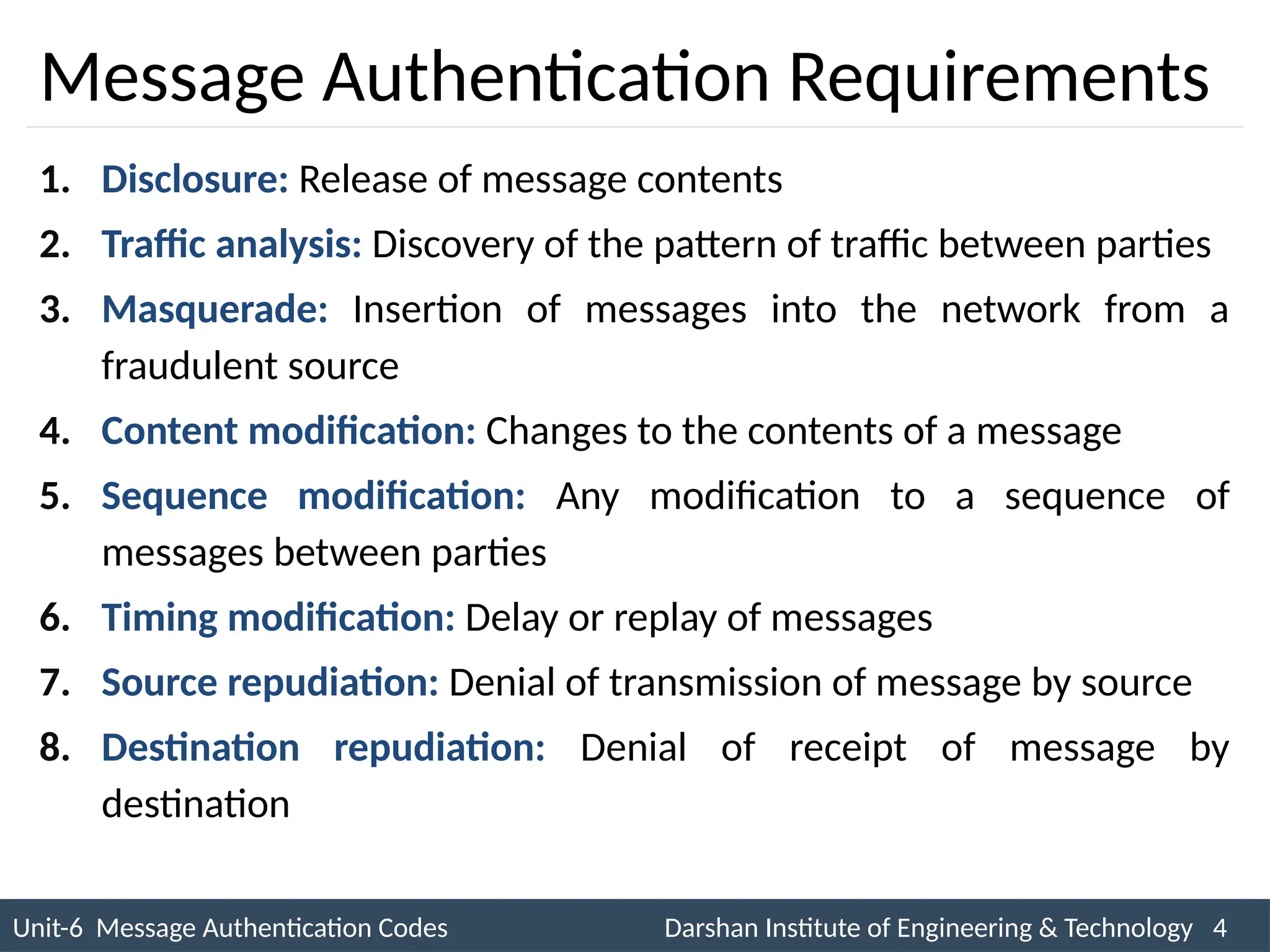
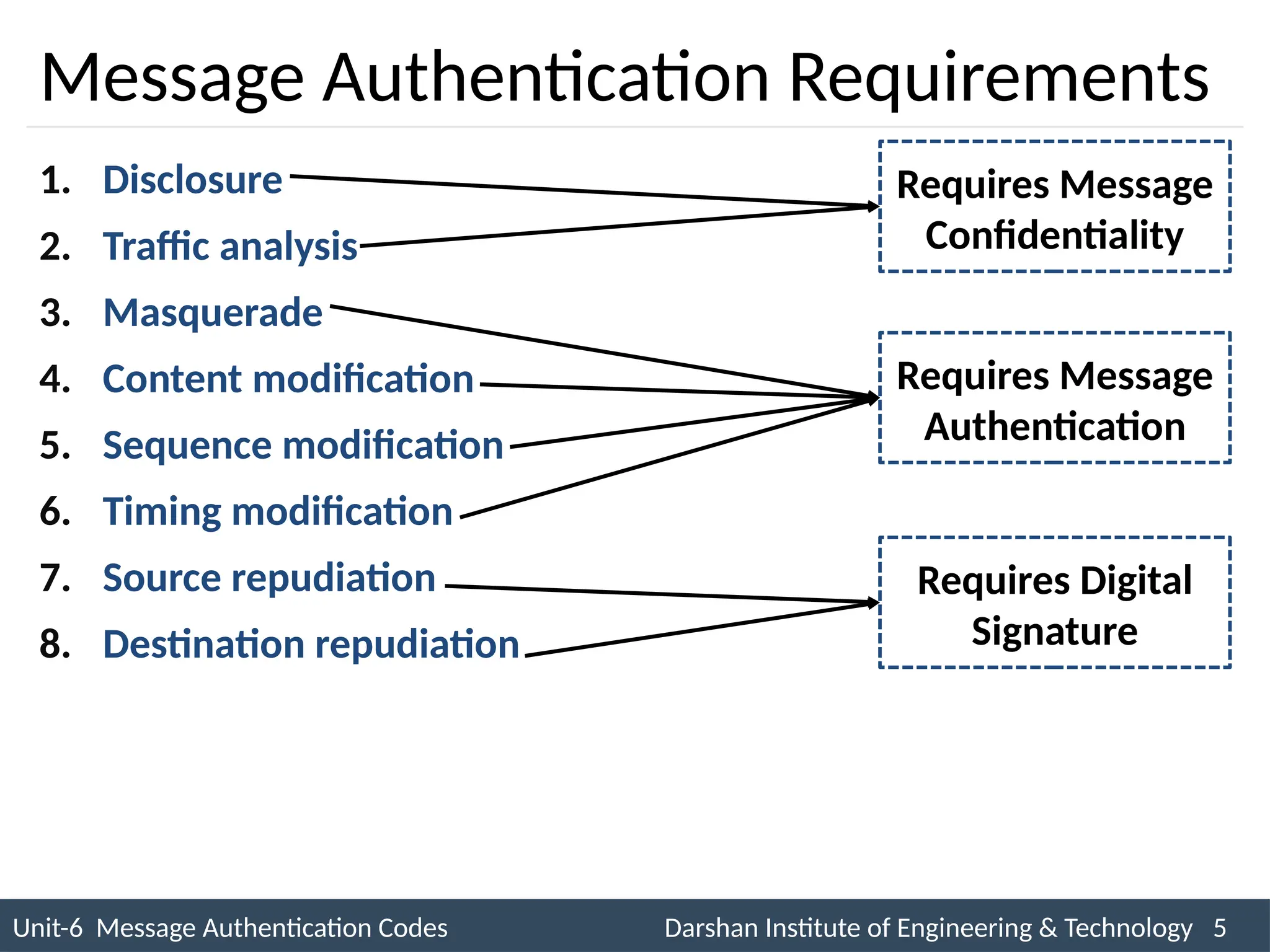
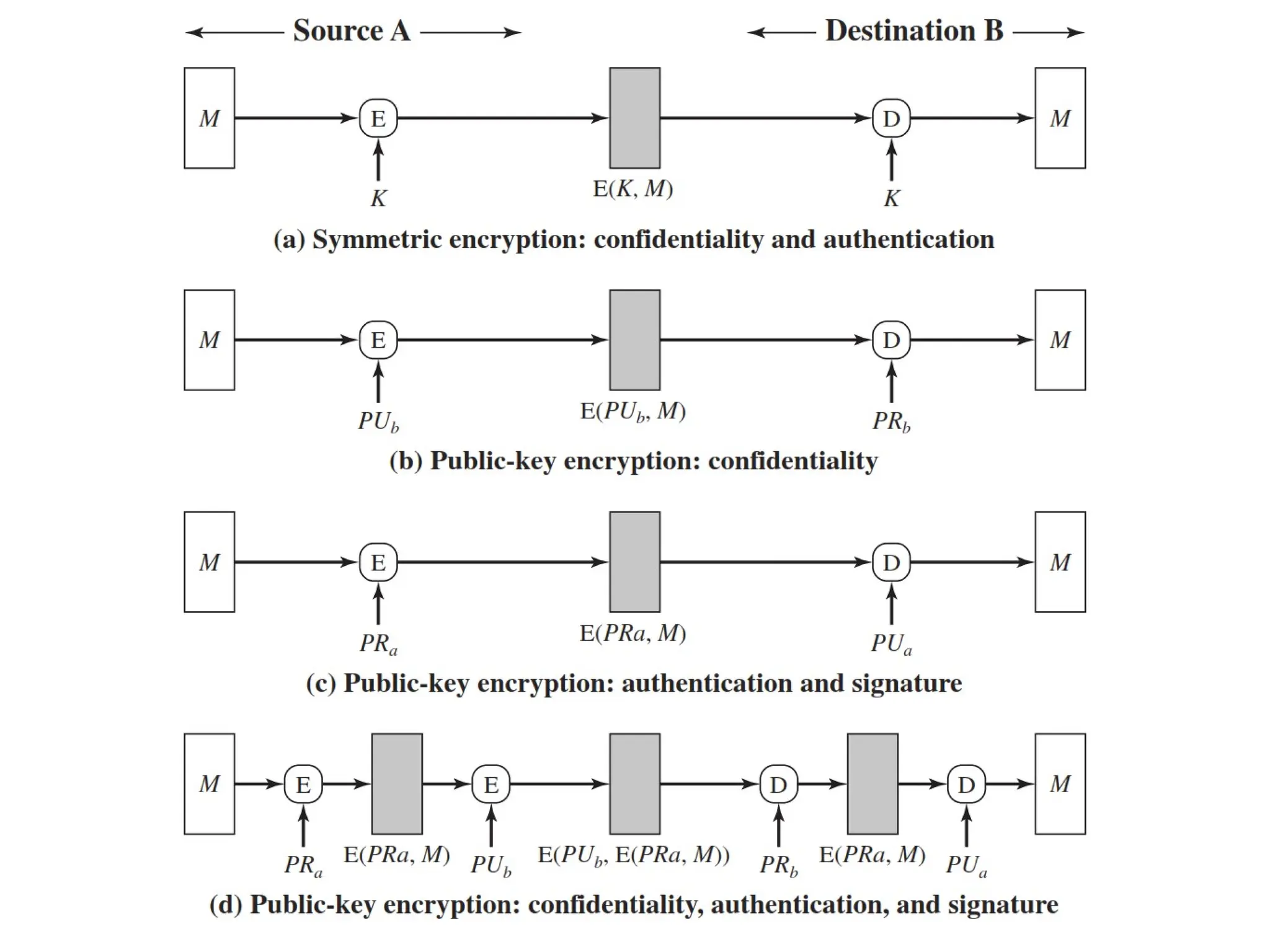
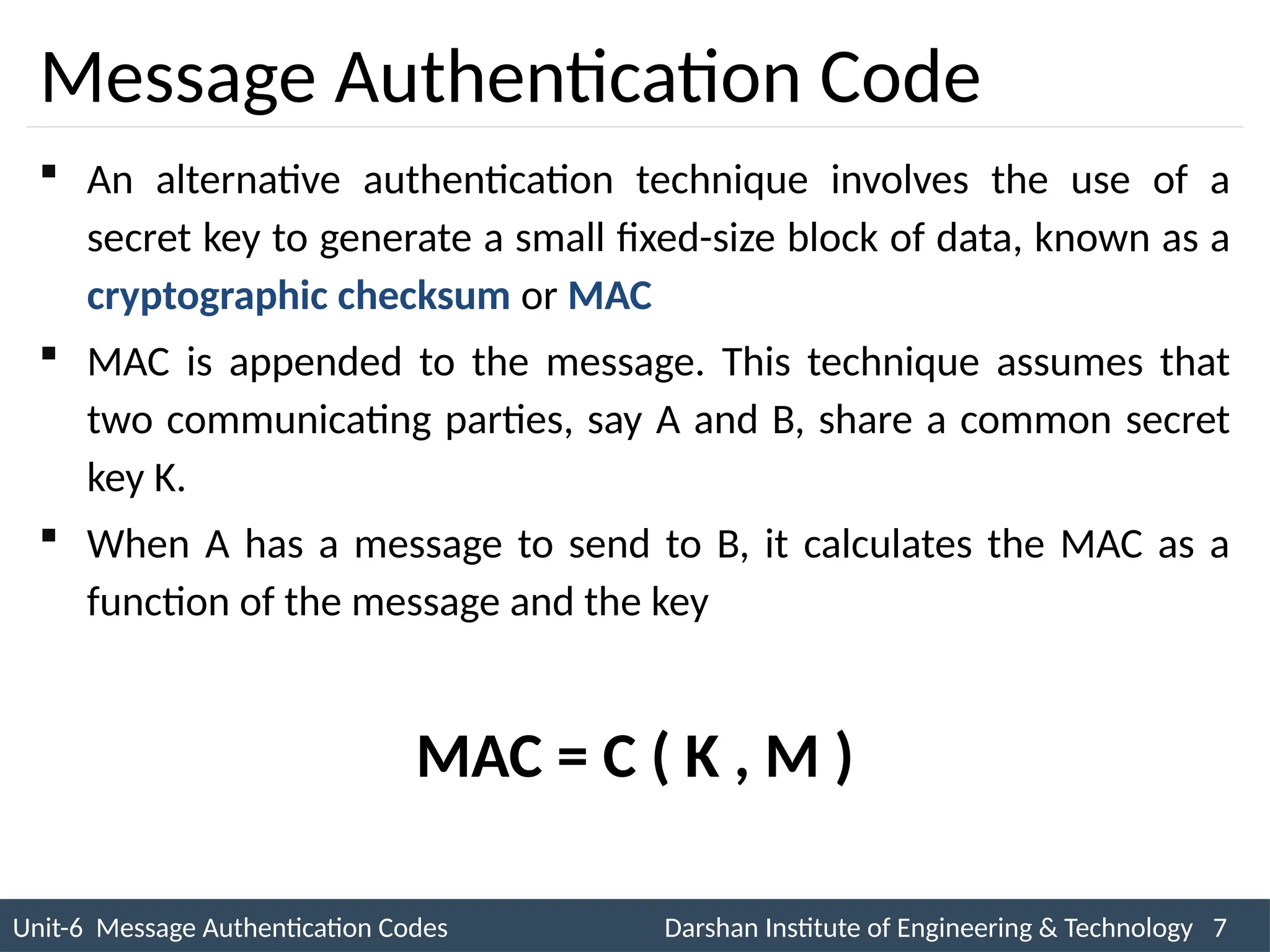
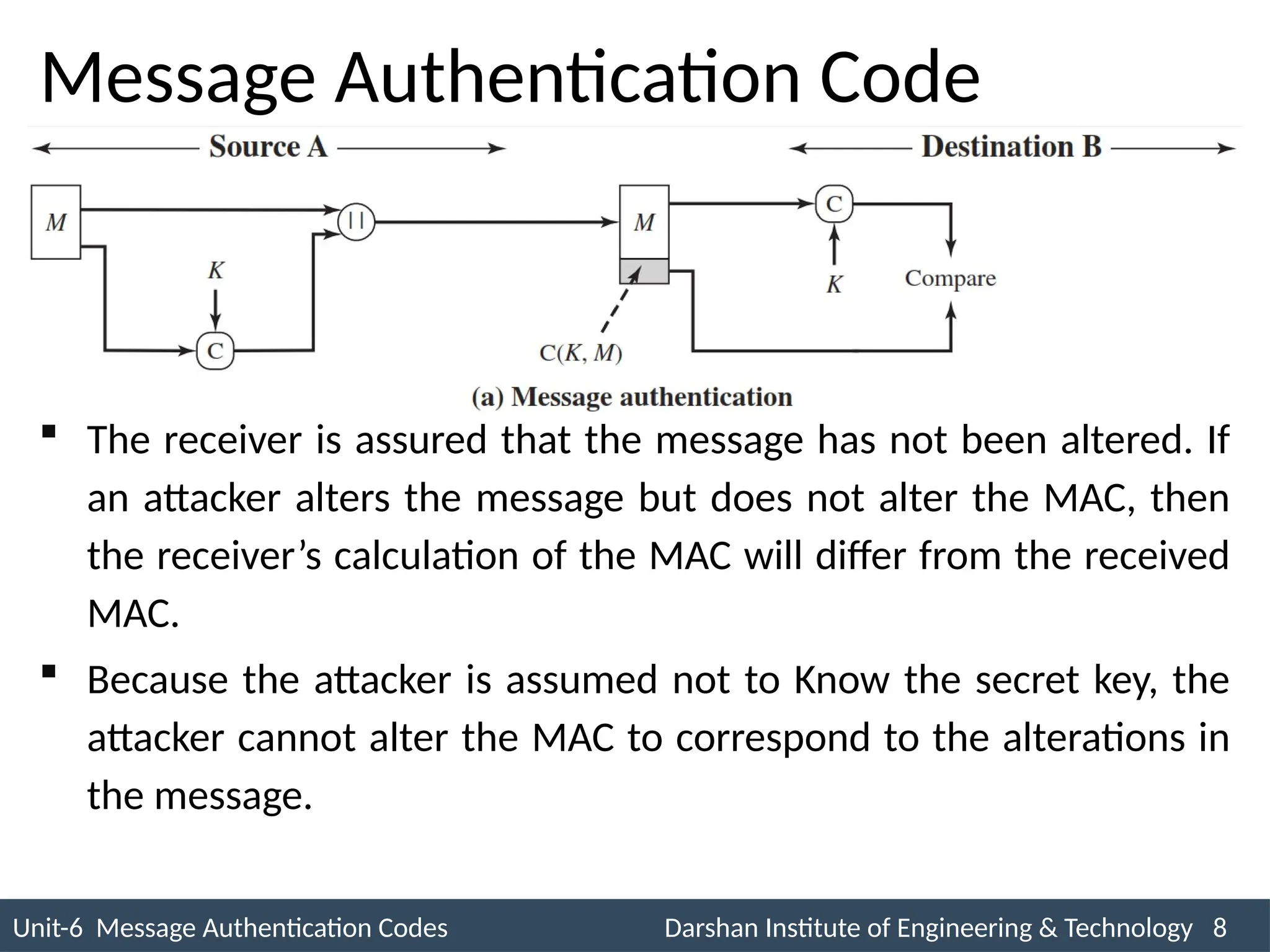
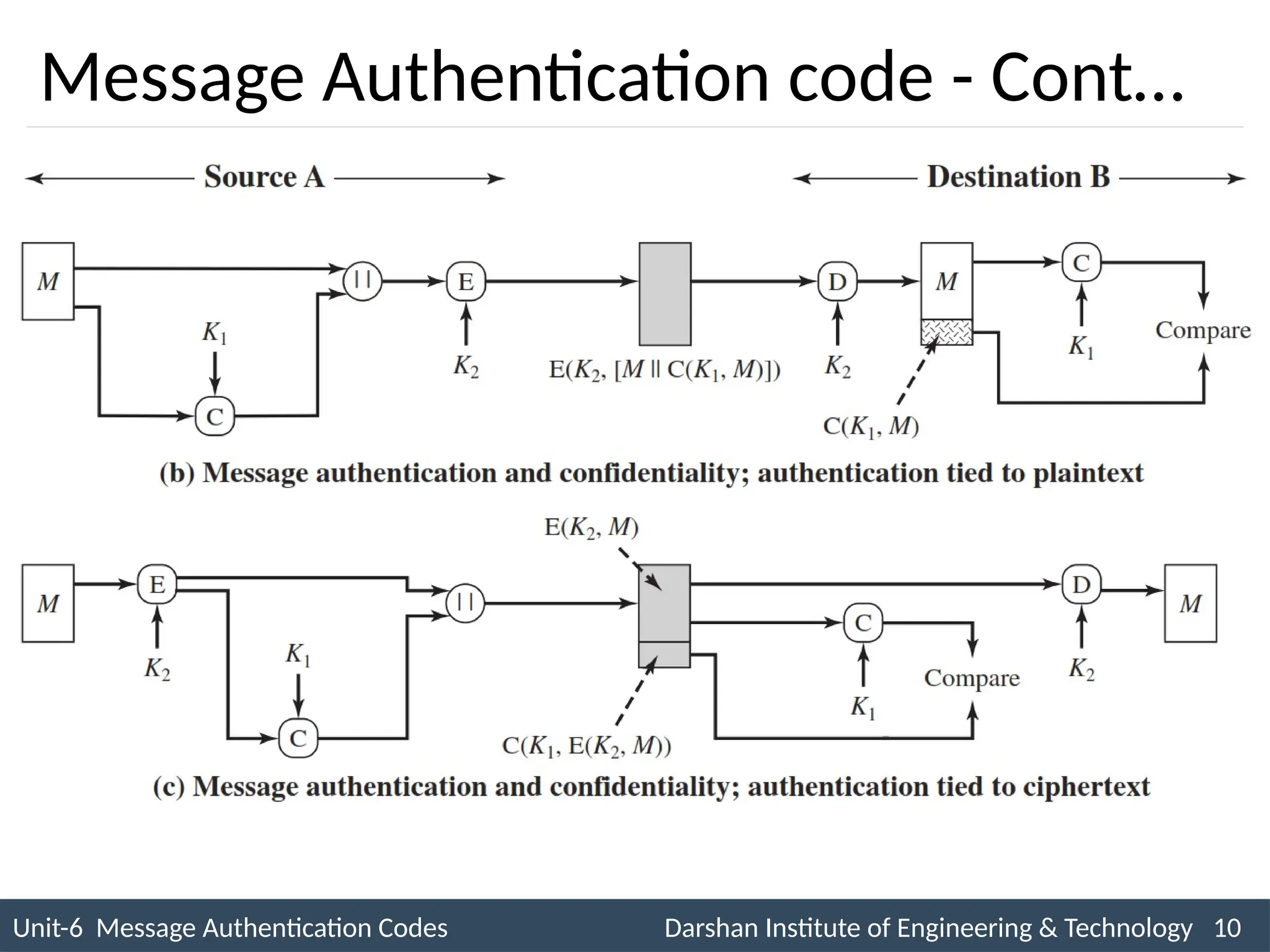
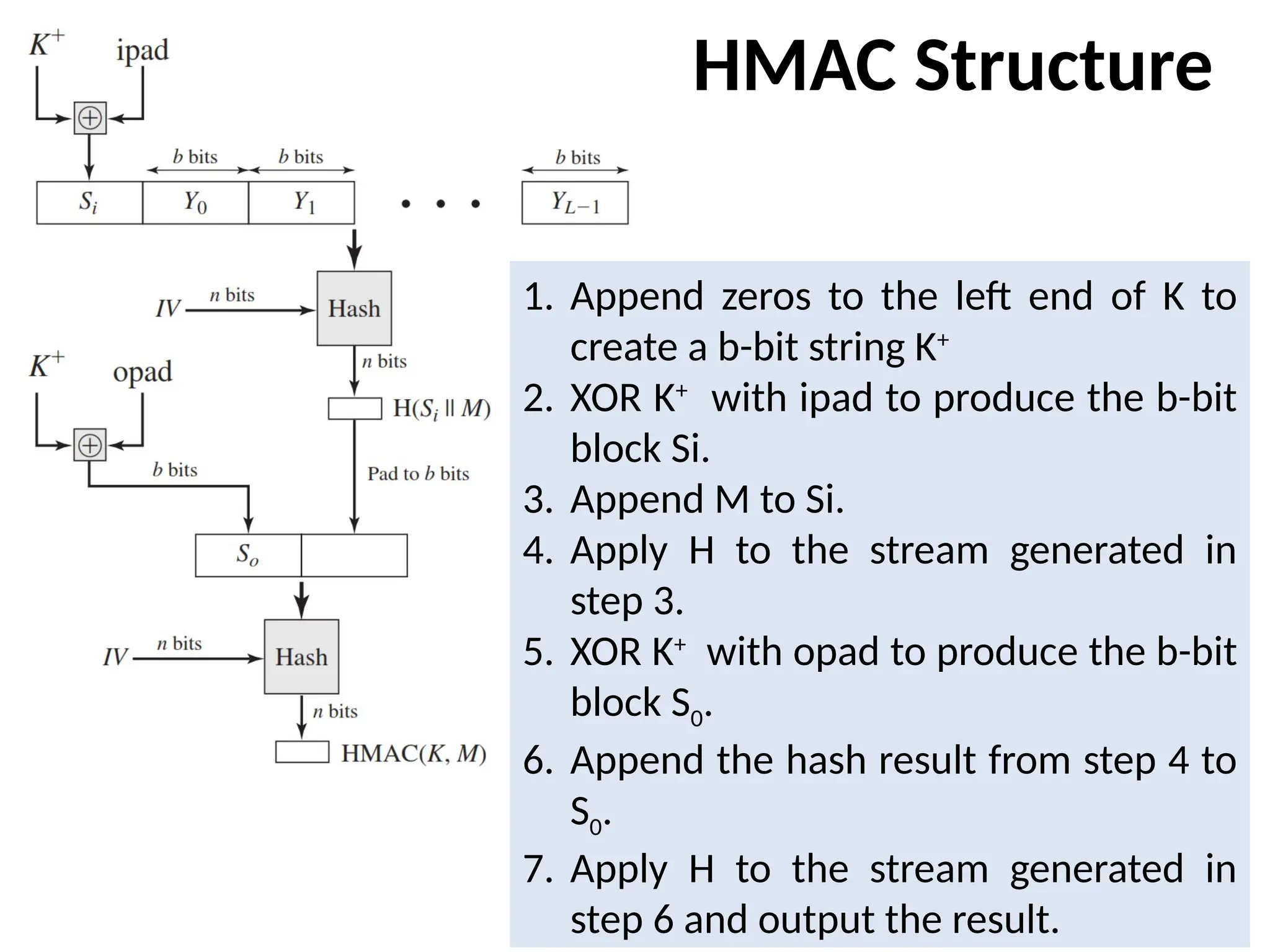
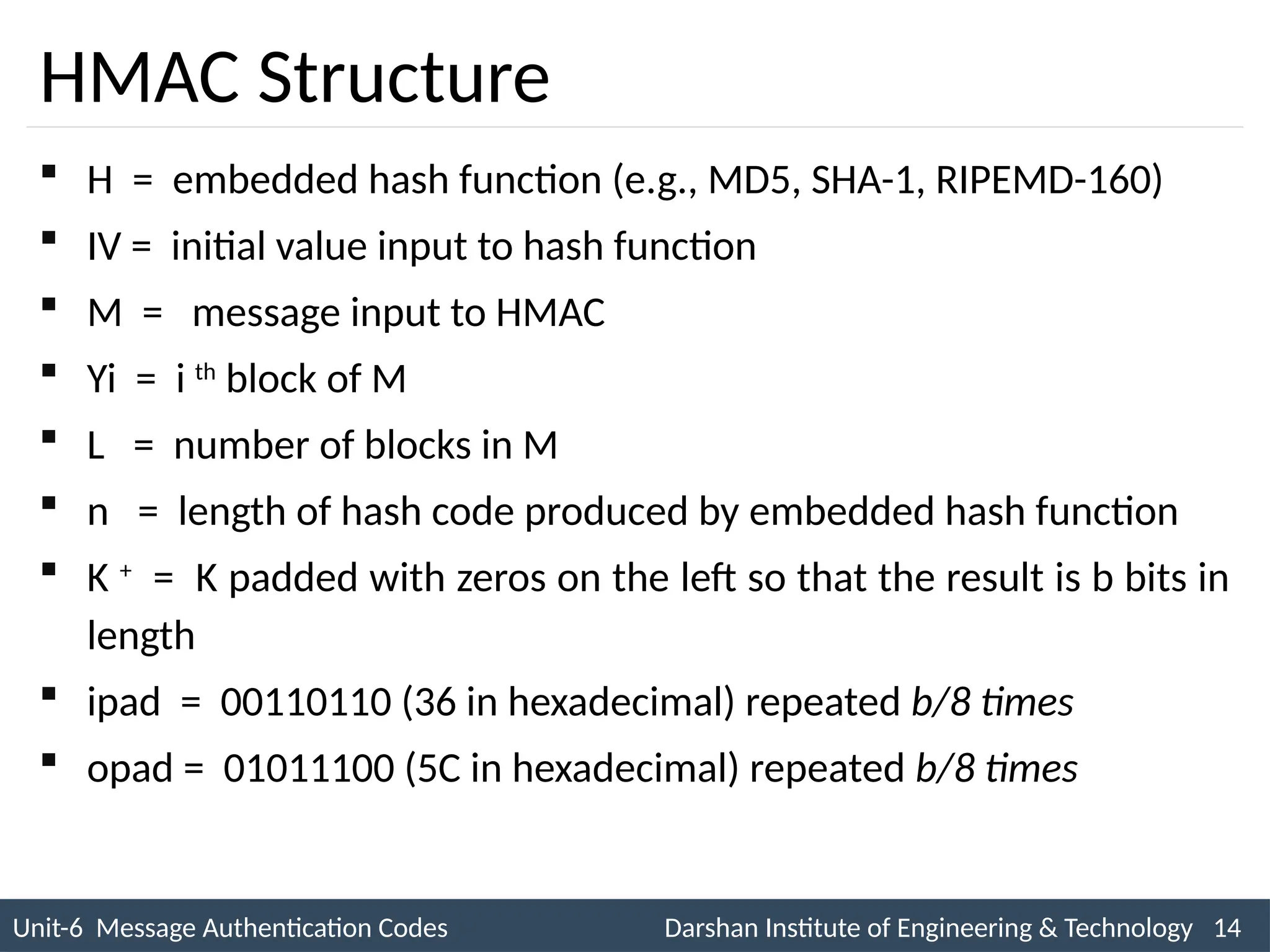
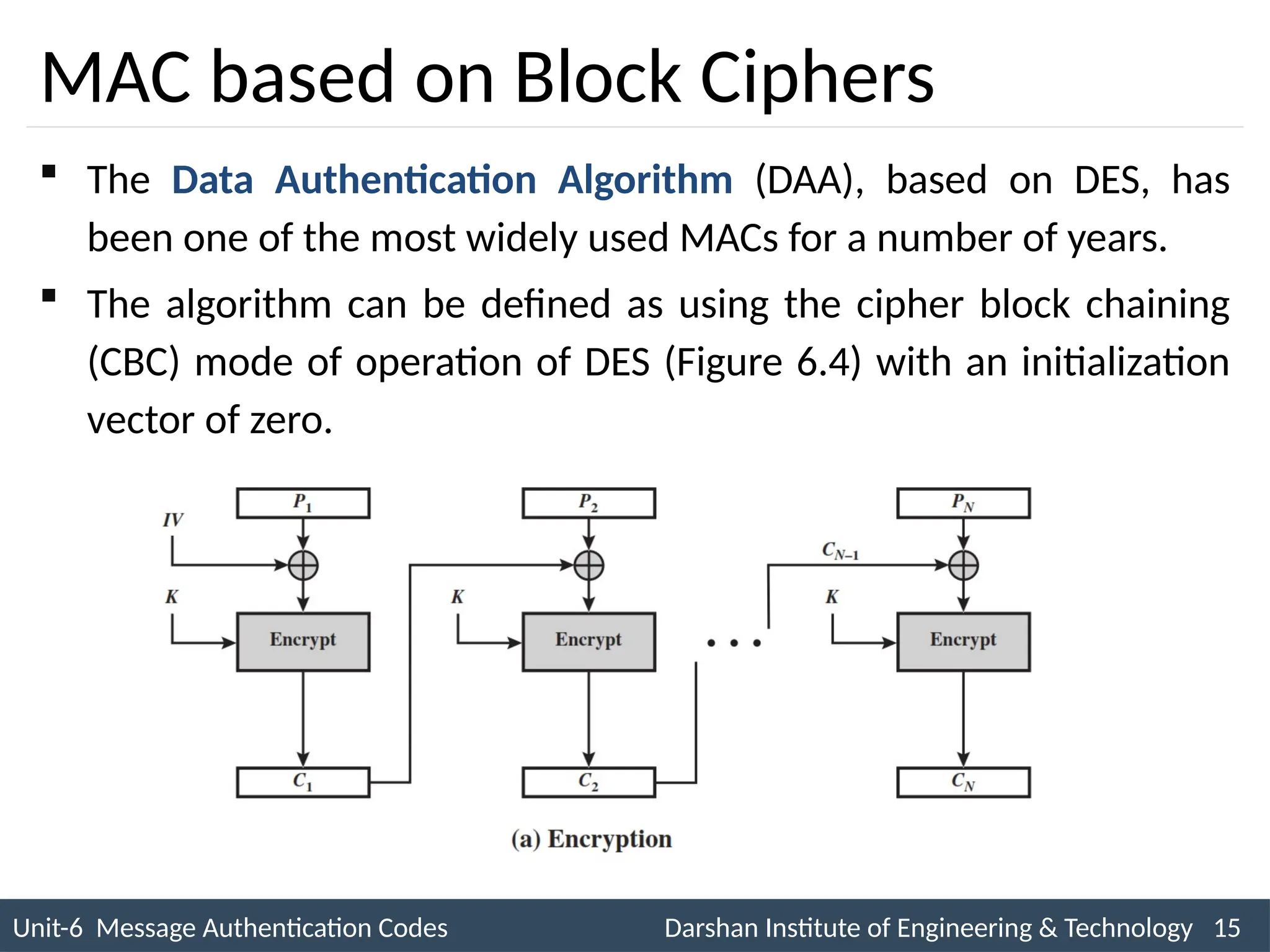
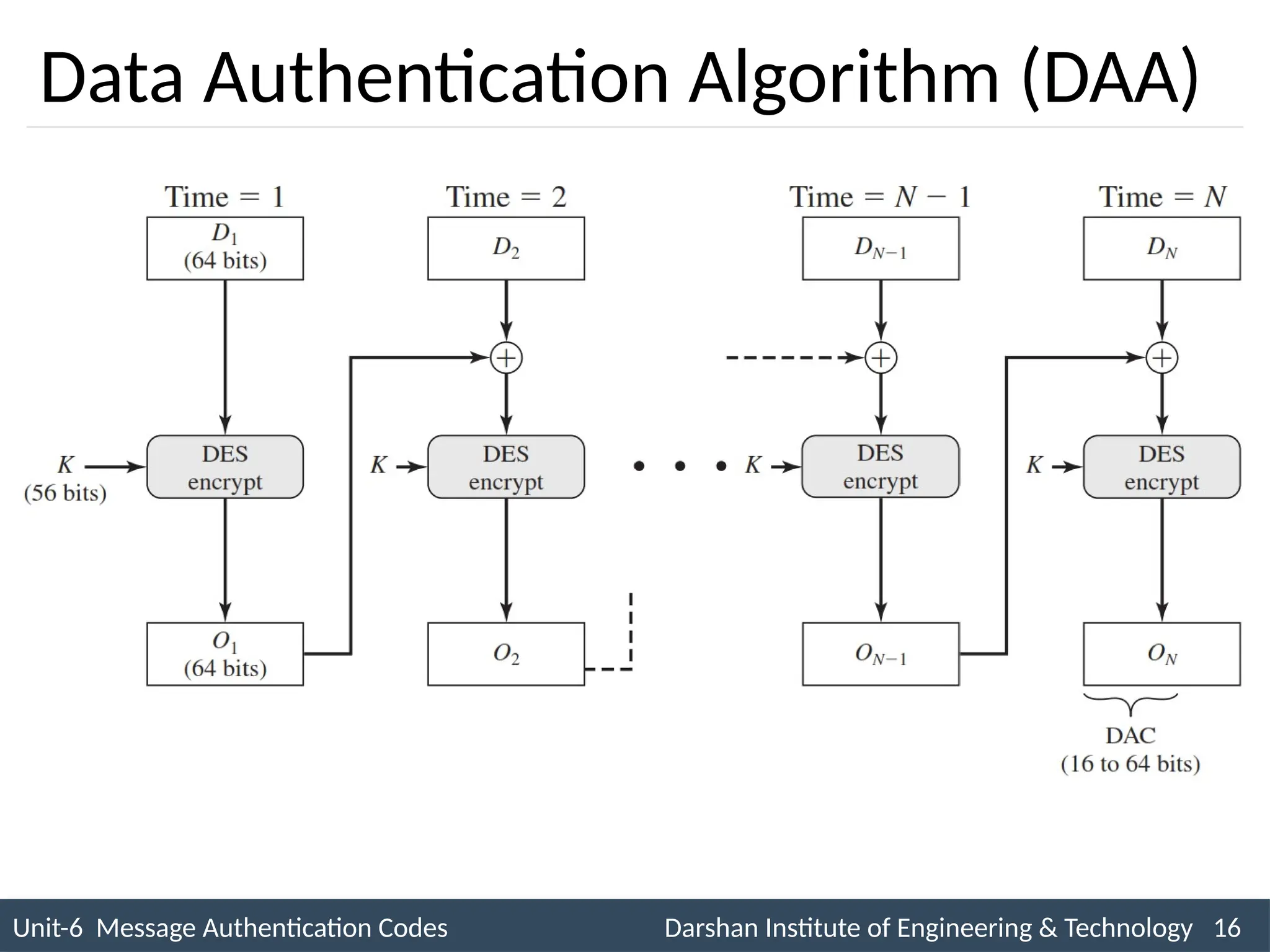
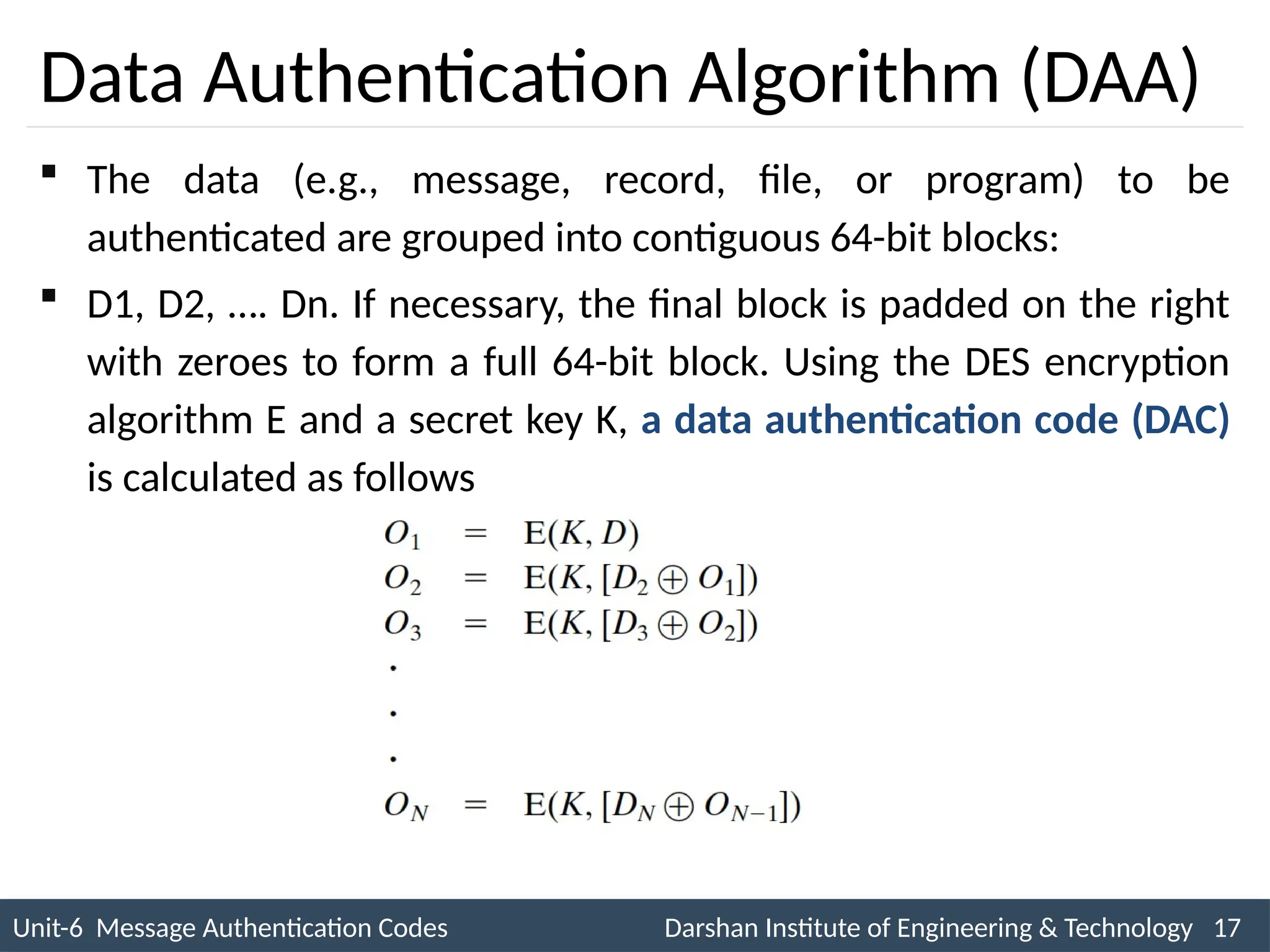
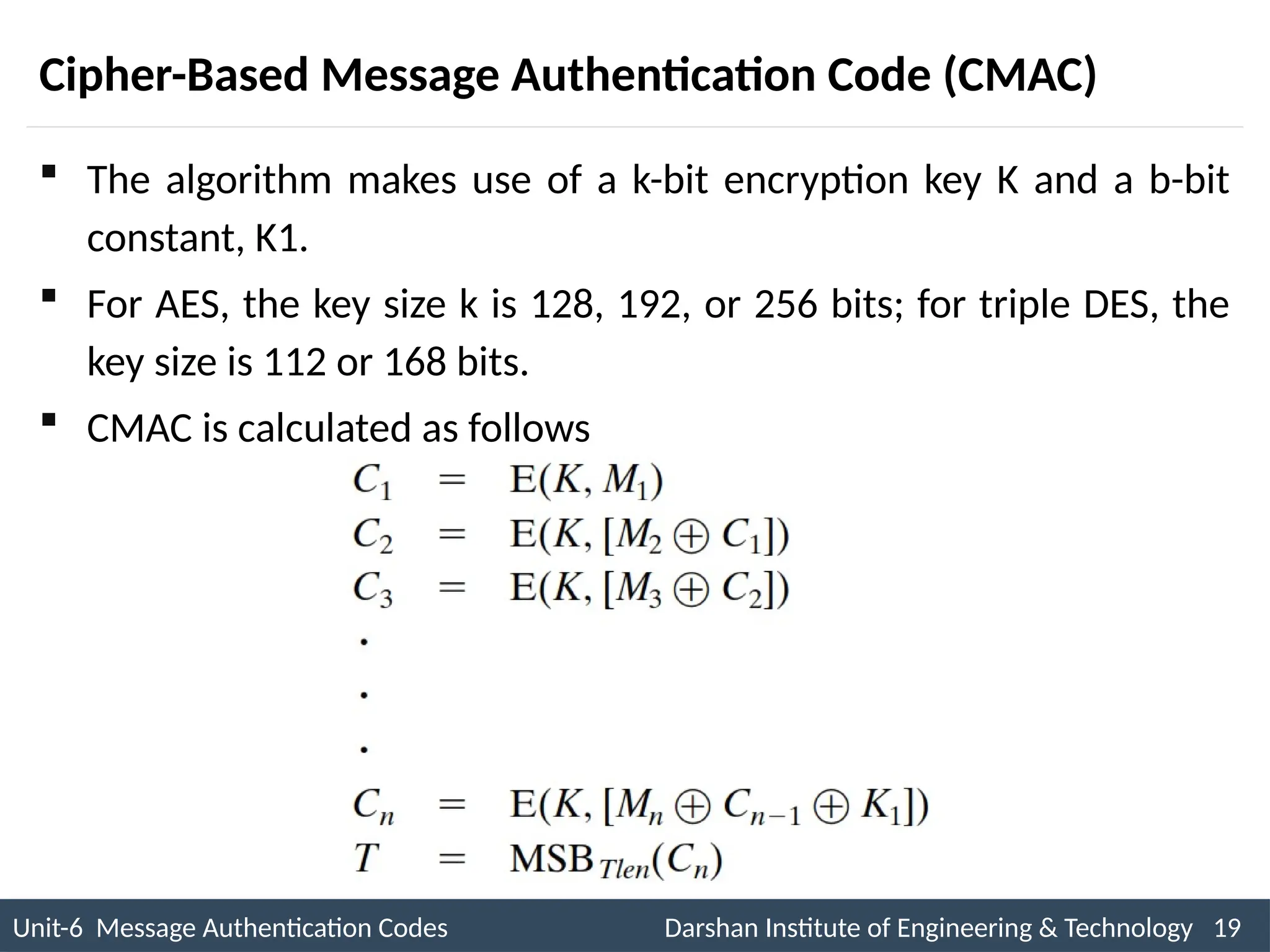
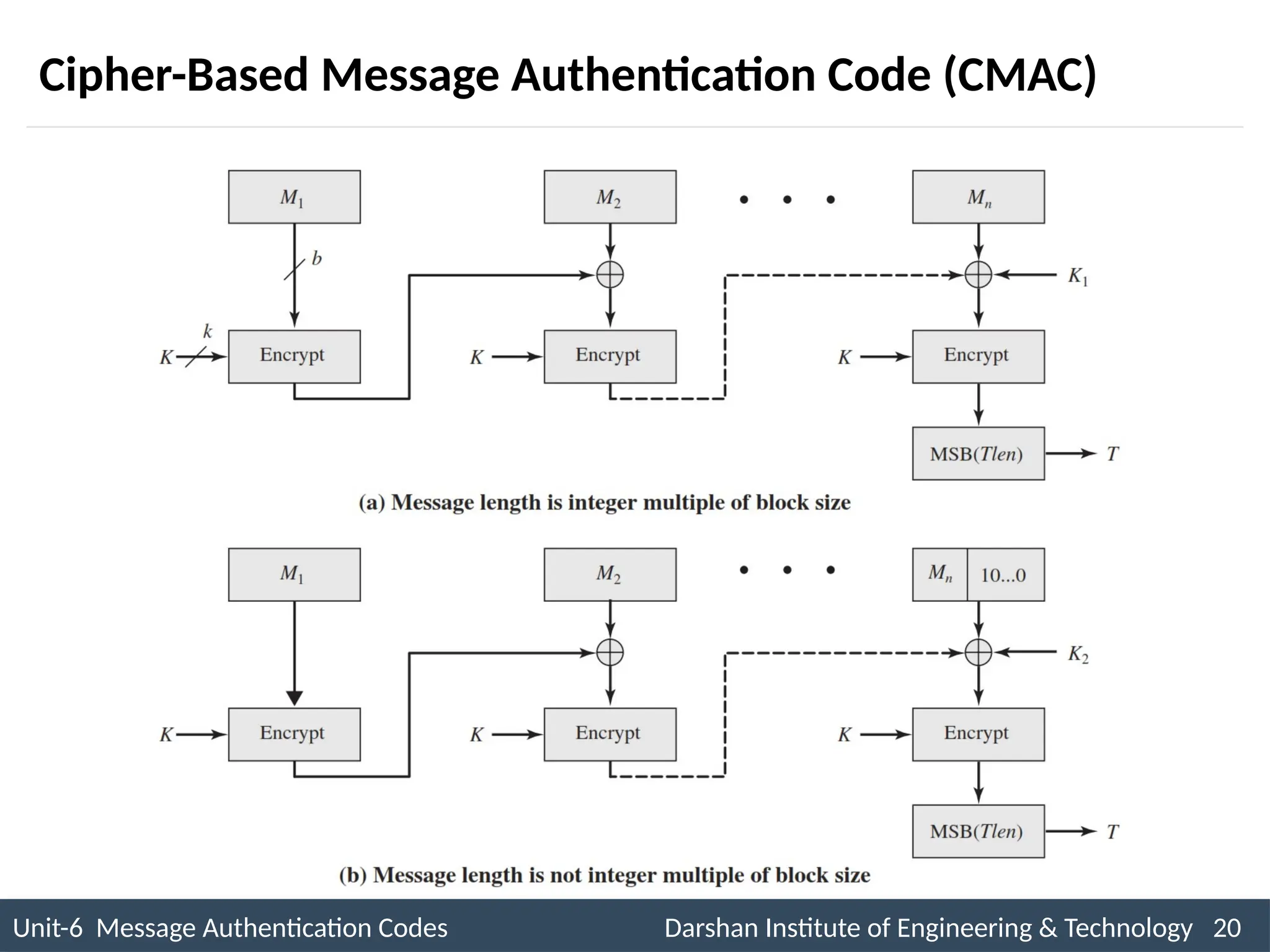
The document outlines message authentication codes (MACs), focusing on their purpose to verify message integrity and authenticity. It discusses the requirements for message authentication, techniques involving hash functions like HMAC, and block cipher-based approaches such as CMAC. The text details the processes involved in generating and utilizing MACs to ensure secure communication between parties.