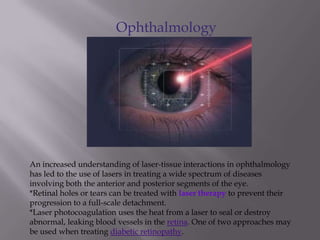
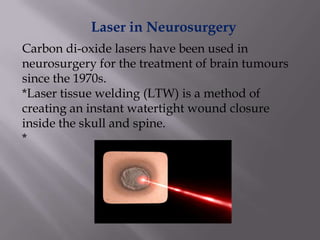
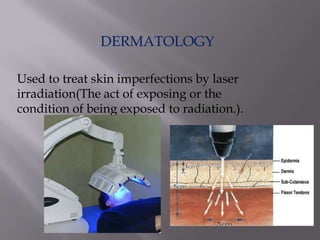
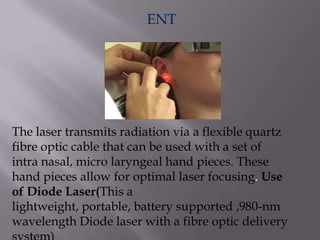
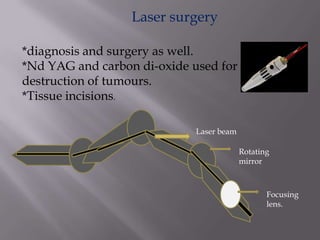
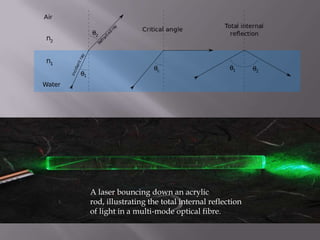
This document discusses the various medical applications of lasers. It begins by explaining the key factors that determine how lasers interact with human tissue, including radiation, wavelength, and energy. It then outlines several specific uses of lasers in ophthalmology, neurosurgery, gastroenterology, dermatology, gynecology, ENT, and laser surgery more broadly. Lasers are used to treat retinal issues, seal blood vessels, weld tissues, remove fat, treat skin imperfections and cancers. The document also discusses the advantages of laser surgery like being painless and promoting fast healing, and the disadvantage of high cost. It concludes by providing details on optical fibers and how they transmit laser light through total internal reflection.