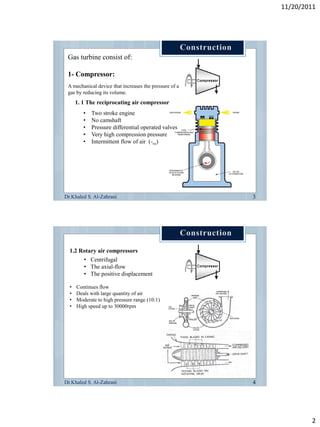
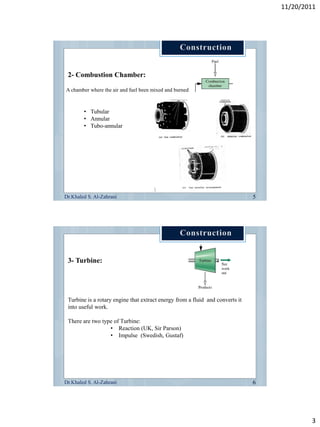
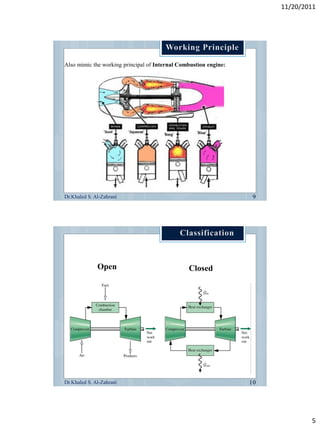
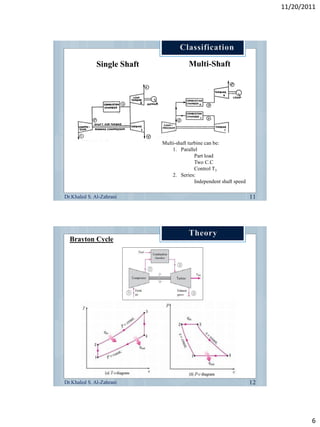
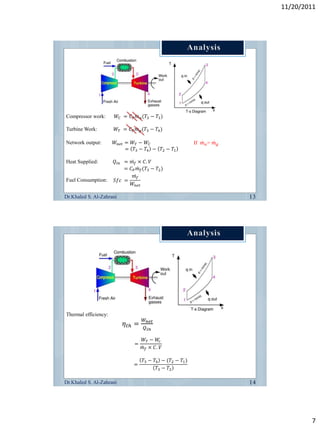
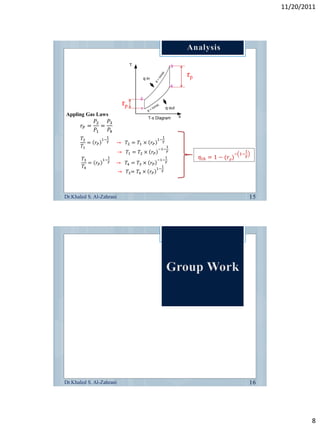
The document discusses the components and workings of a gas turbine engine. It describes the main components as a compressor, combustion chamber, and turbine. The compressor increases the pressure of air taken in, the combustion chamber mixes and burns the compressed air with fuel, and the turbine extracts energy from the expanding gas to power the compressor and provide output power. Gas turbines work on the Brayton cycle of continuous combustion of fuel to power rotation and can have single or multi-shaft configurations.