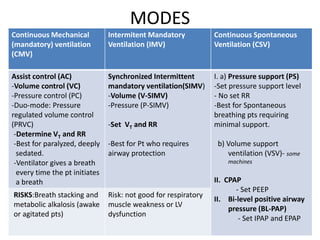
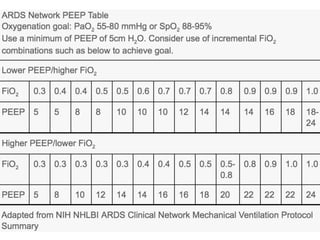
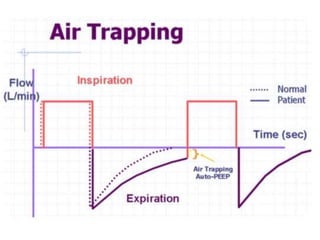
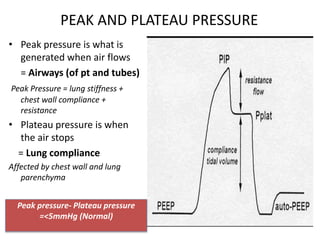
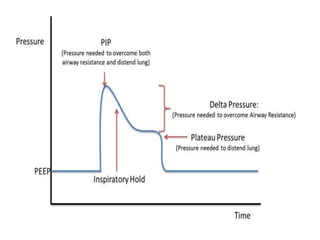
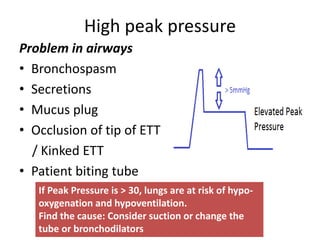
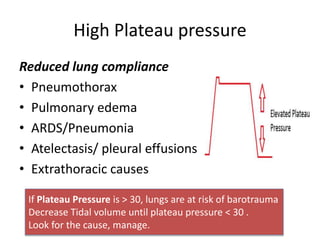
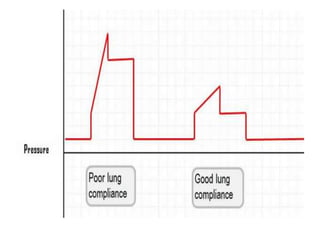
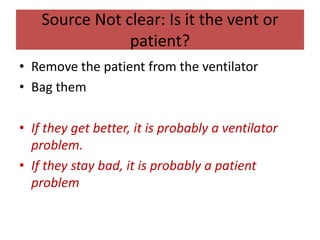
This document outlines the principles and techniques of mechanical ventilation, detailing reasons for intubation, modes of ventilation, and the significance of tidal volume and respiratory rate settings. It discusses troubleshooting methods using the 'DOPES' and 'DOTTS' frameworks, along with case scenarios to illustrate practical application. Additionally, the document provides reference materials for further reading on emergency medicine and critical care practices.