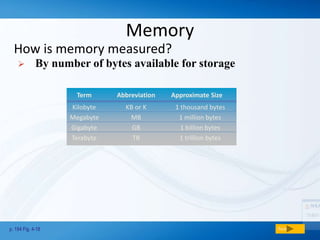
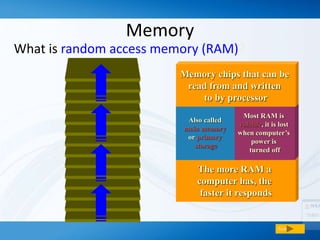
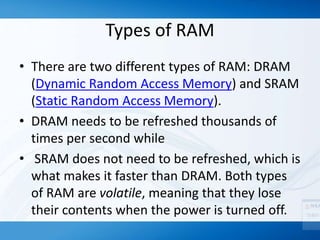
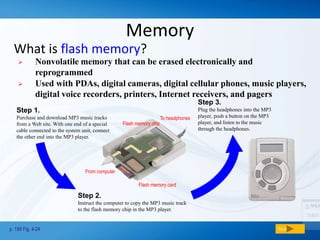
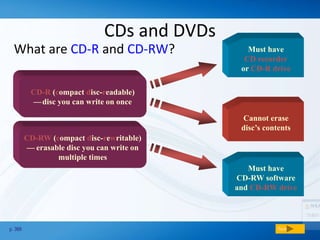
Memory (RAM) is used for temporary storage and processing of data by applications, while storage devices like hard drives are used for long term data retention. There are two main types of RAM - DRAM which must be regularly refreshed, and SRAM which does not need refreshing. Flash memory is a type of non-volatile memory used in devices like MP3 players and cameras. Storage devices include floppy disks, hard disks, CDs/DVDs, and tape, with hard disks being high capacity storage inside computers and removable disks allowing transfer of files.