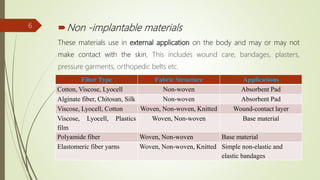
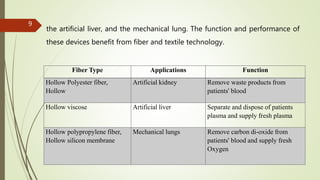
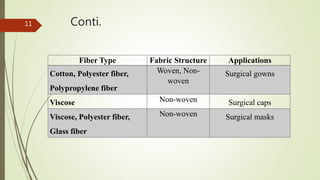
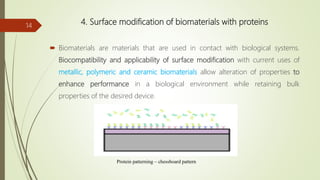
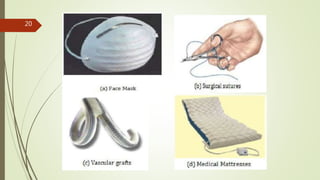
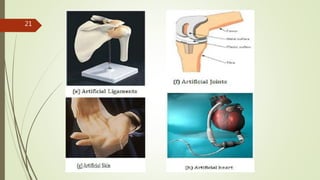
The document provides an overview of biomedical textiles, covering their classification, characteristics, surface modifications, and applications in medical settings. It emphasizes the importance of biocompatibility and the diverse materials used in medical textiles, including both implantable and non-implantable devices. The conclusion highlights the potential for technological advancements to improve healthcare and patient outcomes.