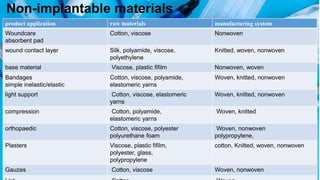
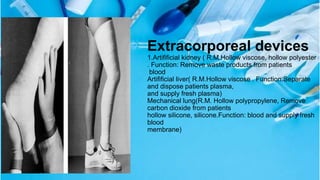
Medical textiles are textile materials engineered for medical applications requiring strength, flexibility, and sometimes permeability. There are four categories: non-implantable materials for external use like wound dressings and bandages; extracorporeal devices like artificial kidneys; implantable materials like sutures and grafts; and healthcare products like surgical gowns and bedding. Key factors for implants are biocompatibility, small fiber size, and lack of toxic substances.