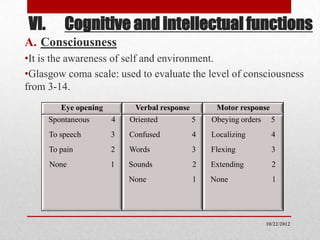
The document provides an overview of a mental state examination. It discusses examining a patient's appearance and behavior, emotions, thinking, speech, perception, cognitive/intellectual functions, and insight. The examination assesses factors such as motor activity, thought content and form, memory, intelligence, and consciousness. Disorders are explored such as thought disorders, hallucinations, delusions, and levels of insight into illness. The mental state exam provides a framework for understanding a patient's psychological state.