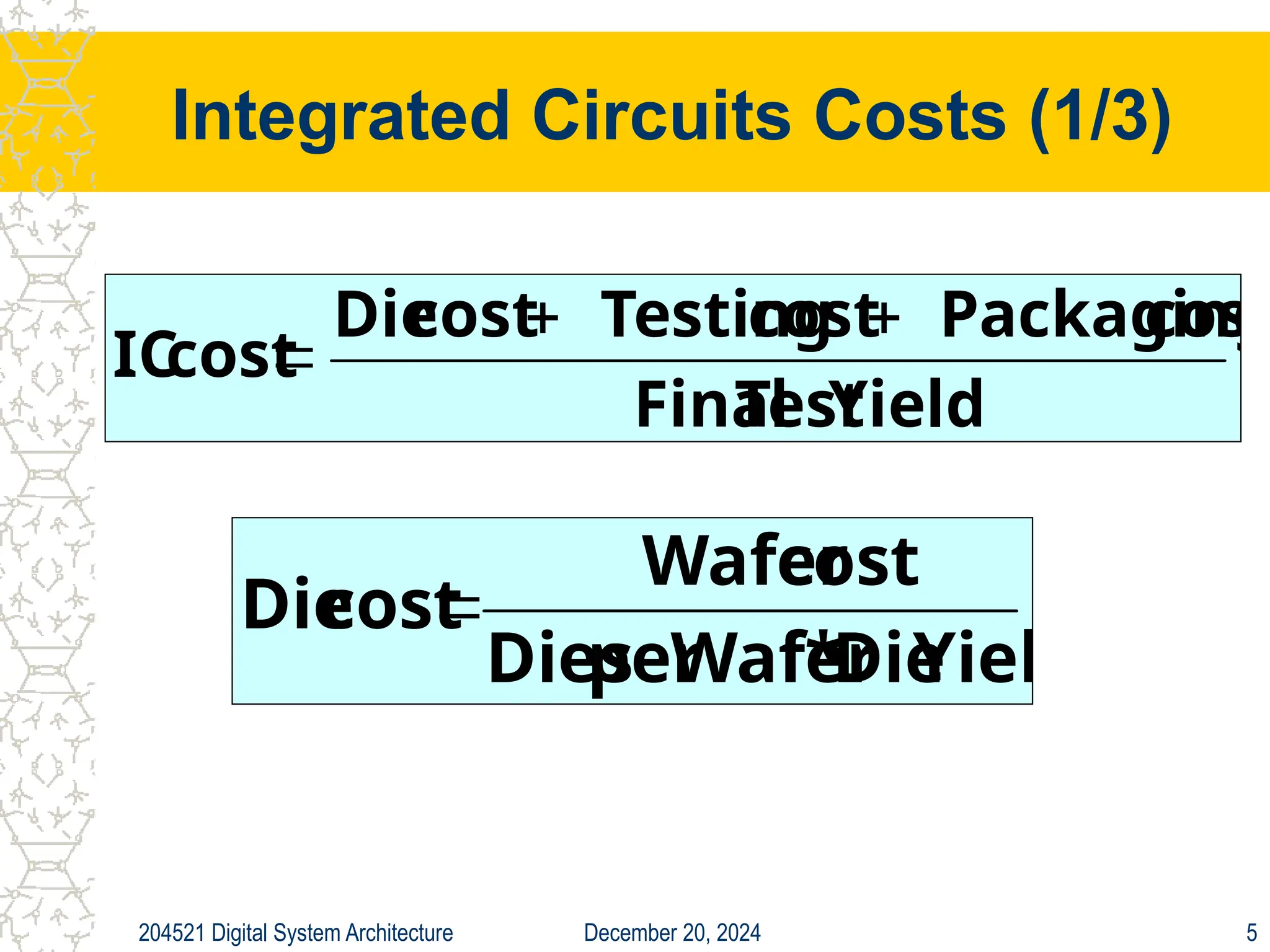
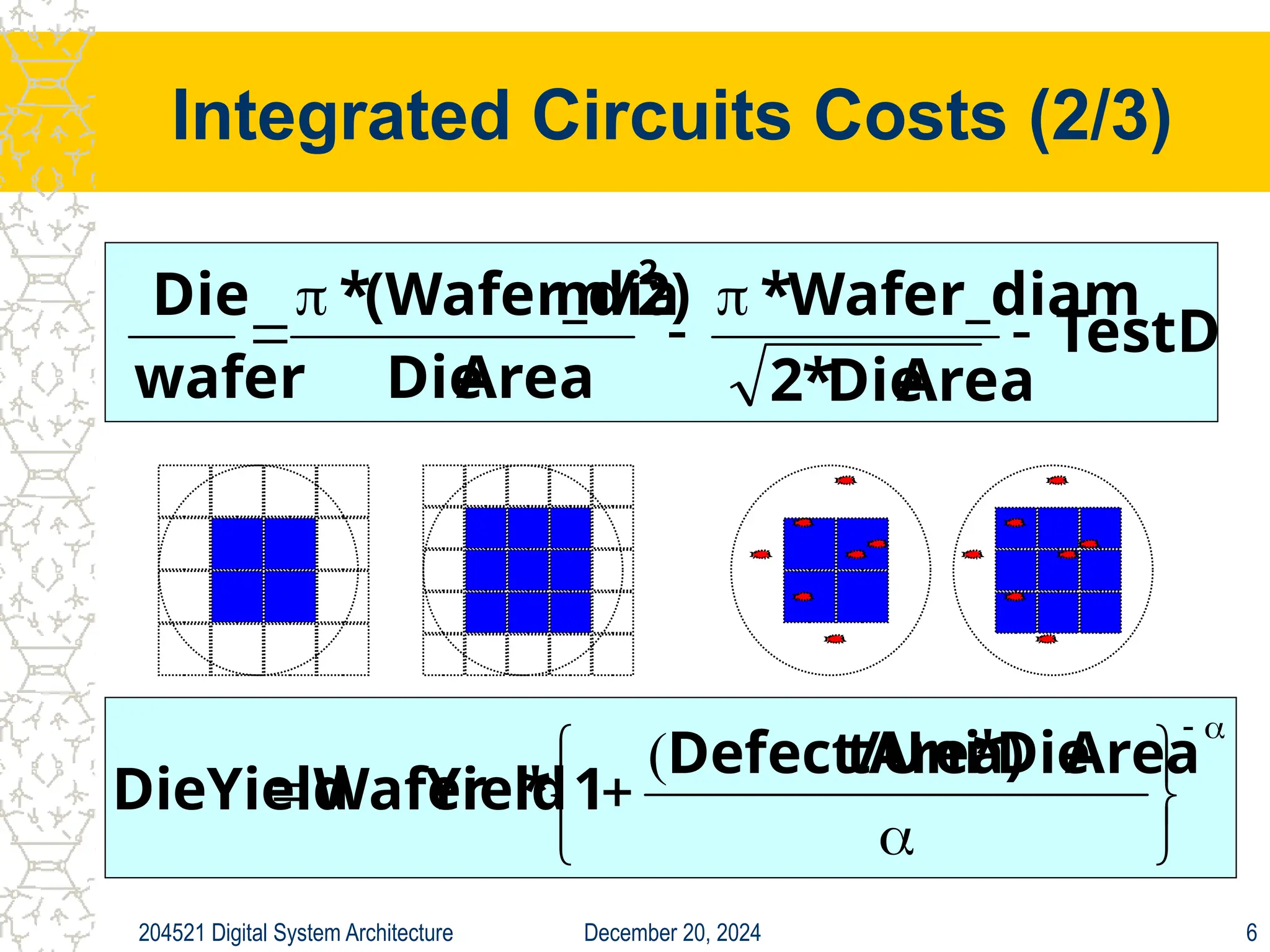
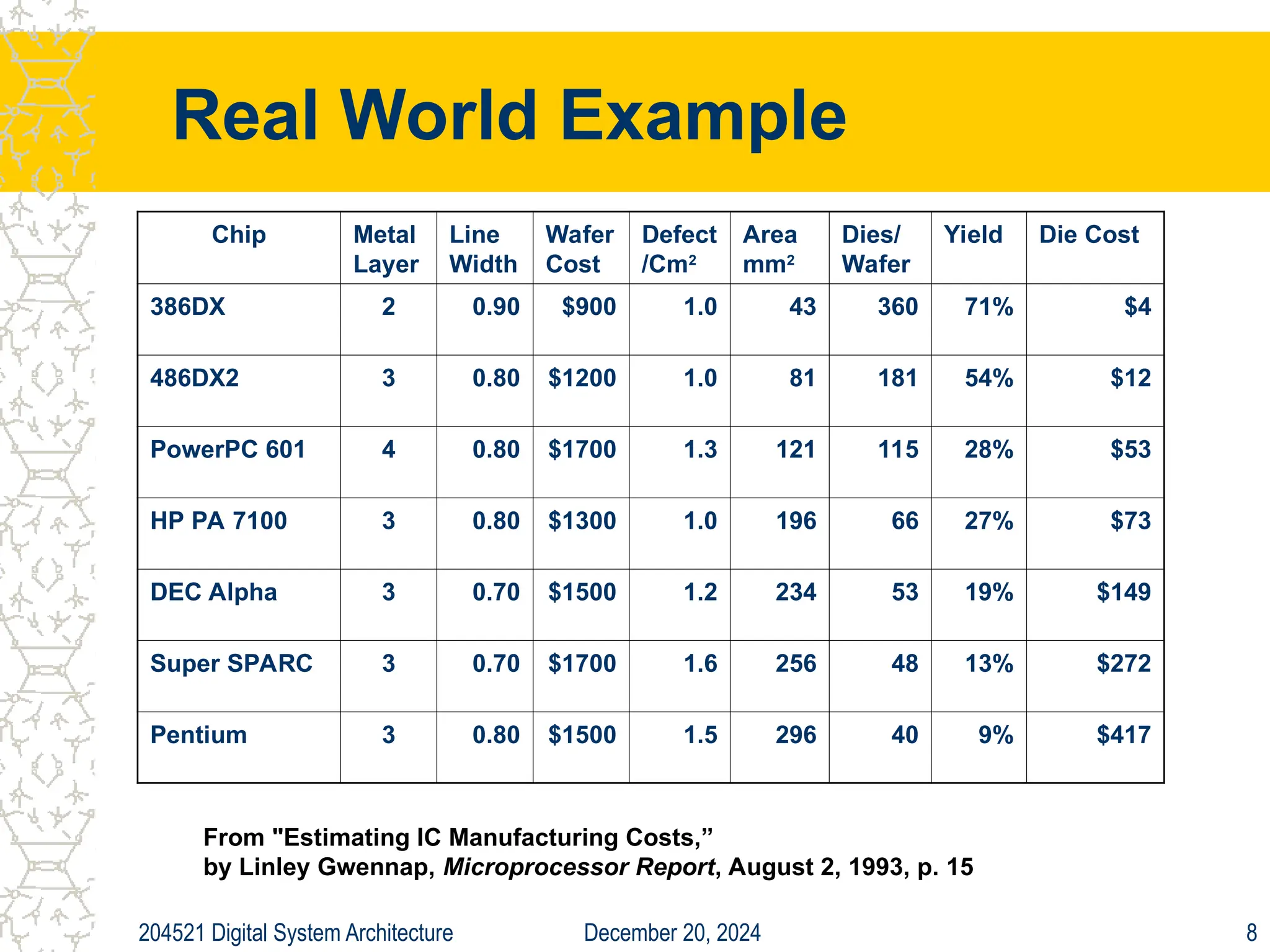
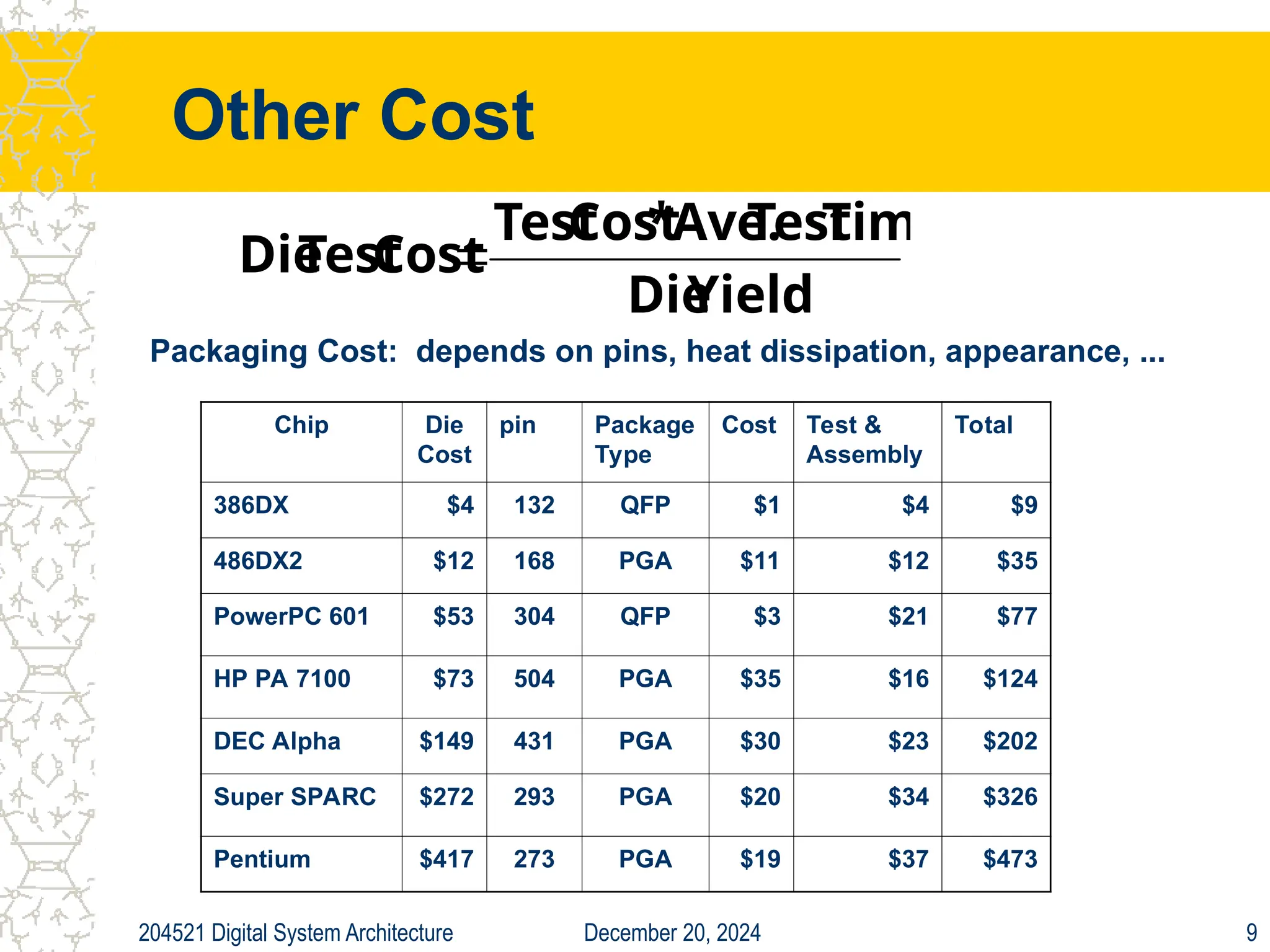
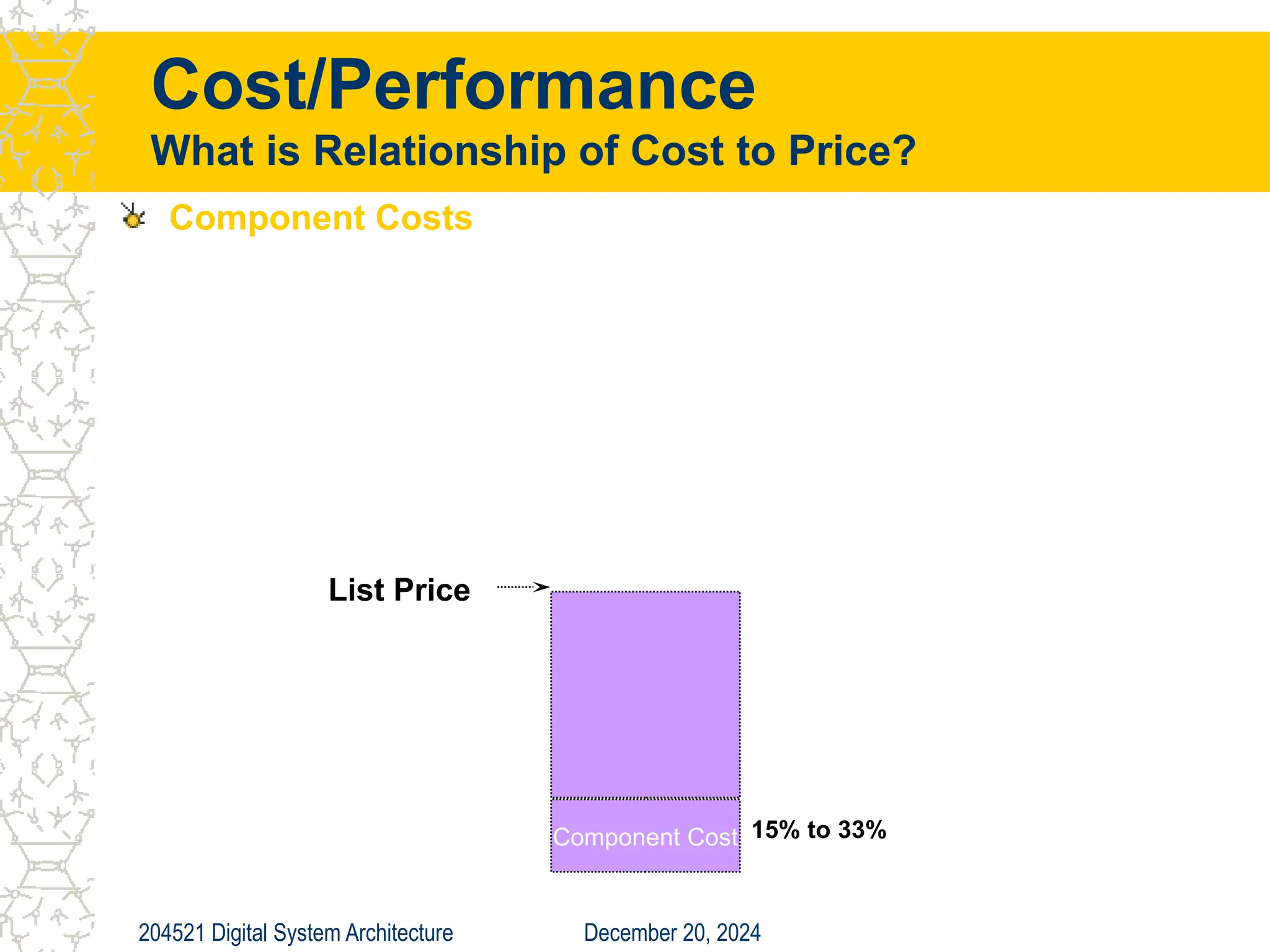
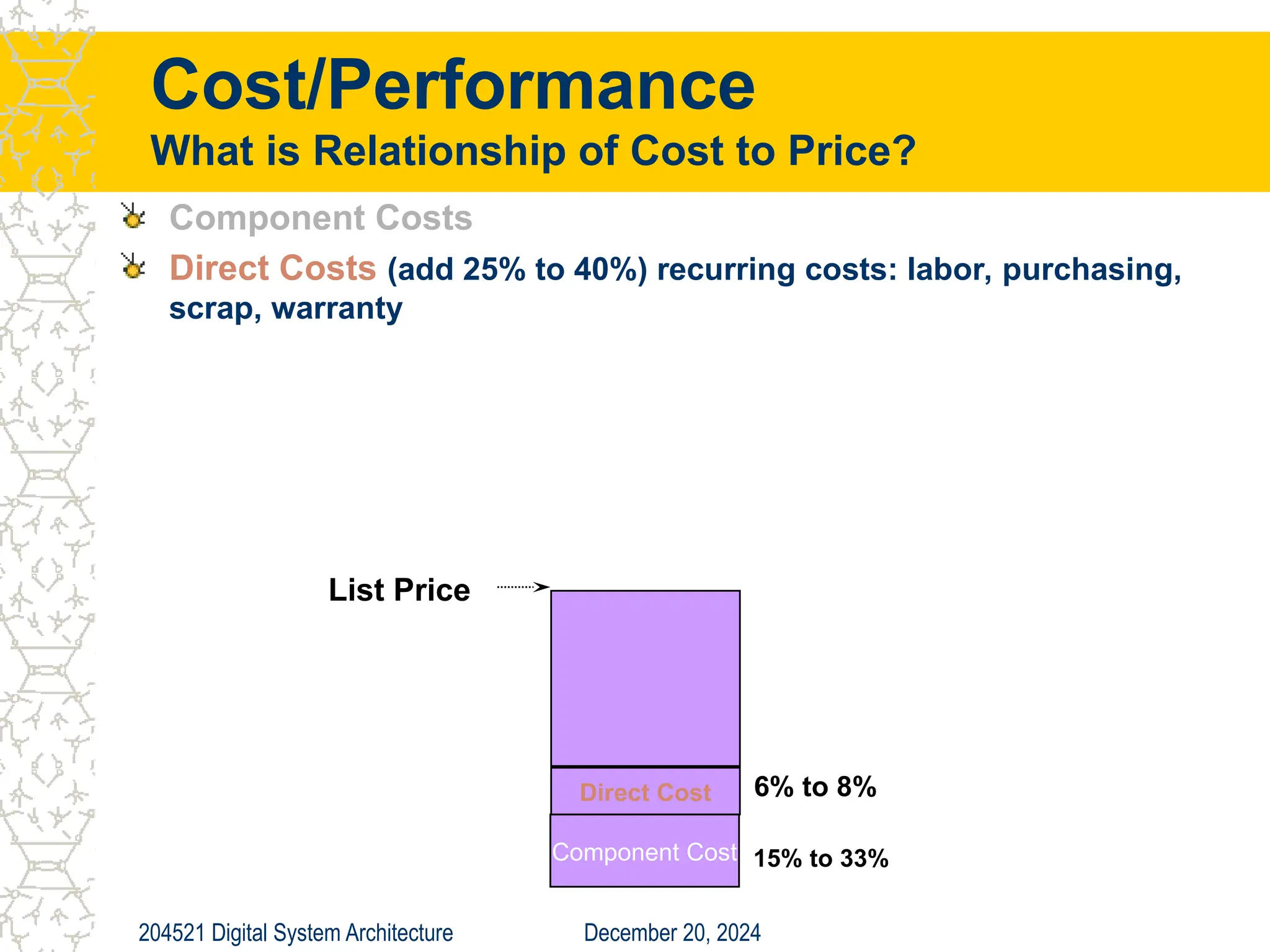
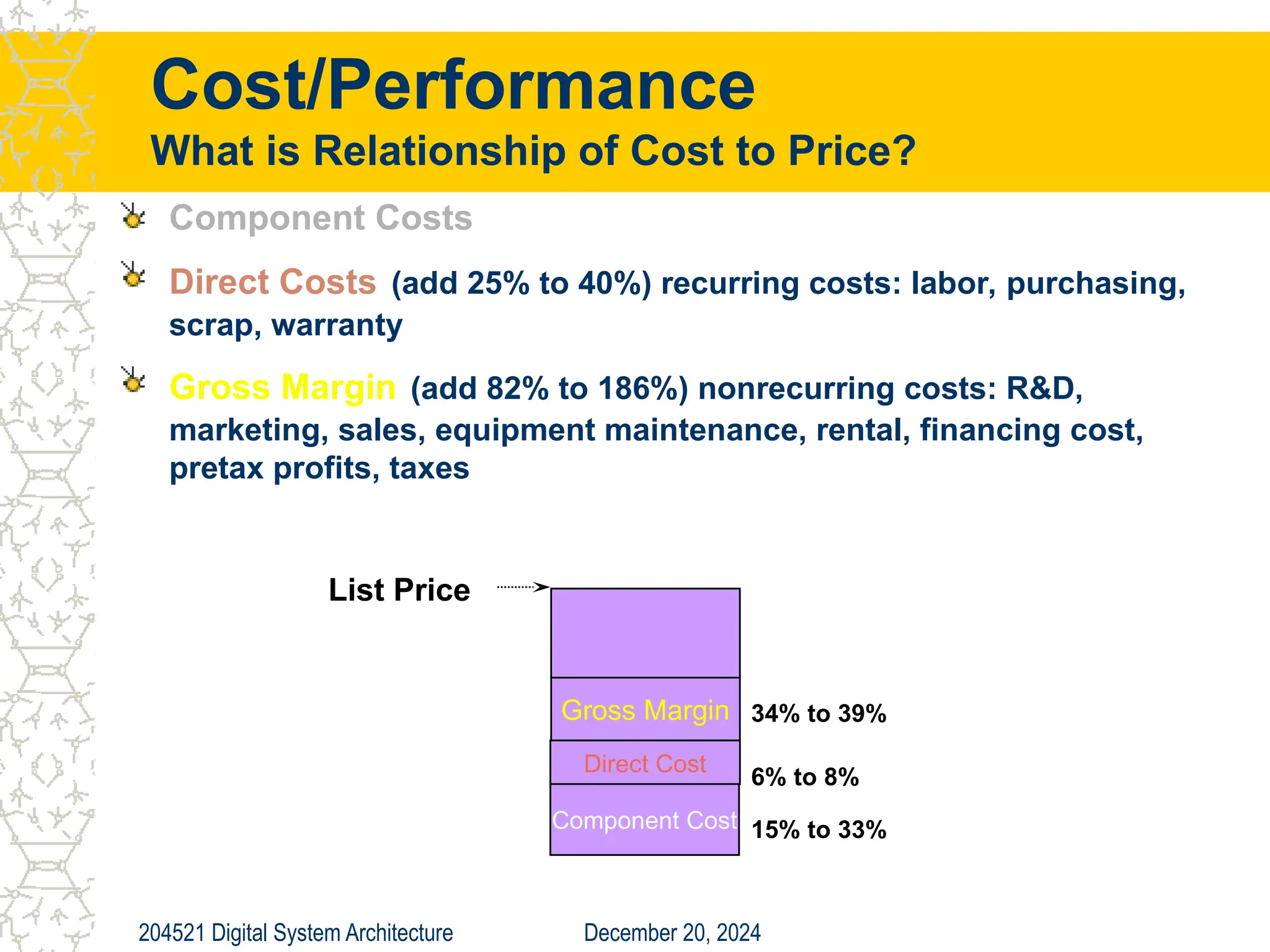
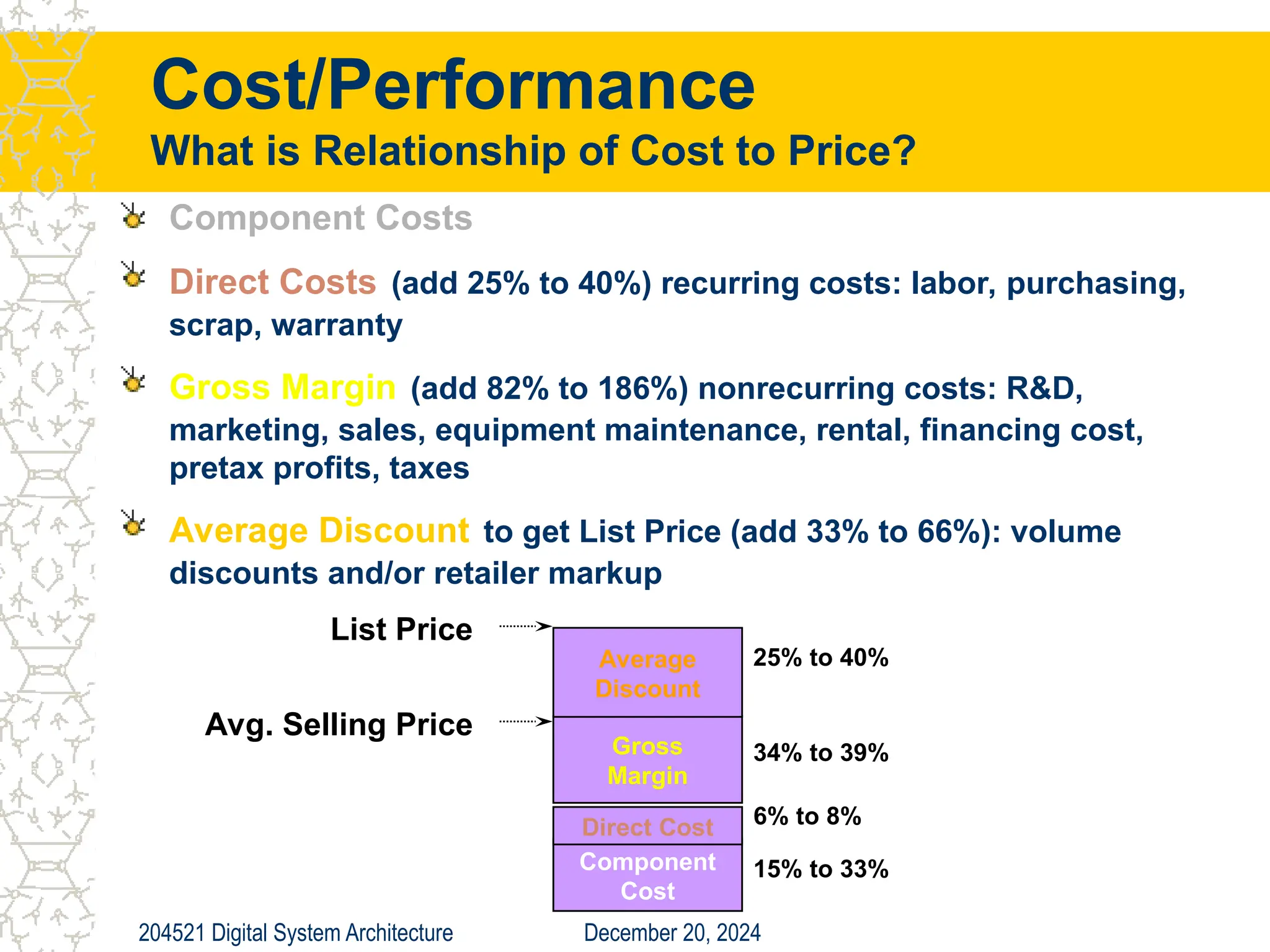
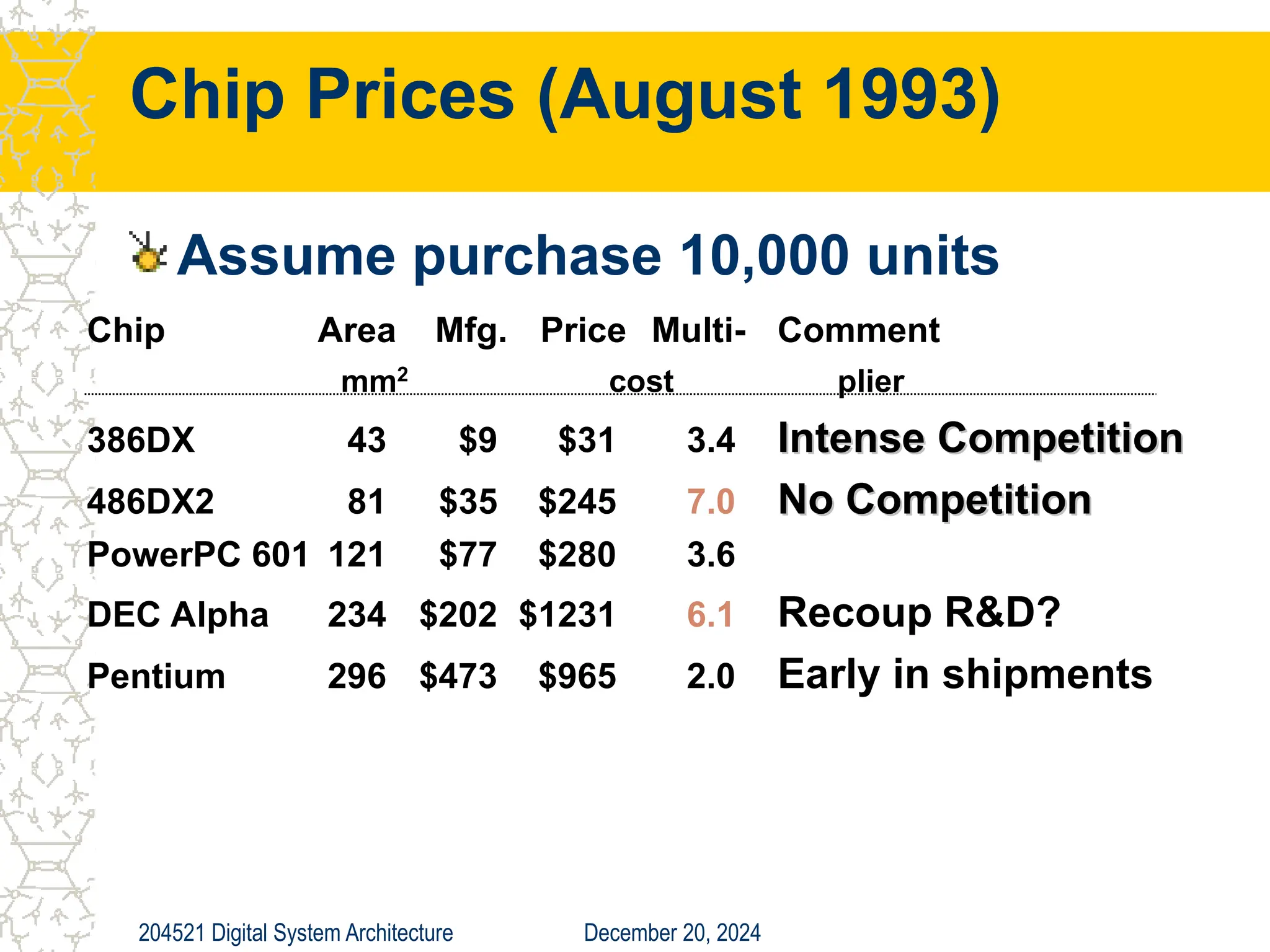
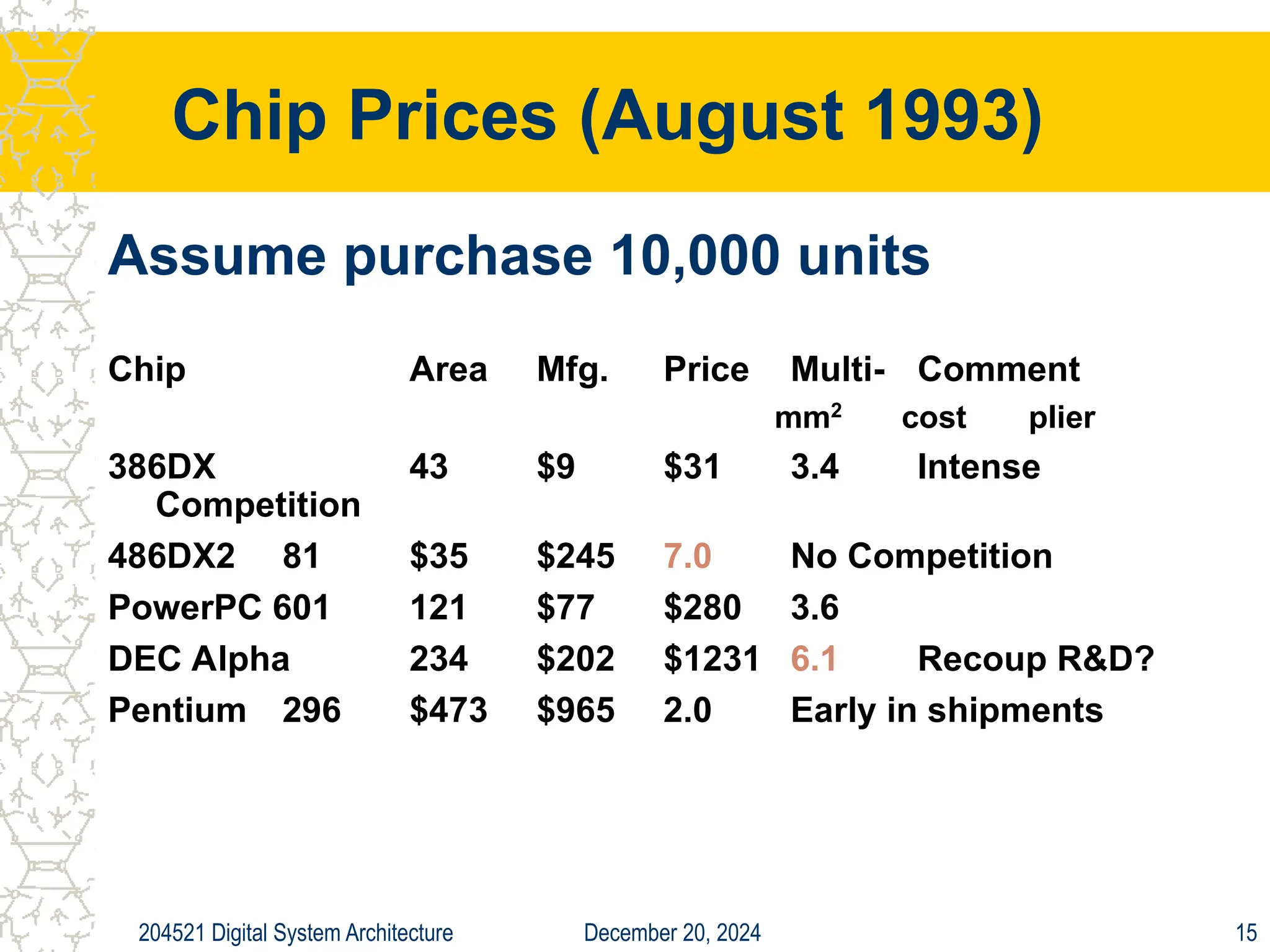
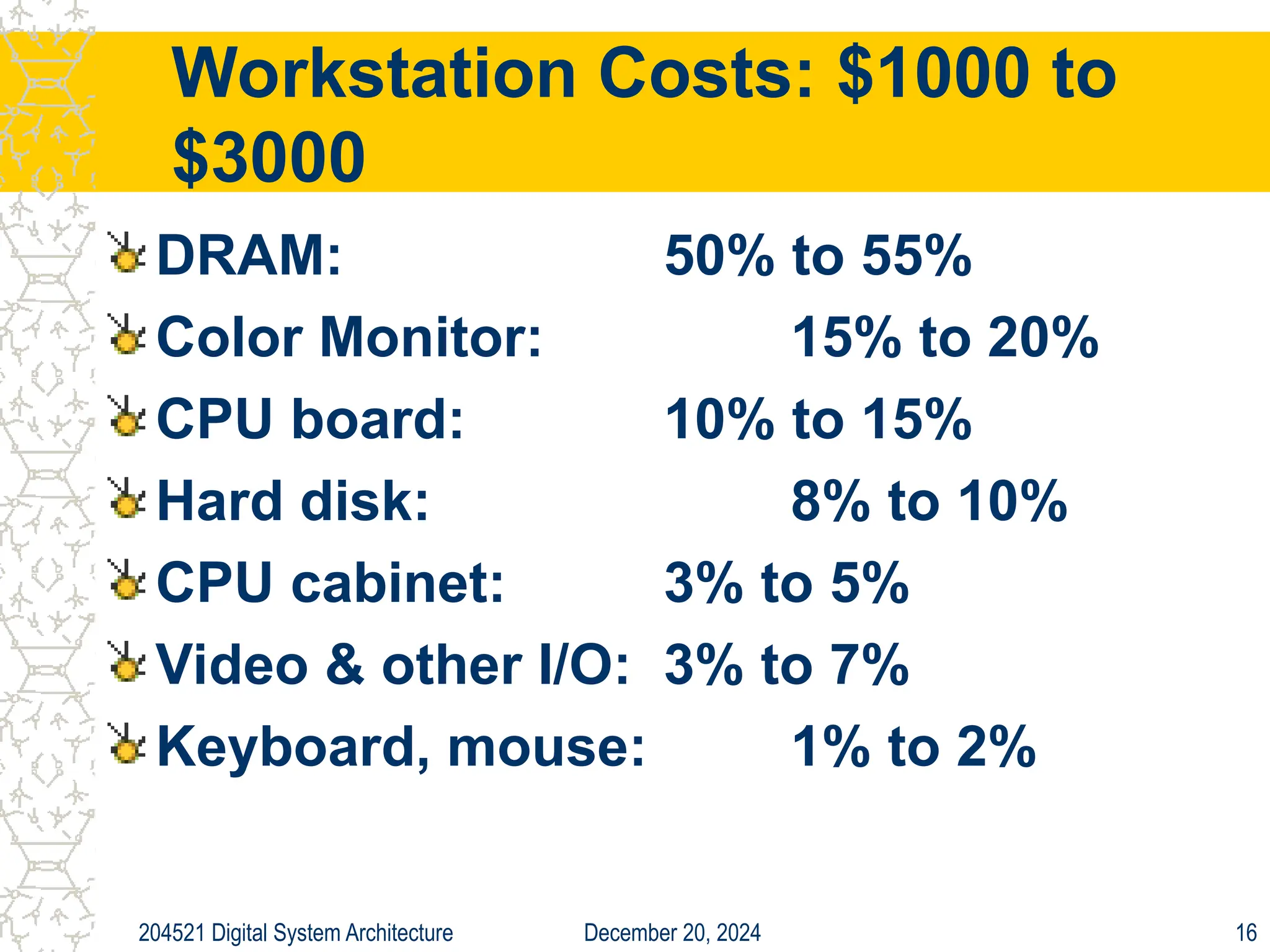
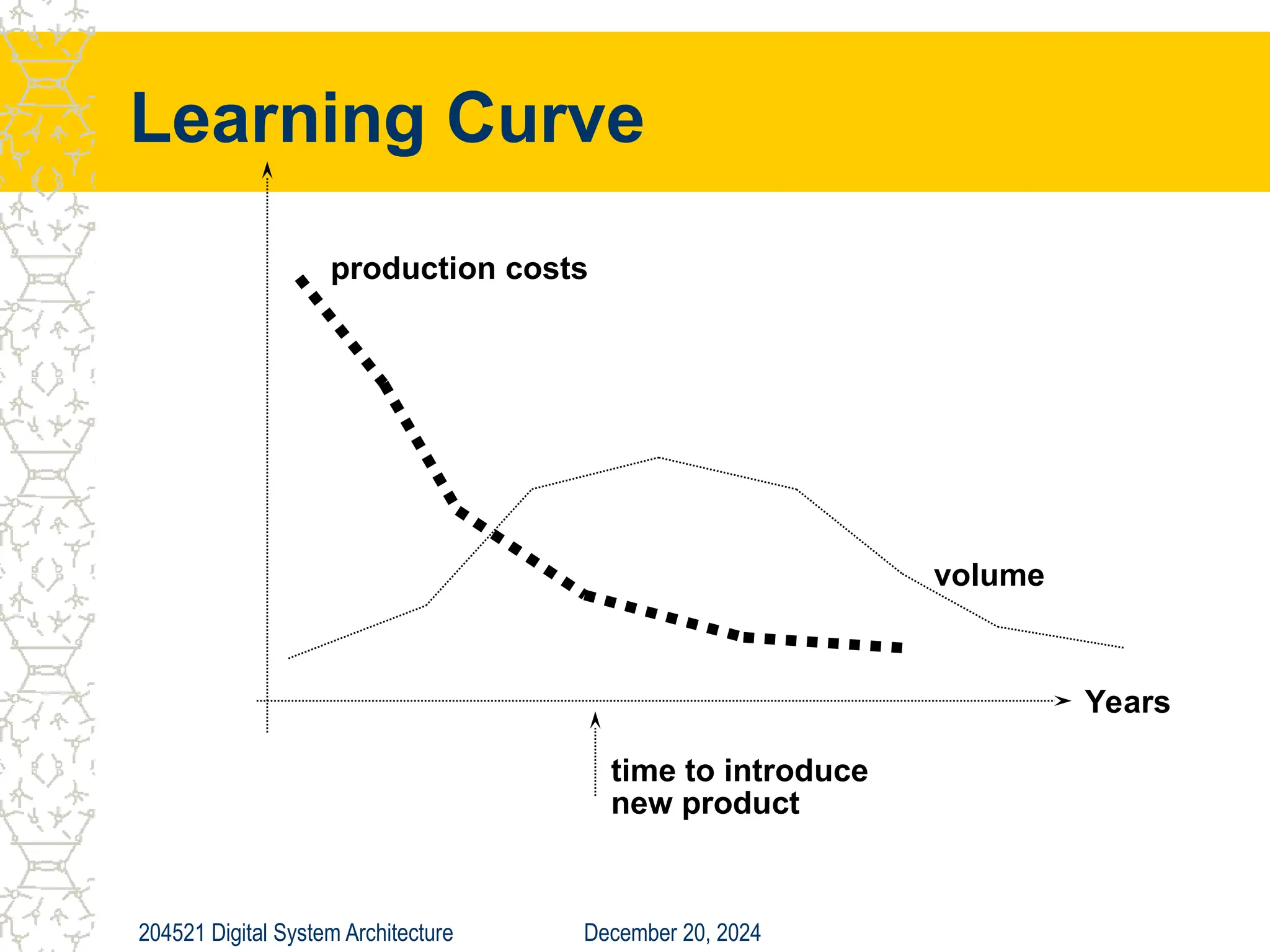
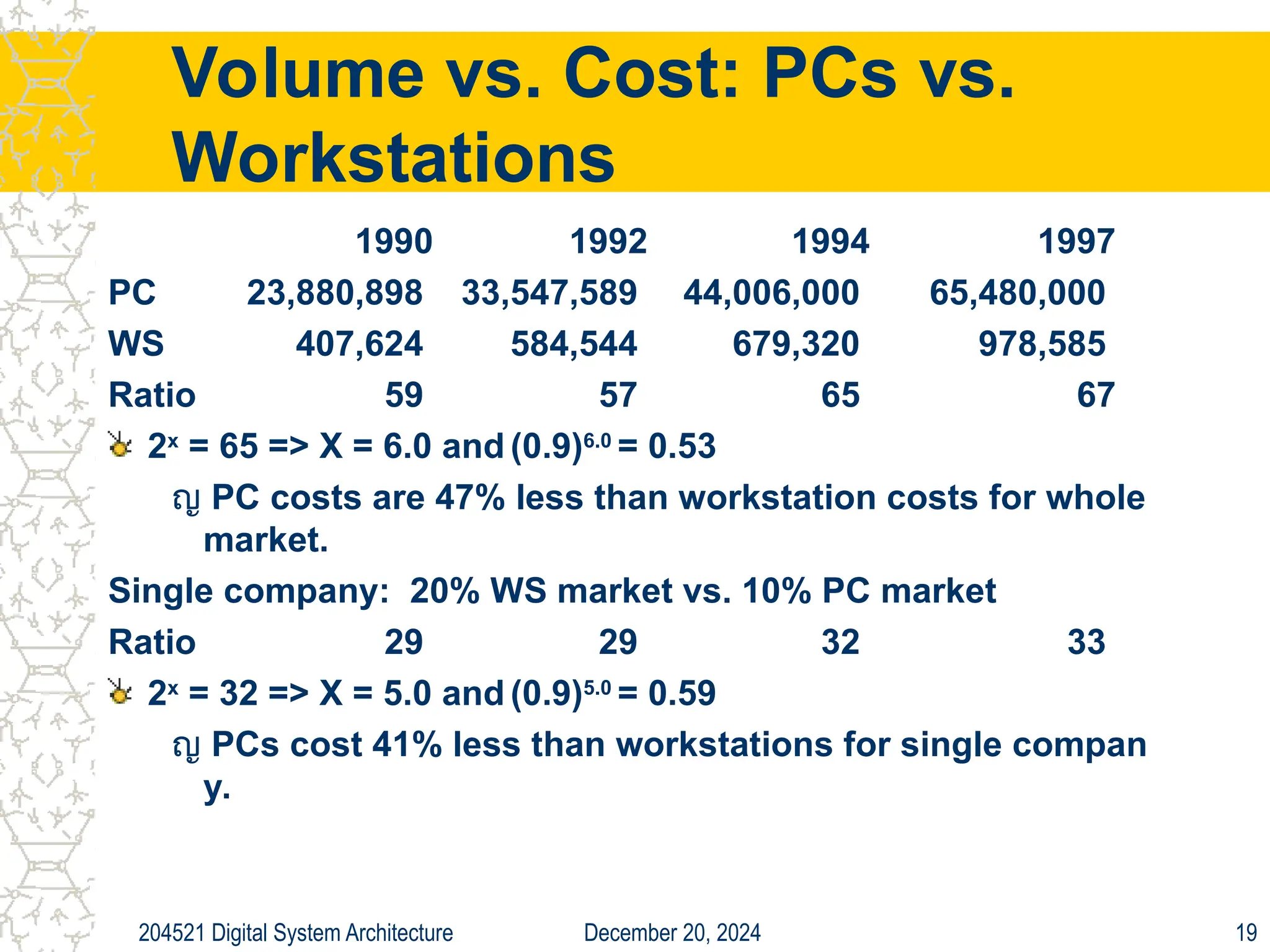
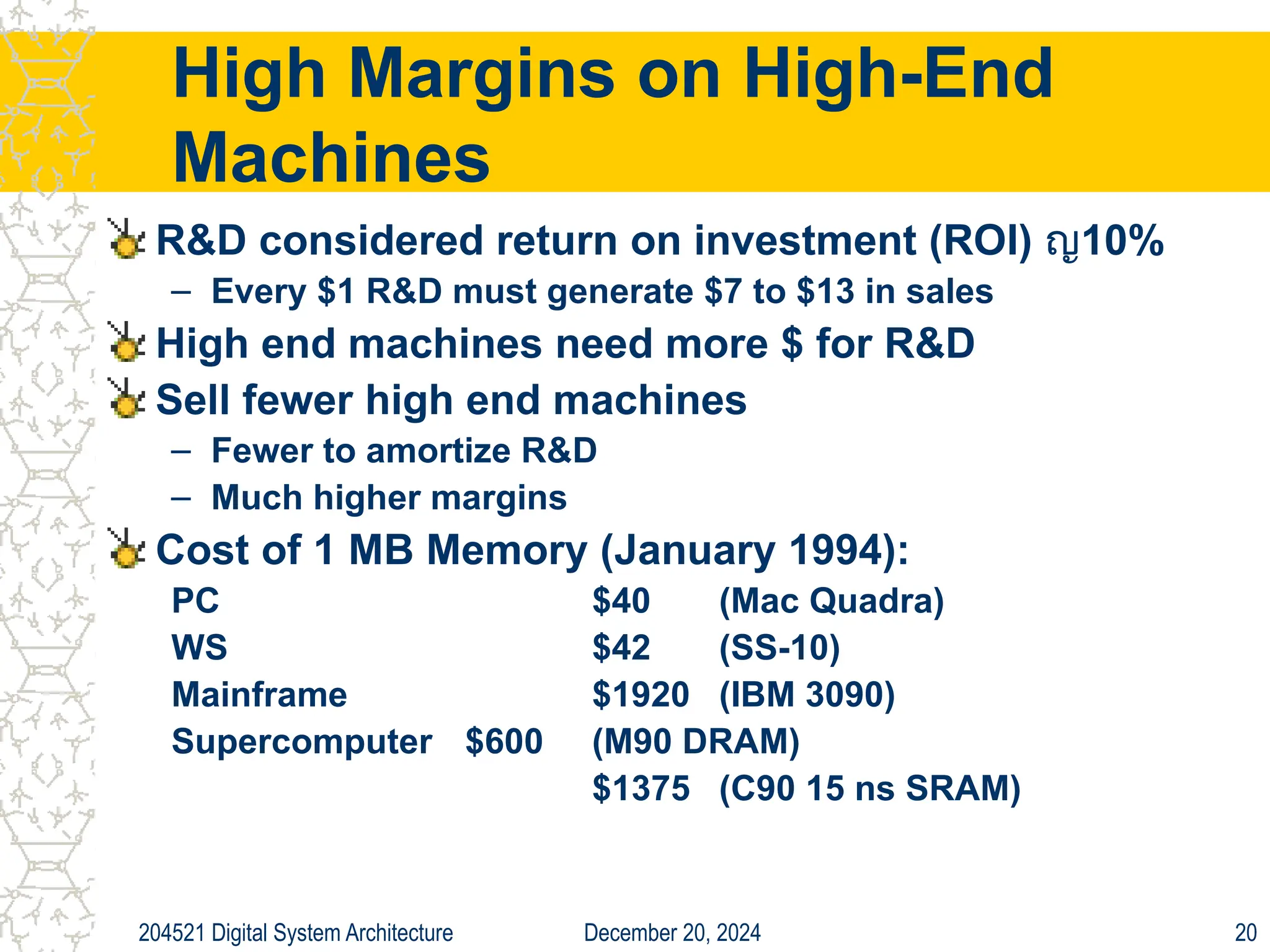
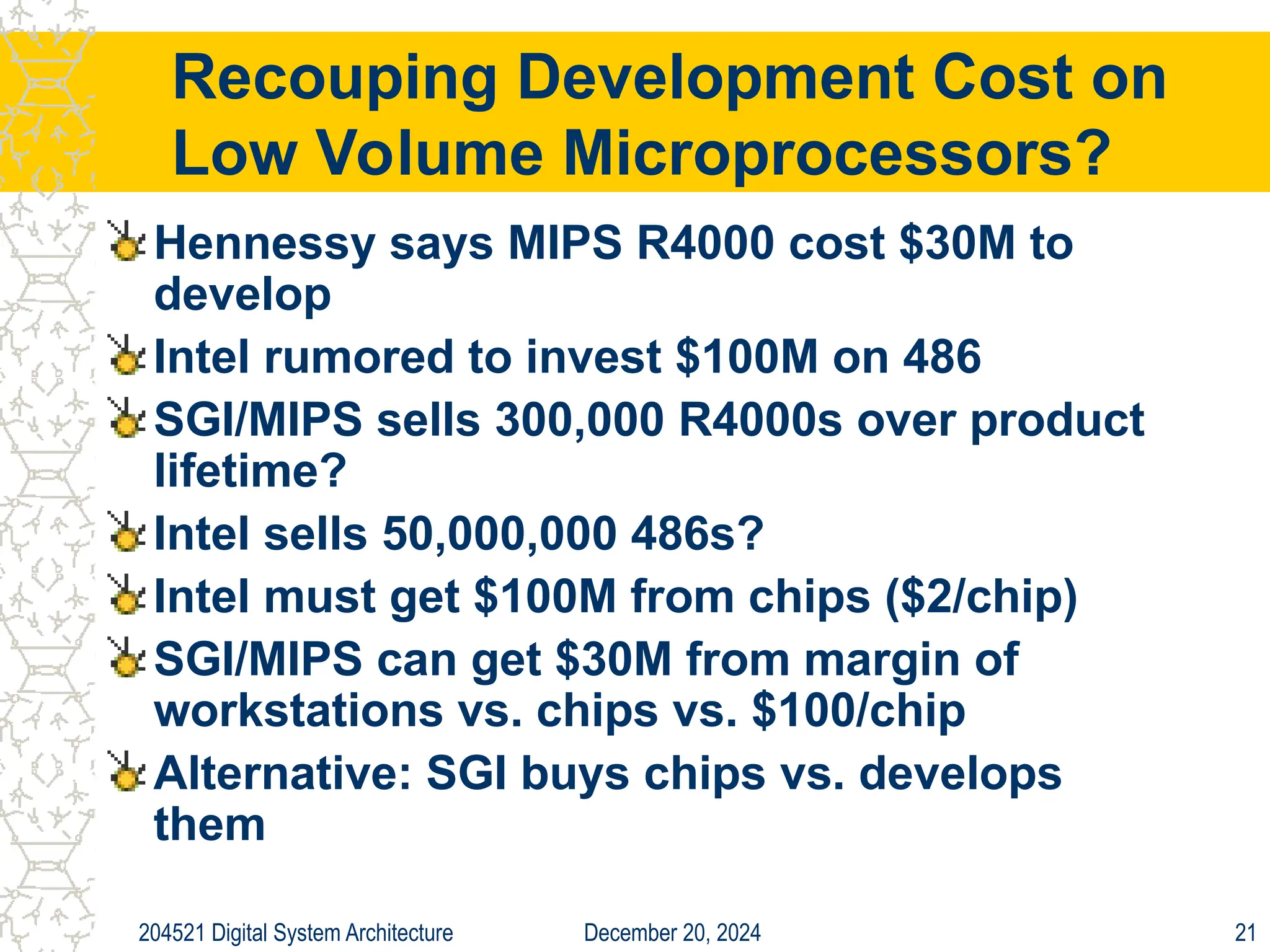
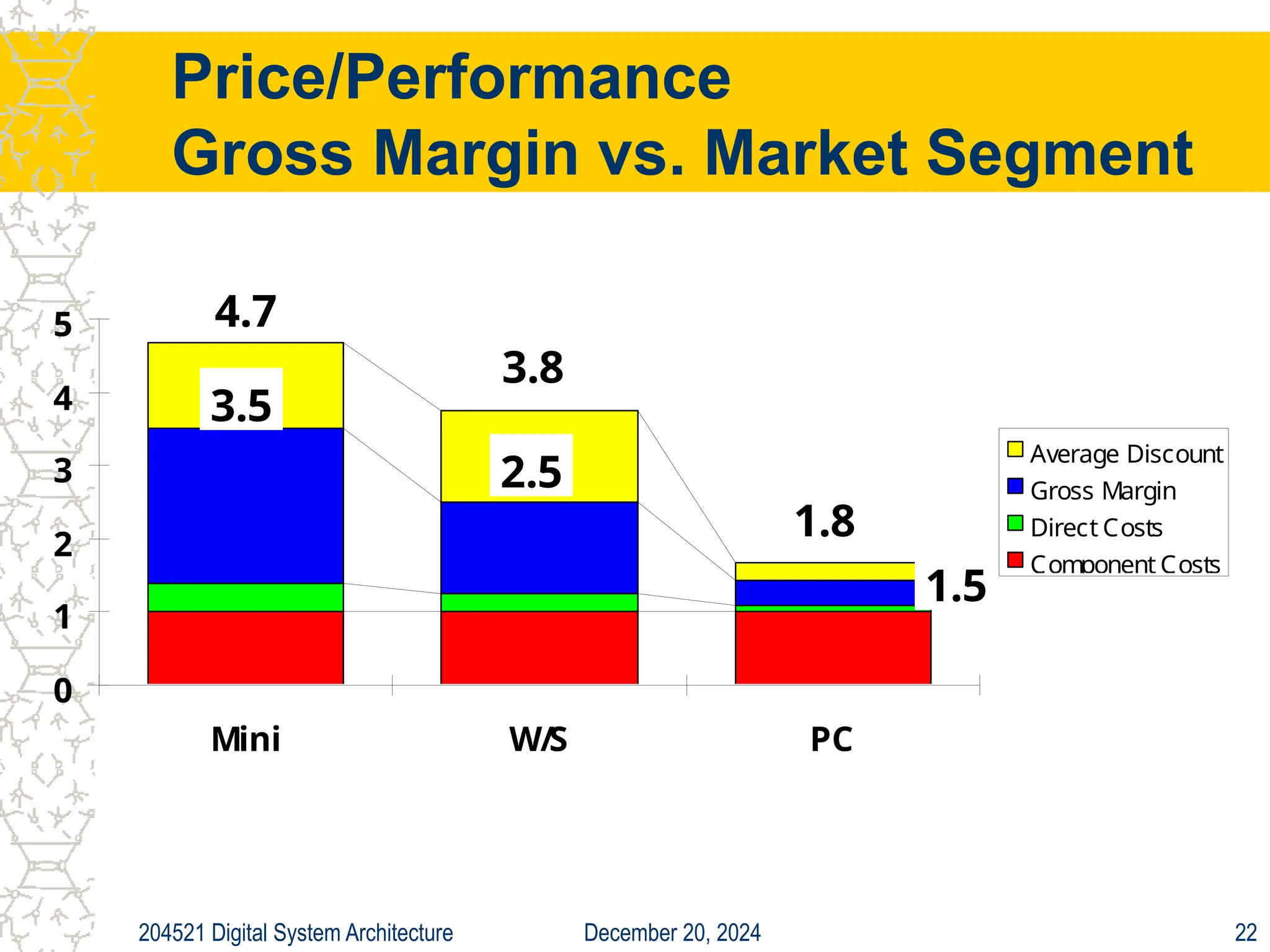
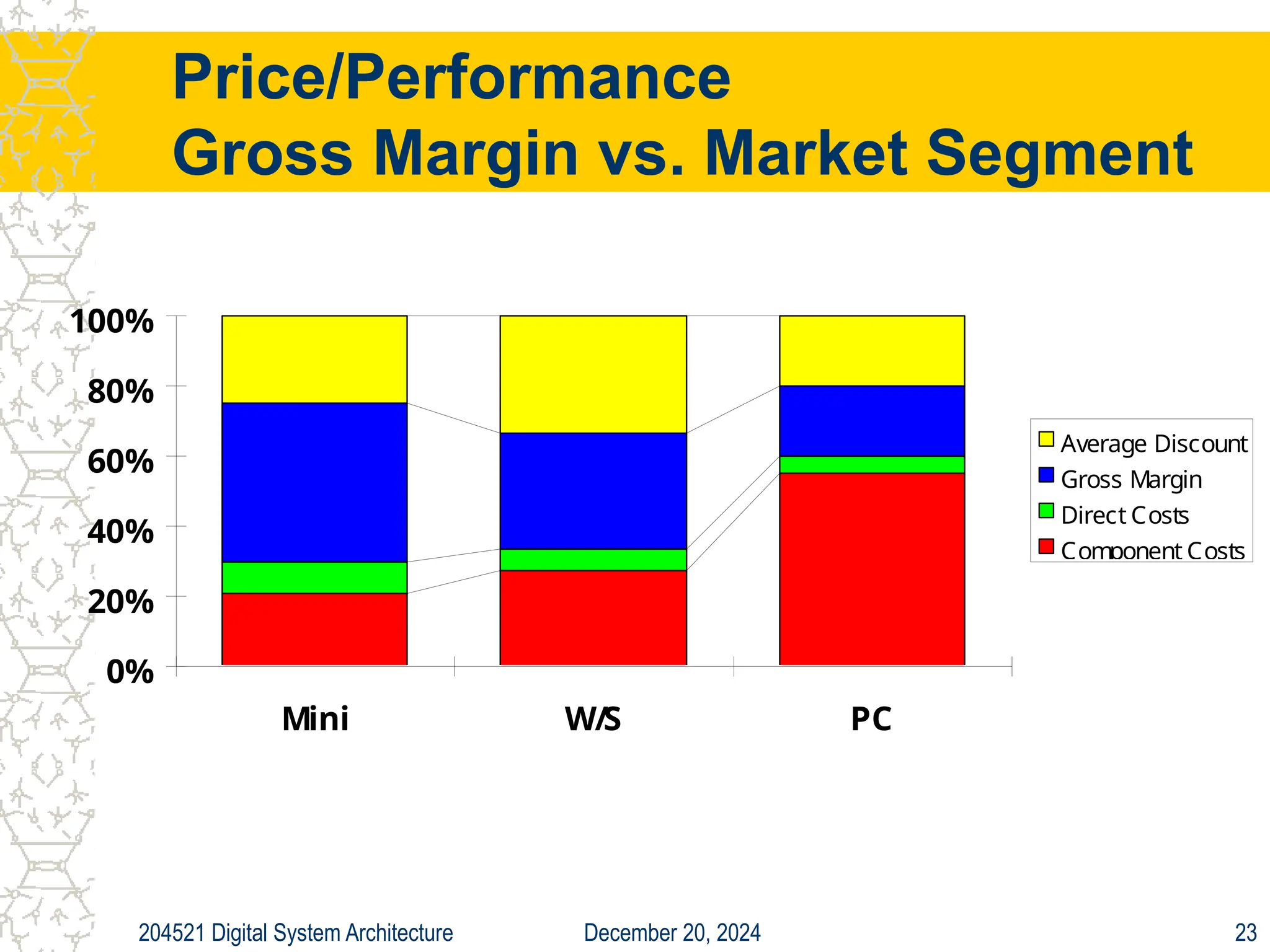
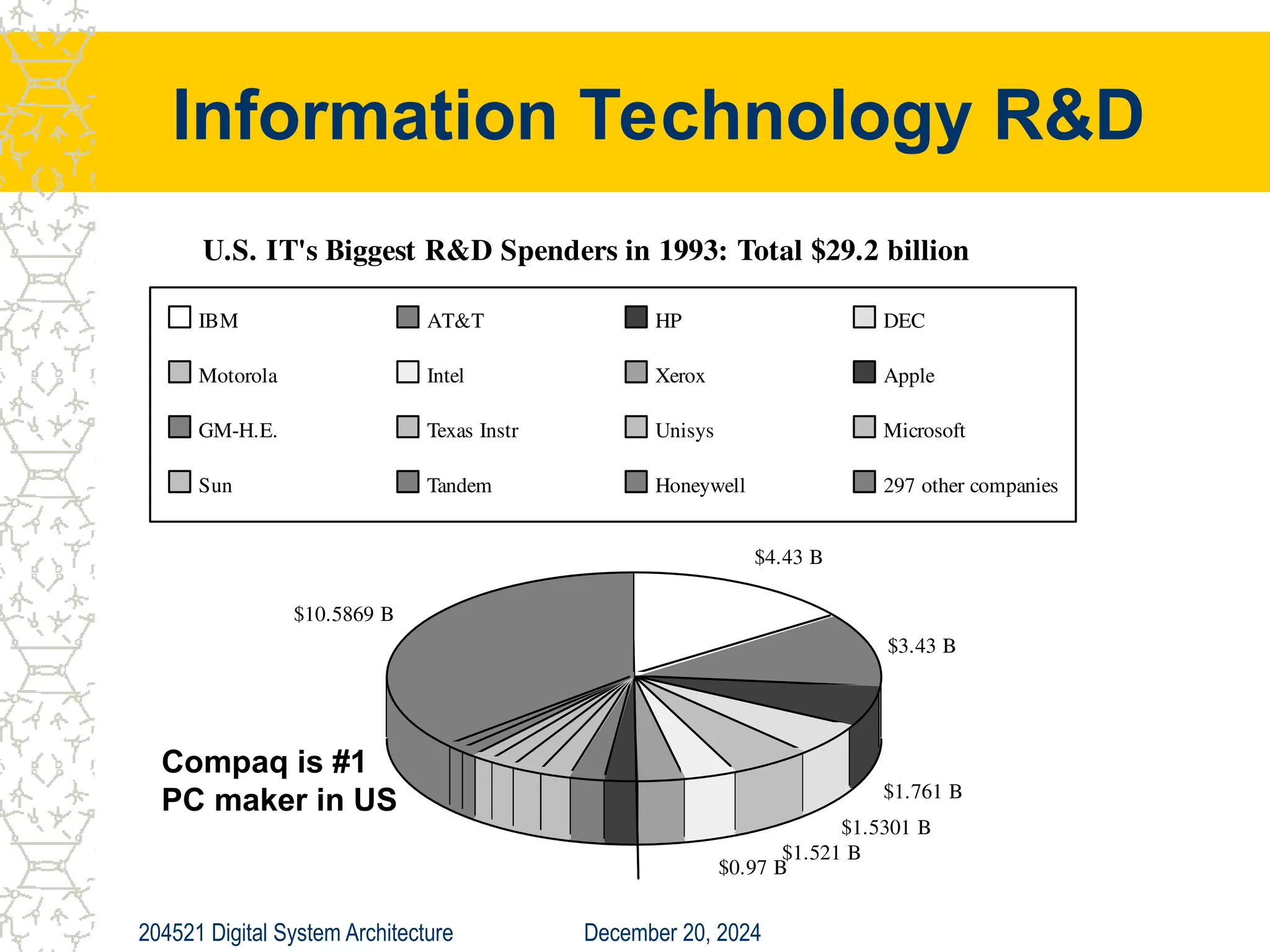
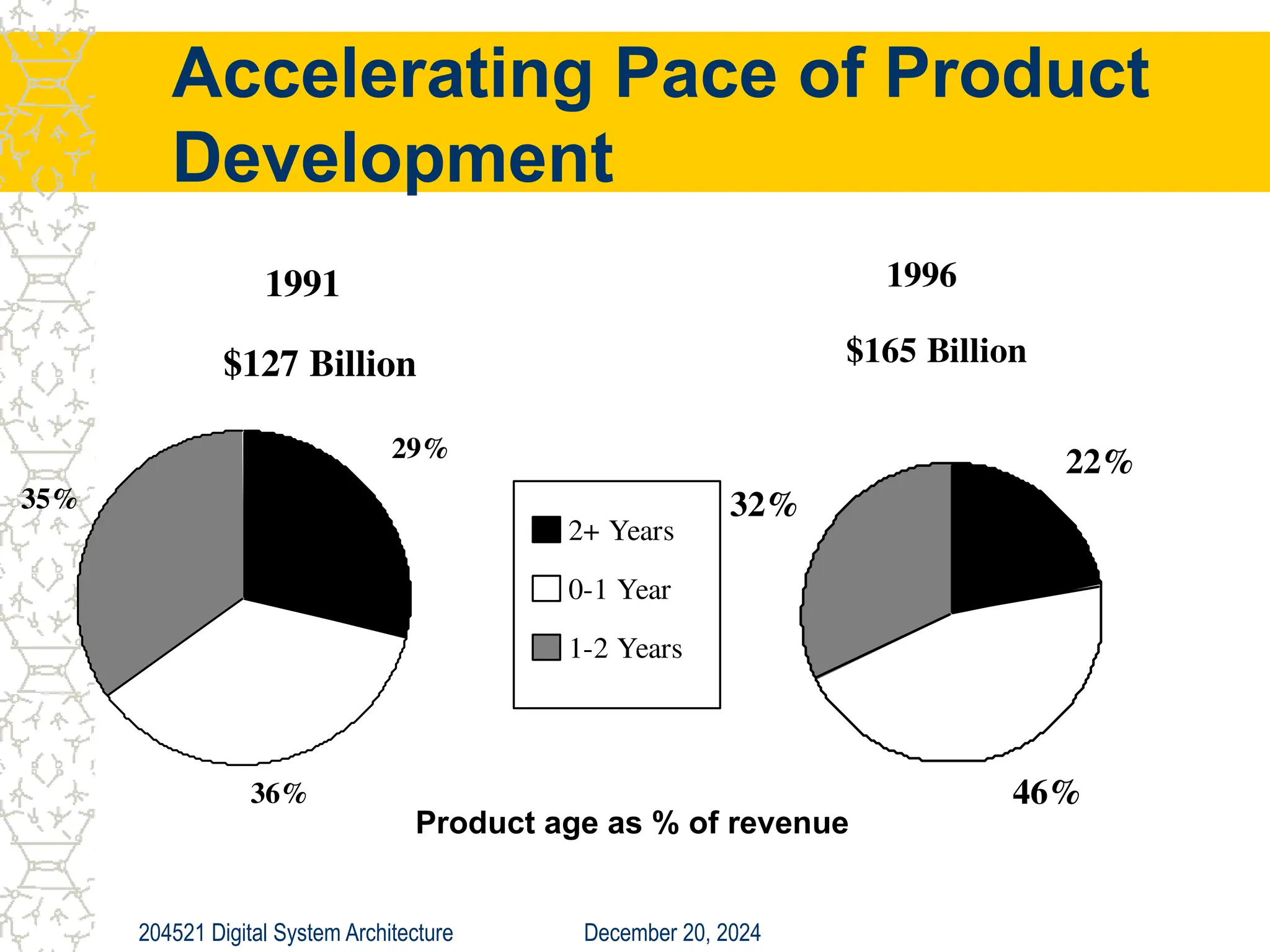
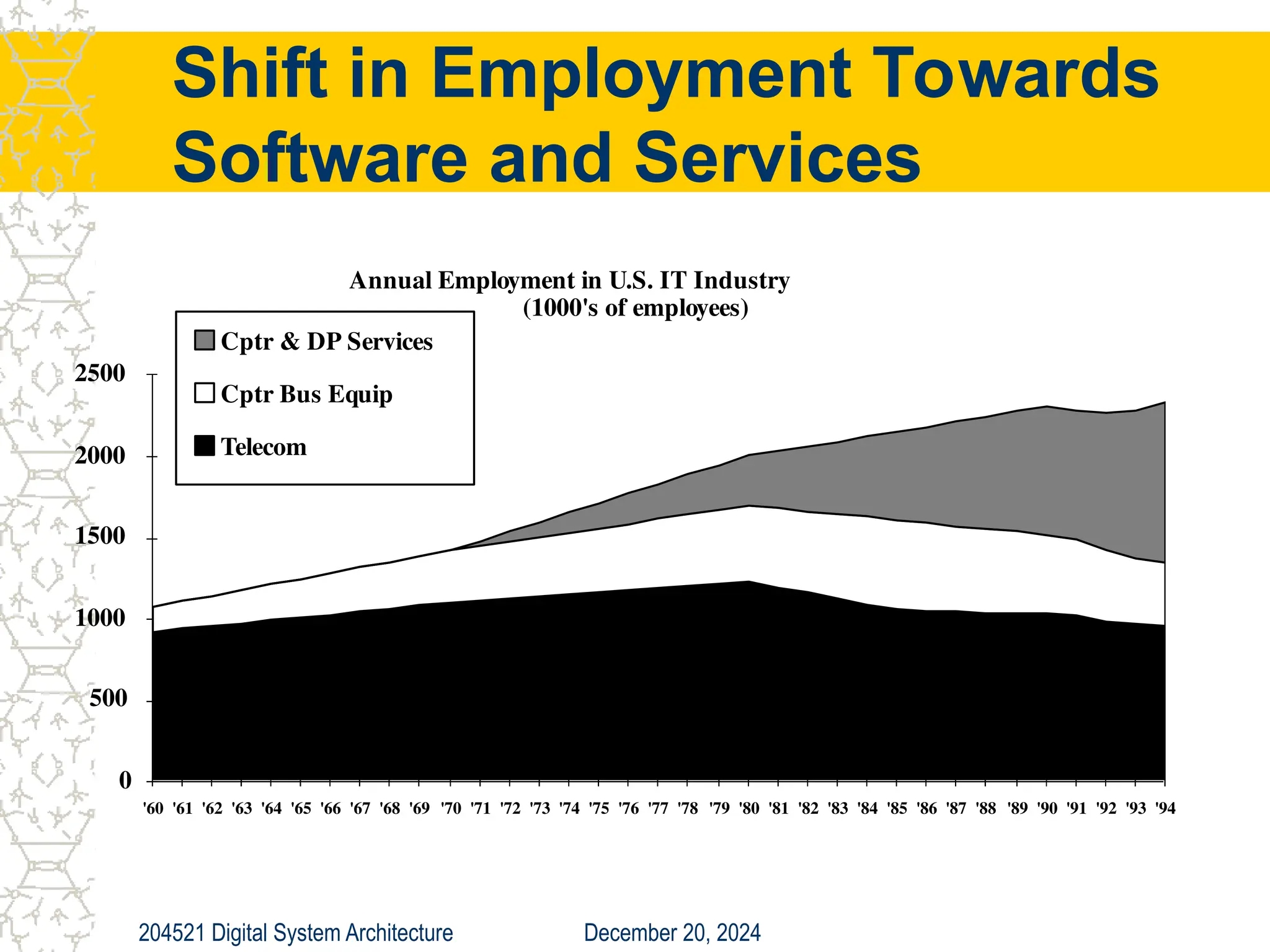
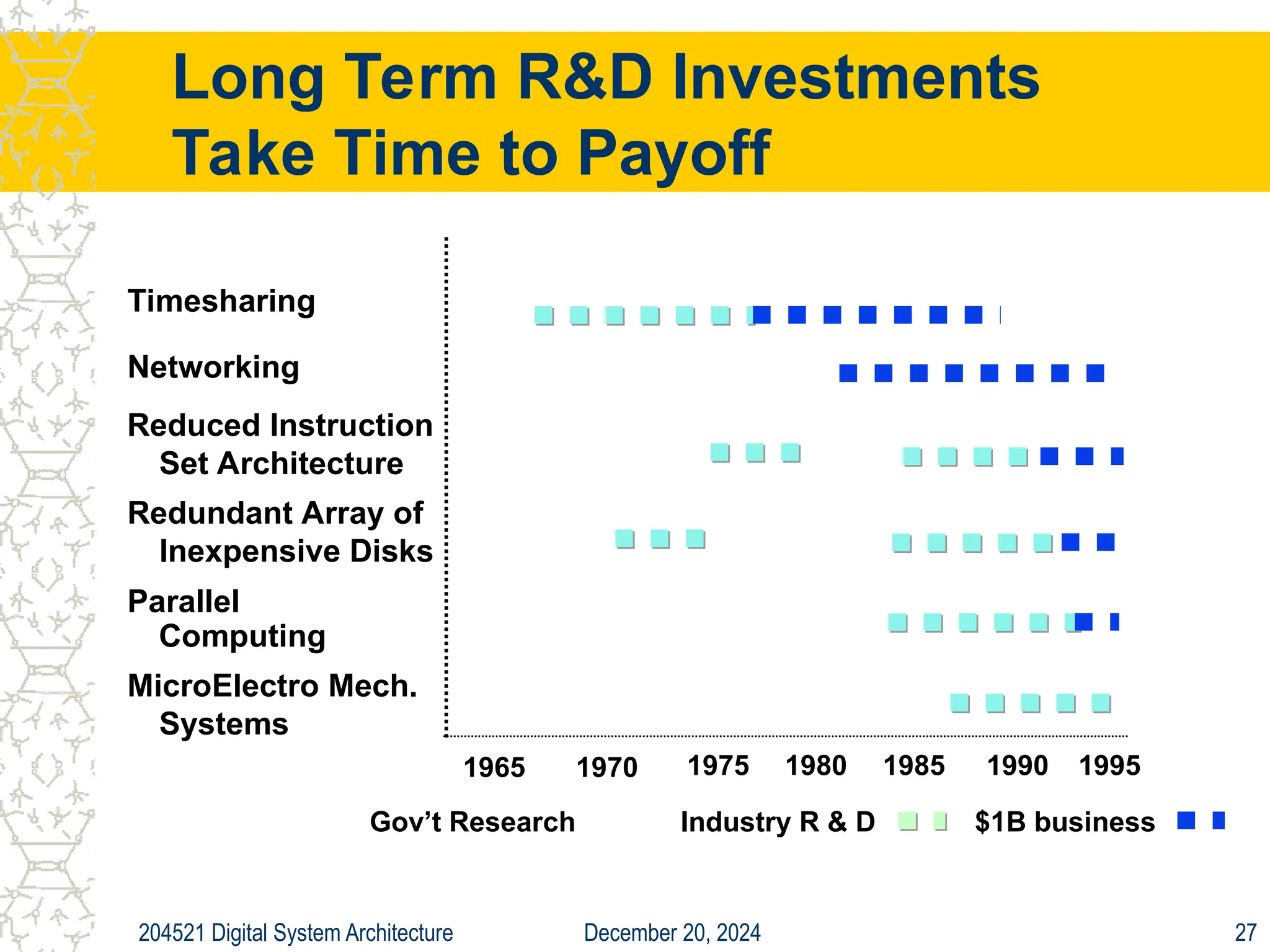
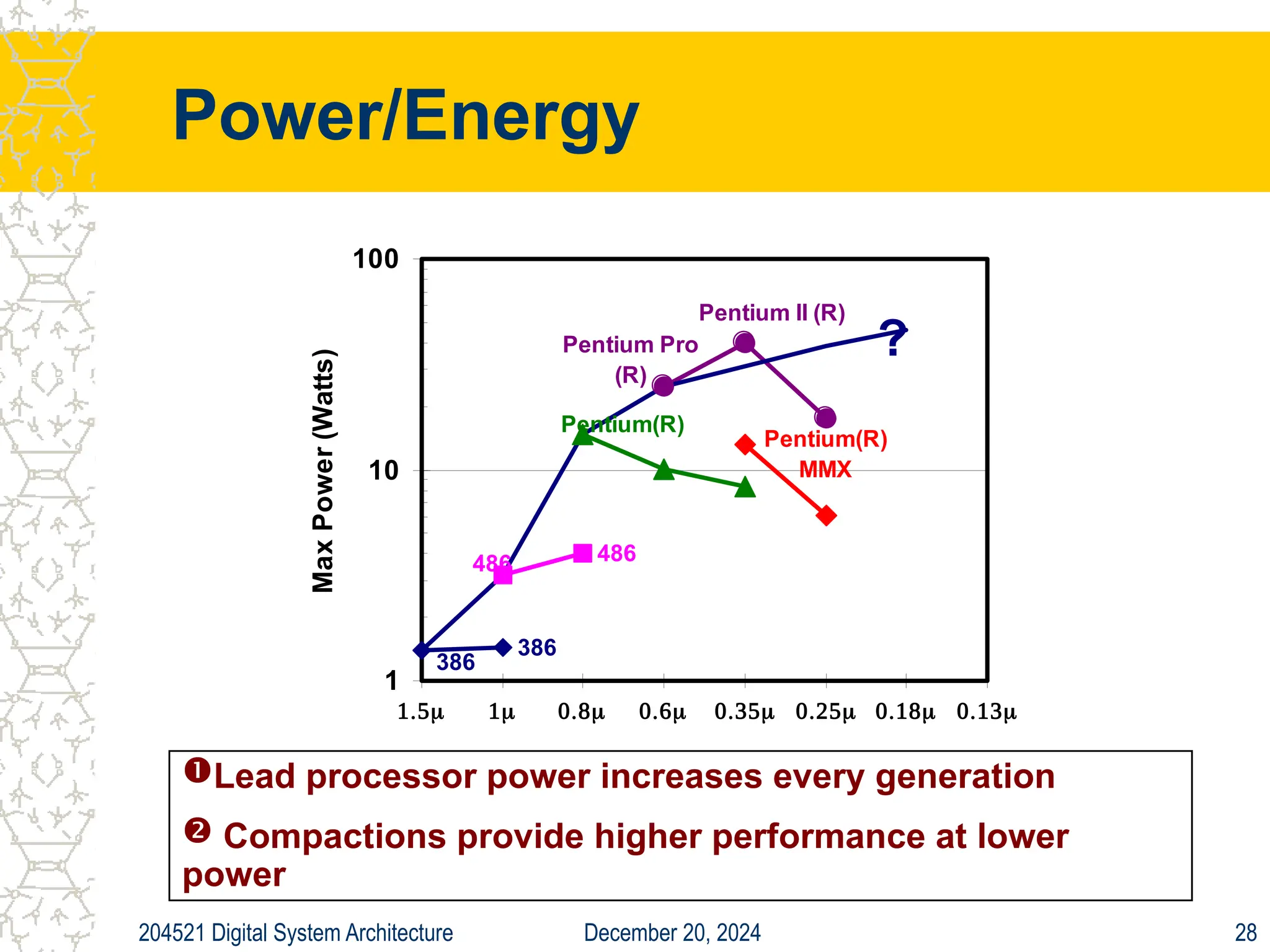
The document discusses digital system architecture focusing on cost, price, and performance, emphasizing the importance of execution time as a measure of computer performance. It details integrated circuit costs, manufacturing complexities, and the impact of market competition on product pricing, along with differences in costs between PCs and workstations. Additionally, it covers the significance of R&D investments and discusses trends in IT employment and product development over time.