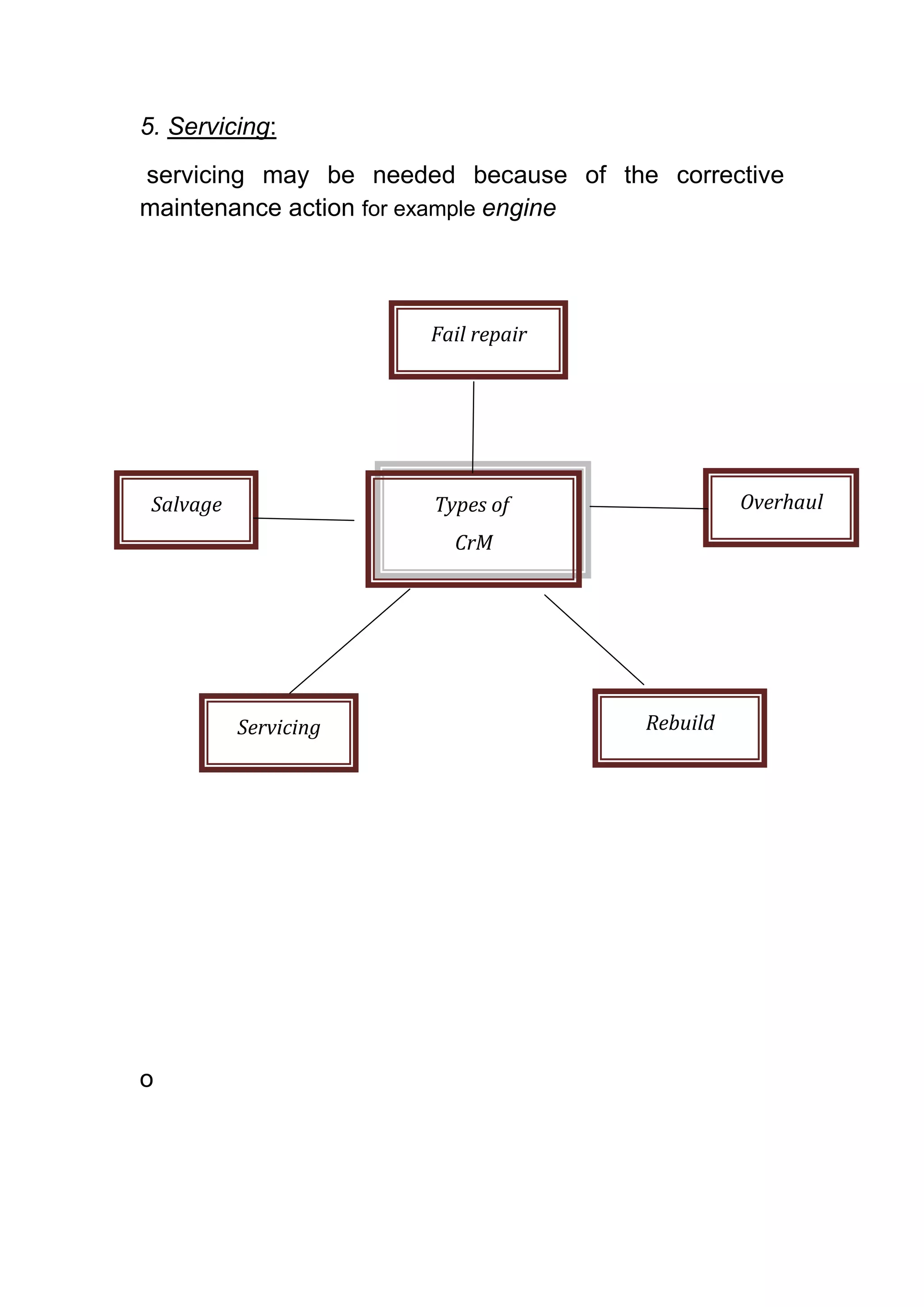
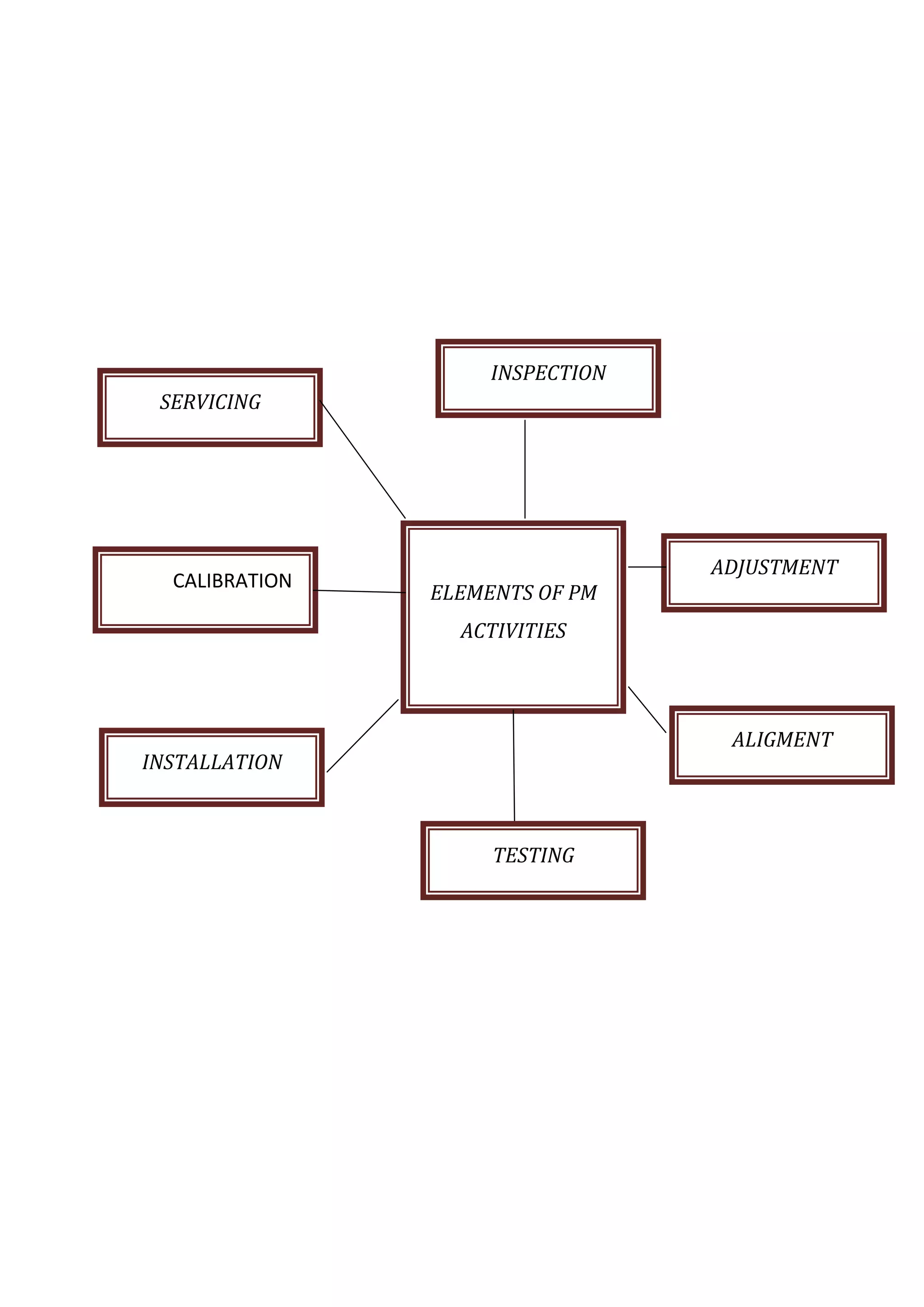
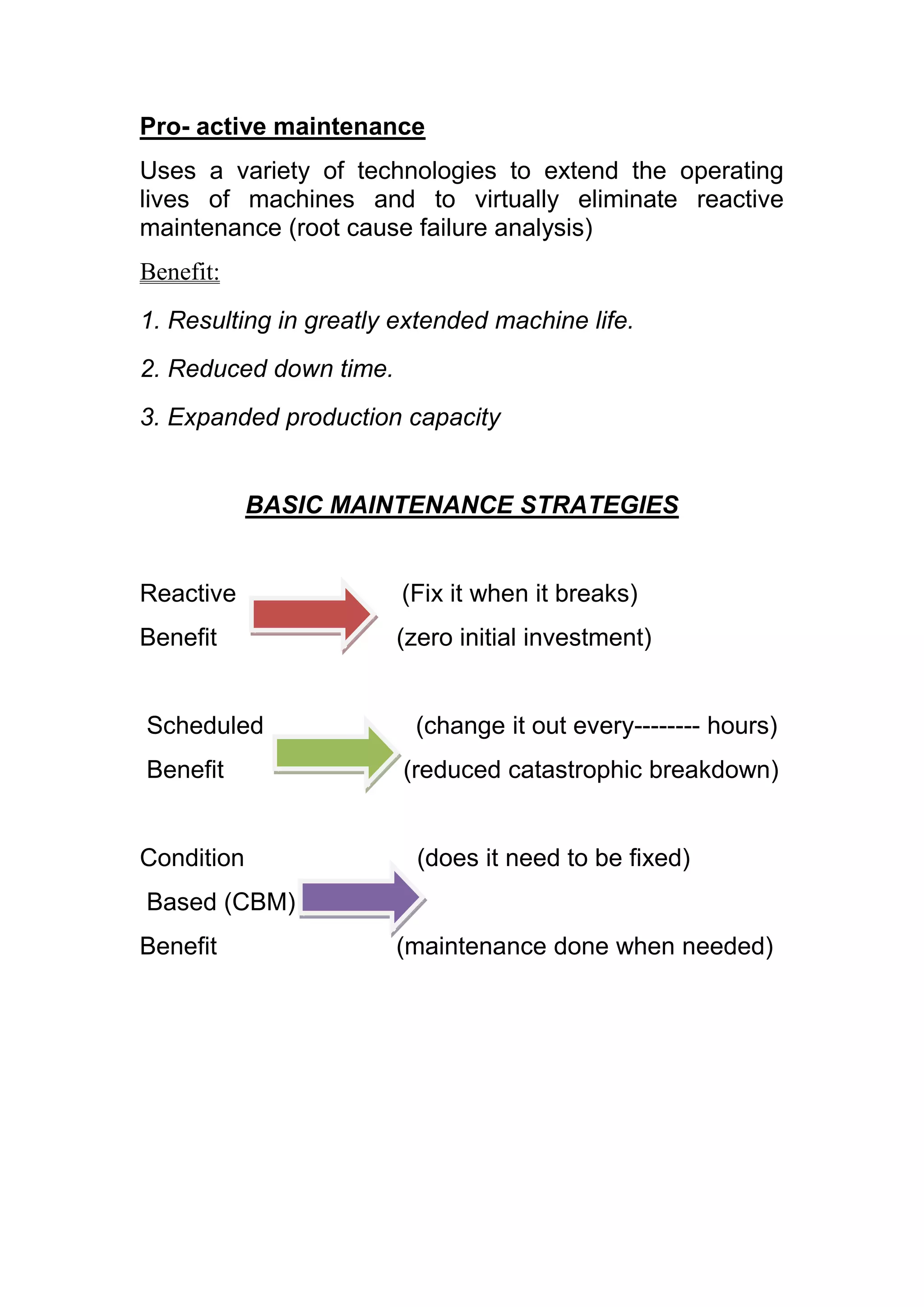
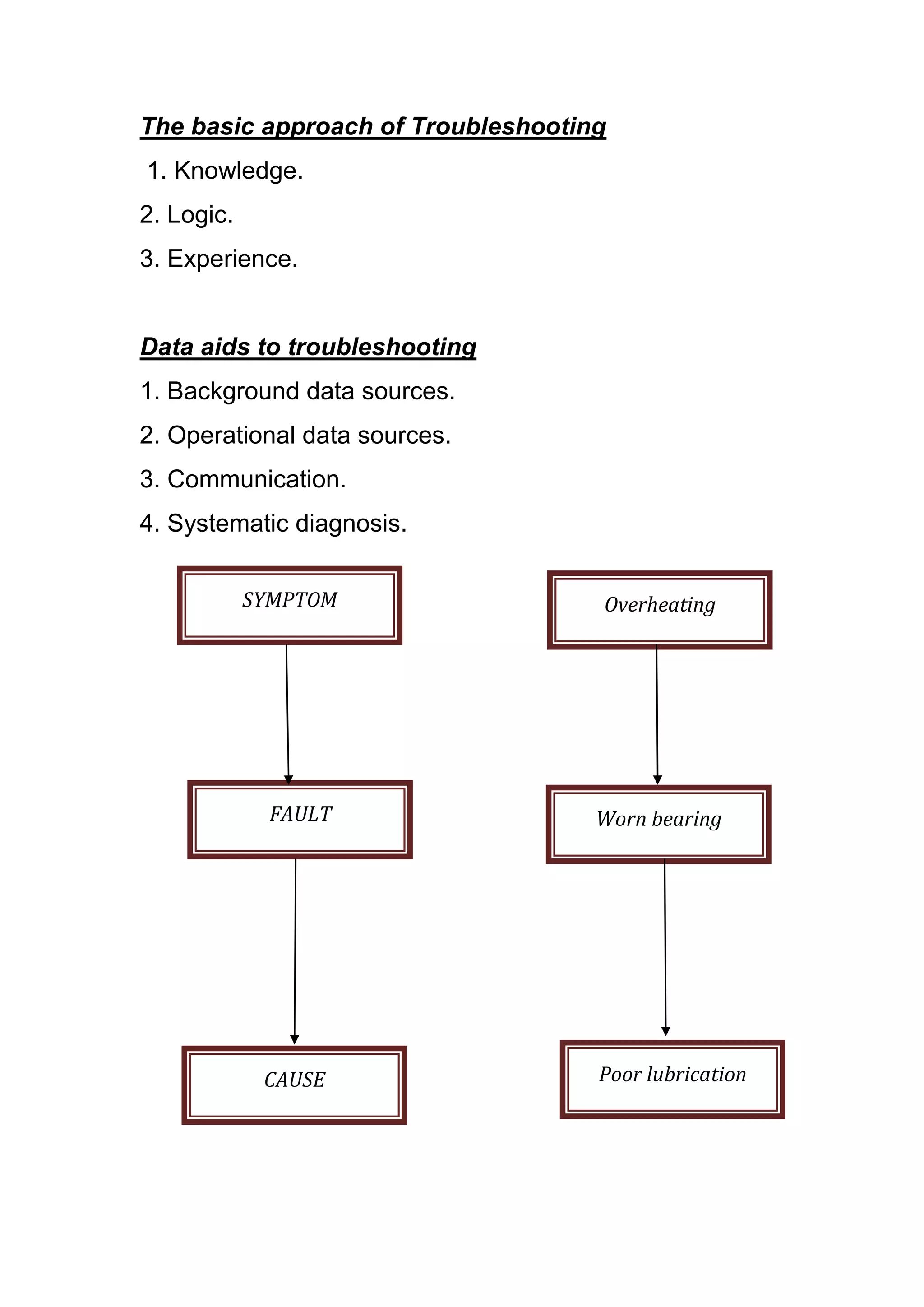
The document discusses the functions and types of maintenance programs. It aims to ensure equipment is available for operation in a satisfactory condition. There are three main types of maintenance programs: corrective, preventive, and predictive. Corrective maintenance involves repair work after a failure. Preventive maintenance is time-based and focuses on inspections, servicing, and minor repairs. Predictive maintenance uses condition monitoring to detect issues and schedule maintenance as needed to avoid breakdowns. The goal is to maximize equipment availability and performance at optimal costs.