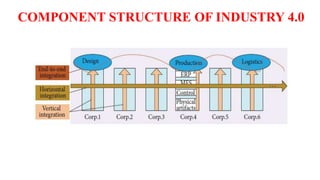
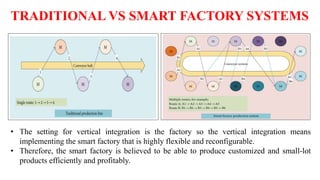
The document discusses the key components of Industry 4.0, which aims to create a new phase of value chain organization through advanced manufacturing technologies. The three main components are horizontal integration between corporations, vertical integration of factory subsystems, and end-to-end digital integration across the product lifecycle. Horizontal integration allows information and materials to flow between cooperating corporations, while vertical integration creates flexible manufacturing systems through integration of sensors, controls and other subsystems. End-to-end engineering integration digitally connects all stages from design to recycling to enable customized product development.