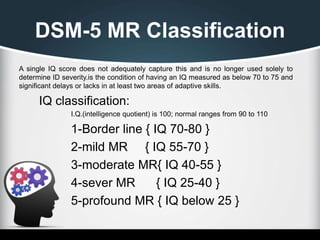
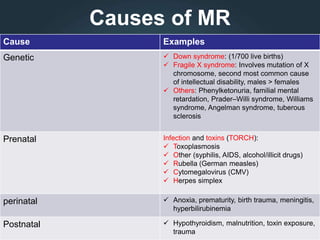
Mental retardation, now called intellectual disability, is characterized by impaired cognitive and adaptive functioning that is present in approximately 1% of the population. It is caused by genetic factors in about 5% of cases, prenatal issues in 30% of cases such as infections, and perinatal problems like prematurity in 10% of cases. The causes can be classified based on genetic testing and family history, prenatal or postnatal onset. Diagnosis involves assessing deficits in intellectual and adaptive functioning through cognitive tests and determining if onset was before age 18. Prevention strategies include public education, neonatal screening, and early intervention programs.