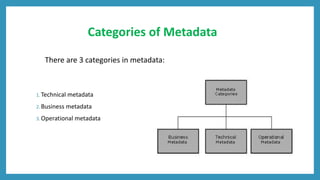
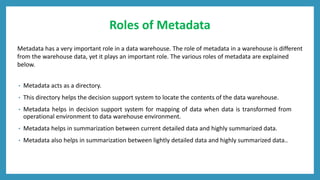
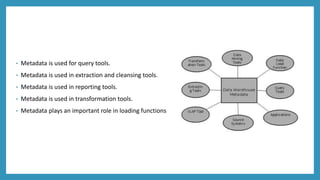
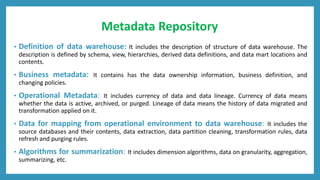
Metadata provides information about other data stored in a data warehouse. It includes technical, business, and operational metadata. Technical metadata describes the warehouse's structure and components. Business metadata provides the business context and meaning of data. Operational metadata includes information about data ingestion and quality processes. Metadata enables functions like data discovery, integration, governance, and business intelligence by serving as a central directory of the warehouse's data. It plays an important role in query, extraction, reporting, transformation, and loading tools. Metadata is stored in a repository that defines the warehouse schema and contains business rules and data lineage information. Challenges with metadata include it being scattered across organizations and a lack of industry-wide standards.