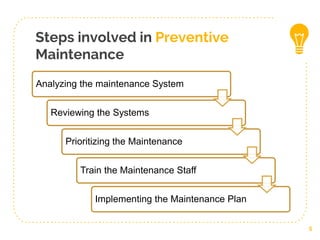
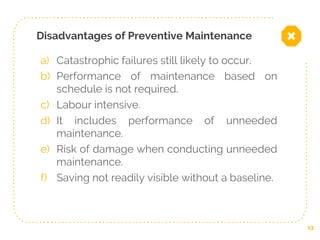
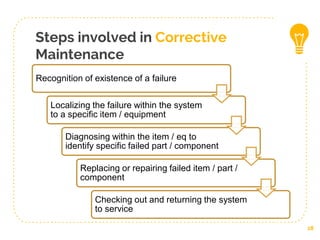
This document discusses different types of planned maintenance including preventive, corrective, predictive, and condition-based maintenance. It provides details on the objectives, elements, and steps involved in preventive maintenance. The key steps in preventive maintenance include analyzing the maintenance system, reviewing systems, prioritizing maintenance, training staff, and implementing the maintenance plan. Predictive maintenance allows maintenance to be performed just before failure based on equipment monitoring rather than on a set schedule. Both preventive and predictive maintenance aim to reduce downtime but predictive maintenance more precisely targets maintenance needs.