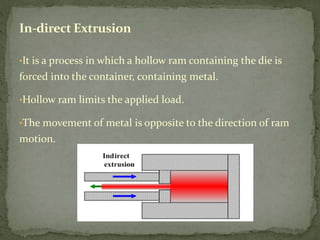
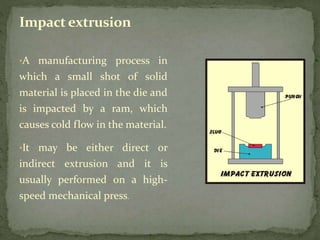
Mechanical forming processes include rolling, forging, and extrusion. Rolling involves passing metal through opposing rollers to reduce thickness. Forging involves compressing metal between dies or a hammer to shape it. Extrusion uses a container and die to force metal through an opening to create a shape. These processes deform metal through compression and are used to make common parts like gears, aircraft components, and tubing.