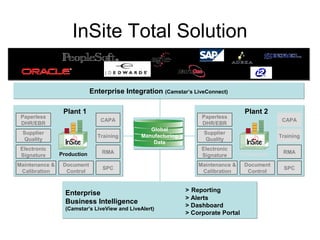
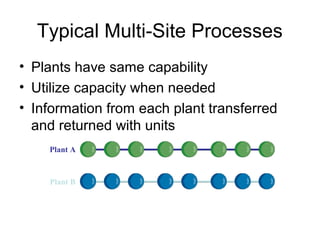
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) fill the gap between plant control systems (PCS) on the factory floor and corporate ERP systems. MES connect disparate factory systems, ensure compliance, and provide critical manufacturing data and alerts. They are implemented by specialized MES vendors who understand production needs better than traditional ERP vendors. Camstar's InSite is an MES that provides enterprise integration, business intelligence, and production execution across multiple plants through solutions like LiveConnect, LiveView, and LiveRelay. InSite supports multi-site manufacturing processes through information sharing and unit transfers between specialized or general plants and subcontractors. While still a developing market, MES are poised to transform manufacturing IT systems.