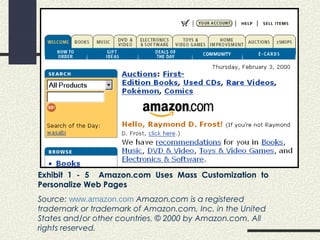
This document discusses various aspects of merchandising, point-of-purchase displays, e-marketing, and customer service. It defines merchandising and point-of-purchase (POP) displays, explaining that POP displays are critical for attracting customers and "selling the product" at the point of purchase. The document also discusses different types of retail displays, merchandising by category and brand, and tips for effective merchandising and signage. It covers challenges and opportunities in e-marketing, including how e-marketing can increase marketing efficiency and add customer value. Finally, it defines customer service and the importance of both material and personal aspects of customer service.