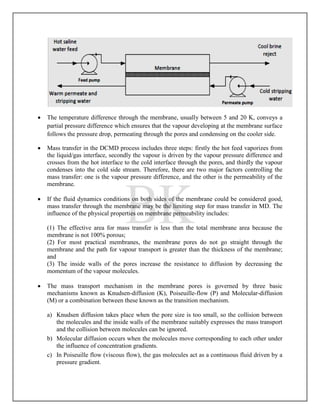
Membrane distillation is a thermally-driven separation process that uses a hydrophobic microporous membrane. Only water vapor molecules transfer through the membrane, driven by a vapor pressure difference induced by a temperature difference across the membrane. There are two main membrane configurations - hollow fiber membranes and flat sheet membranes - which are commonly made from polytetrafluoroethylene, polypropylene, or polyvinylidenefluoride. Membrane distillation has applications in desalination, wastewater treatment, and food processing.