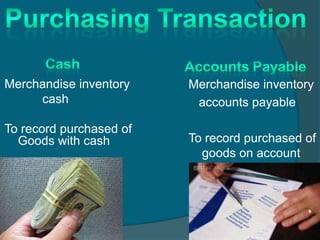
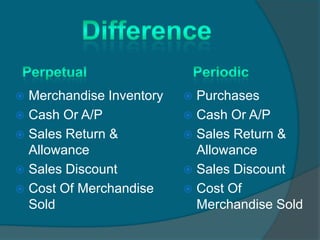
The document discusses key concepts related to inventory accounting including:
1) It defines merchandise inventory as goods owned by a business that are held for sale to customers.
2) It explains the difference between perpetual and periodic inventory systems, with perpetual updating inventory records continuously and periodic conducting a physical count annually.
3) It outlines different inventory costing methods including FIFO, LIFO, and average cost.