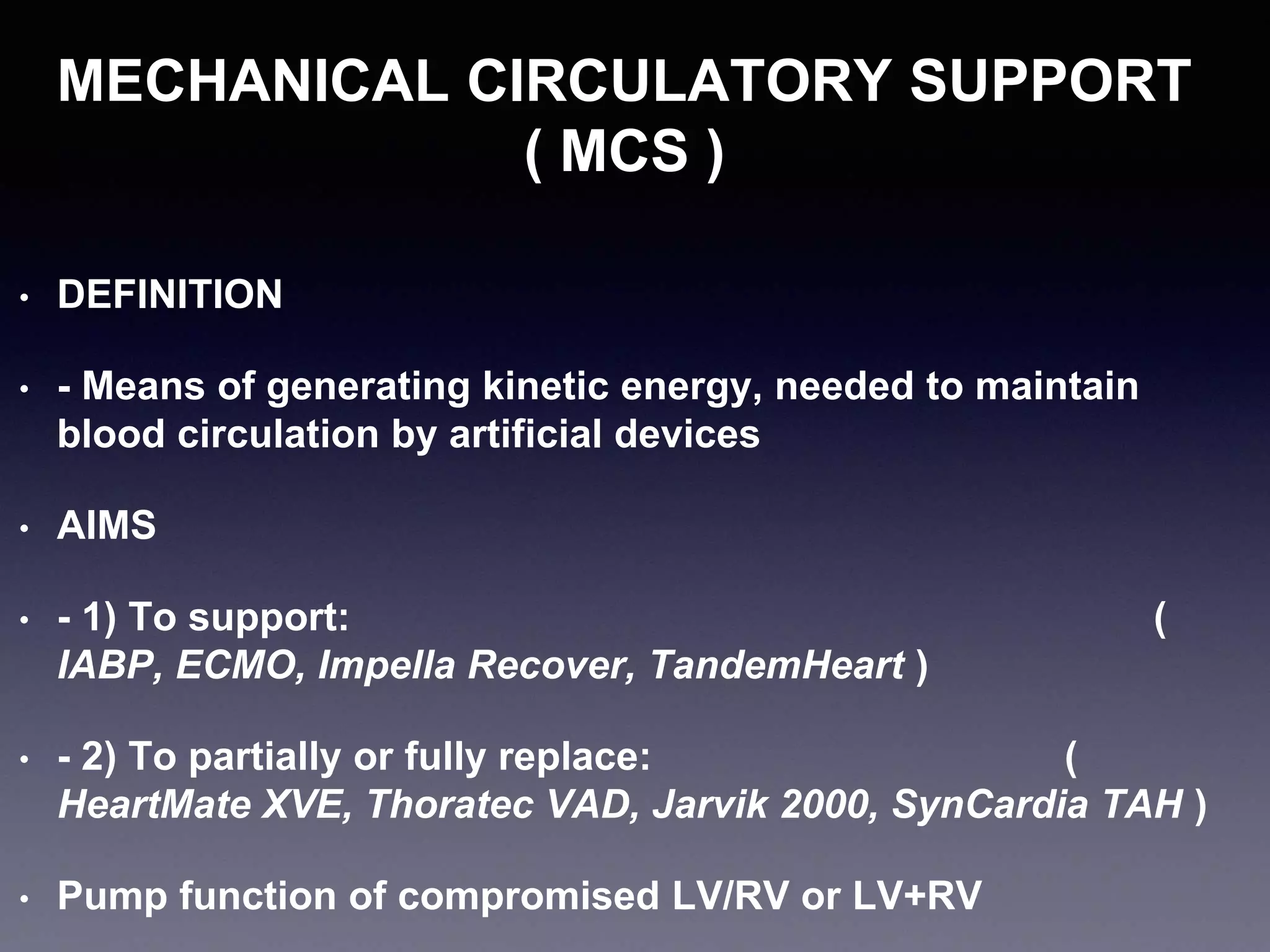
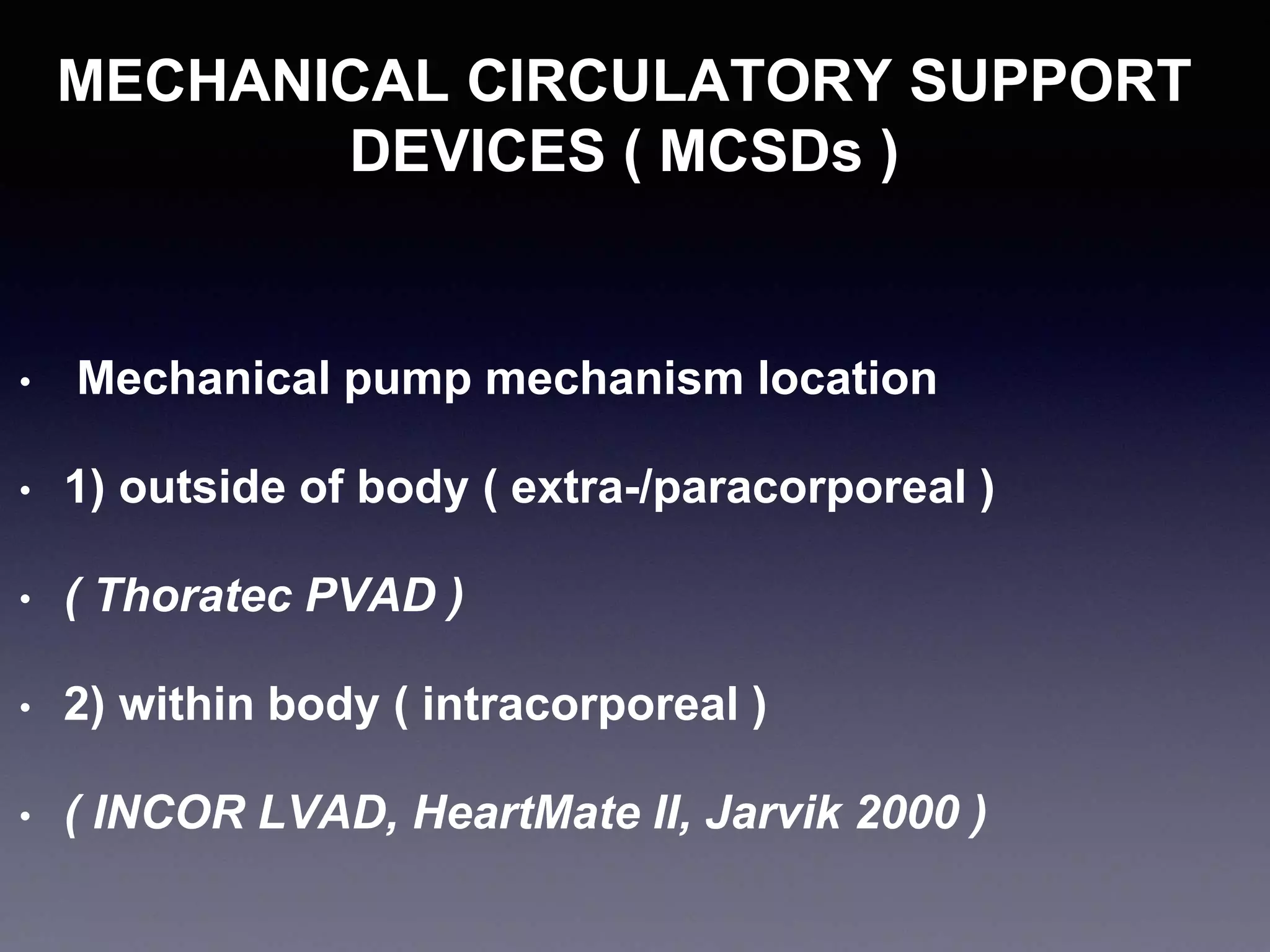
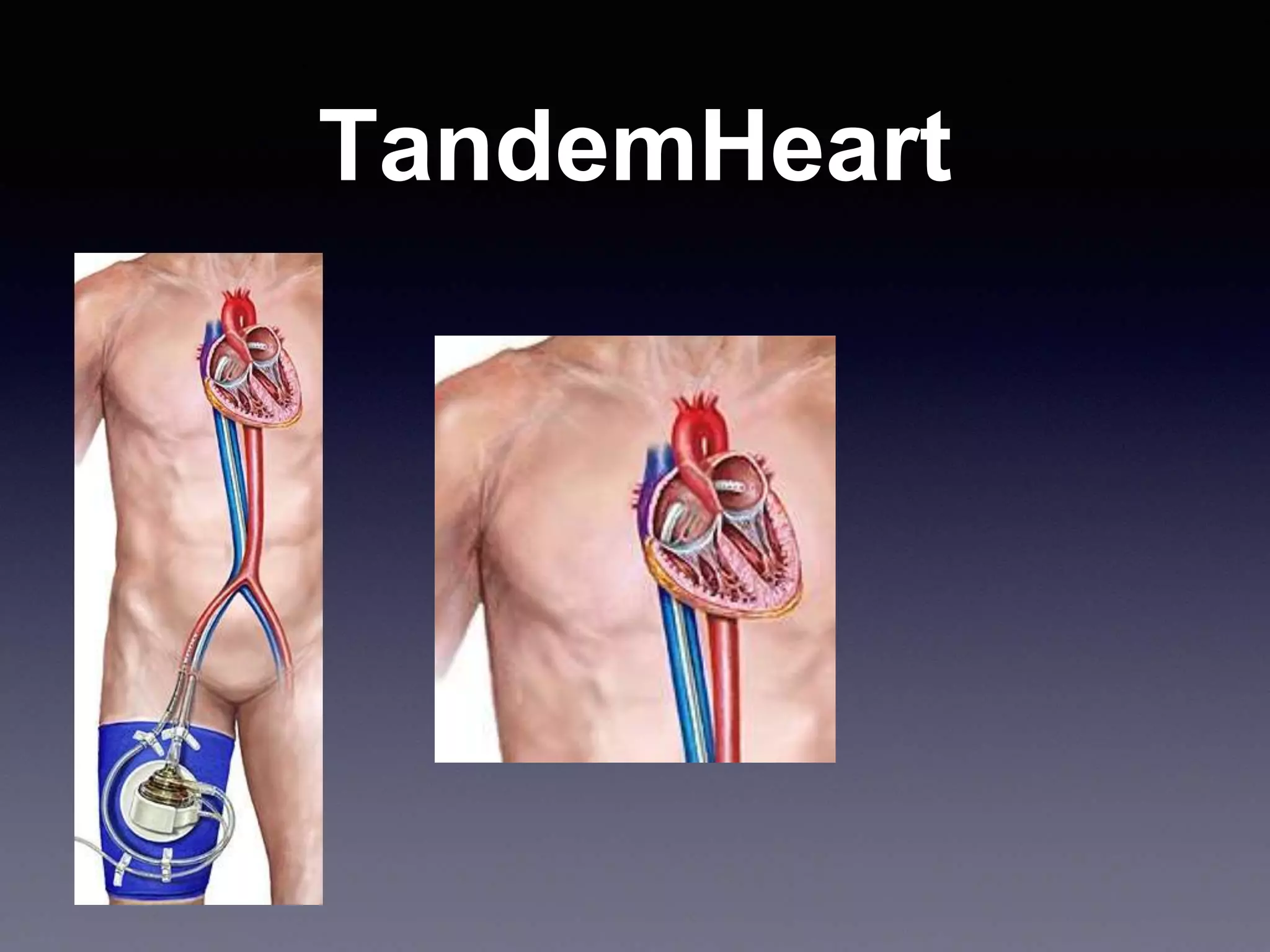
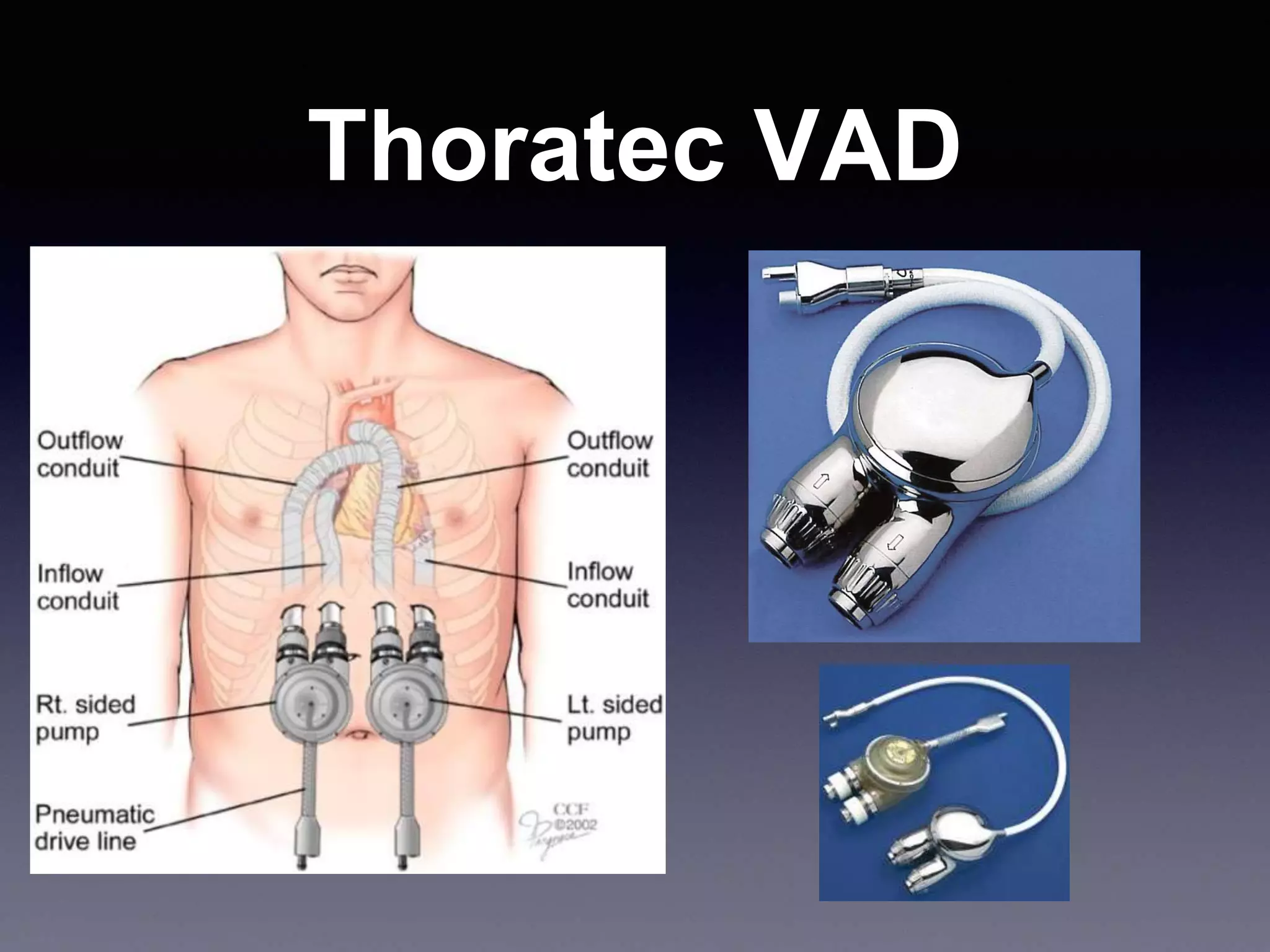
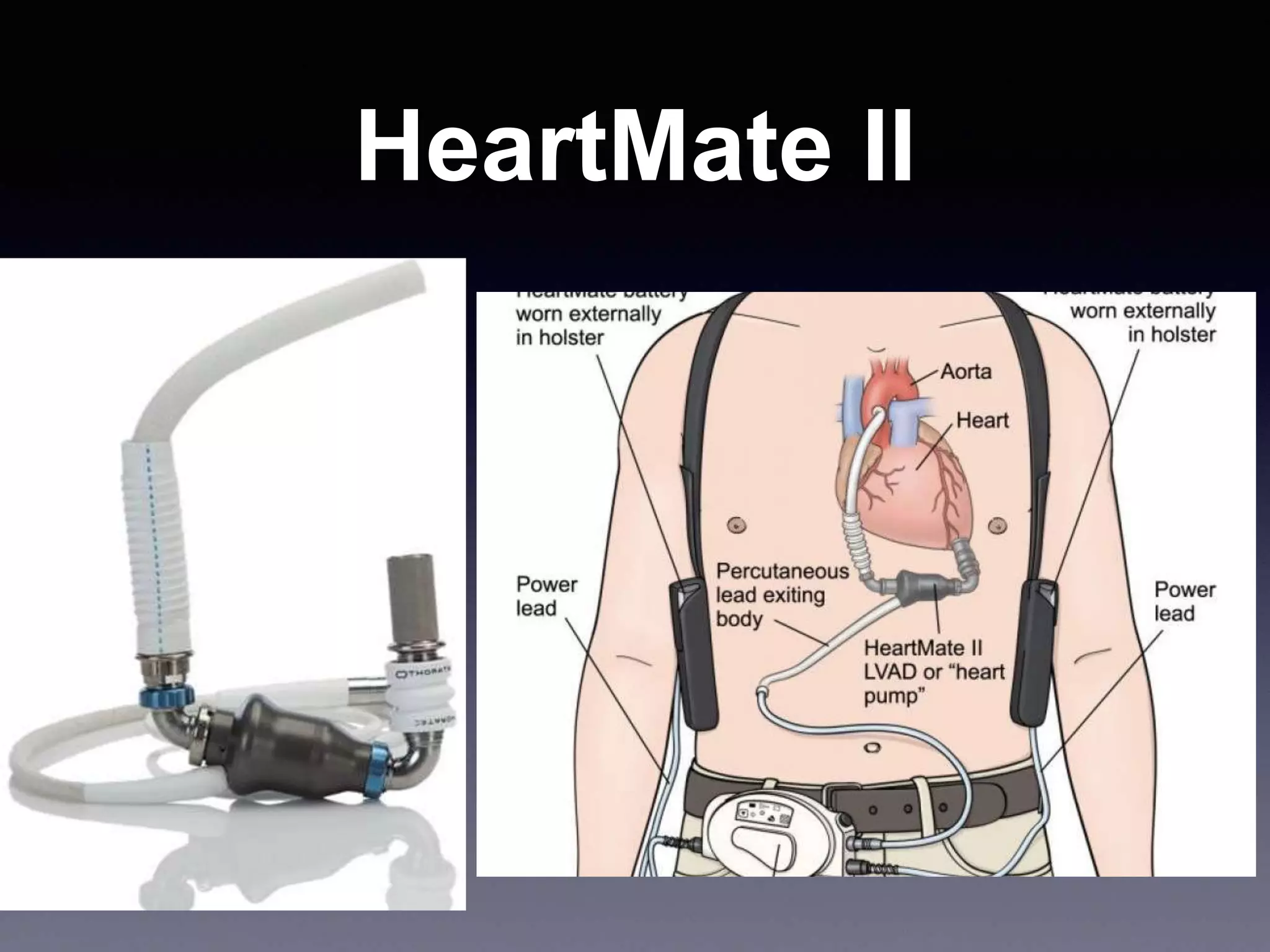
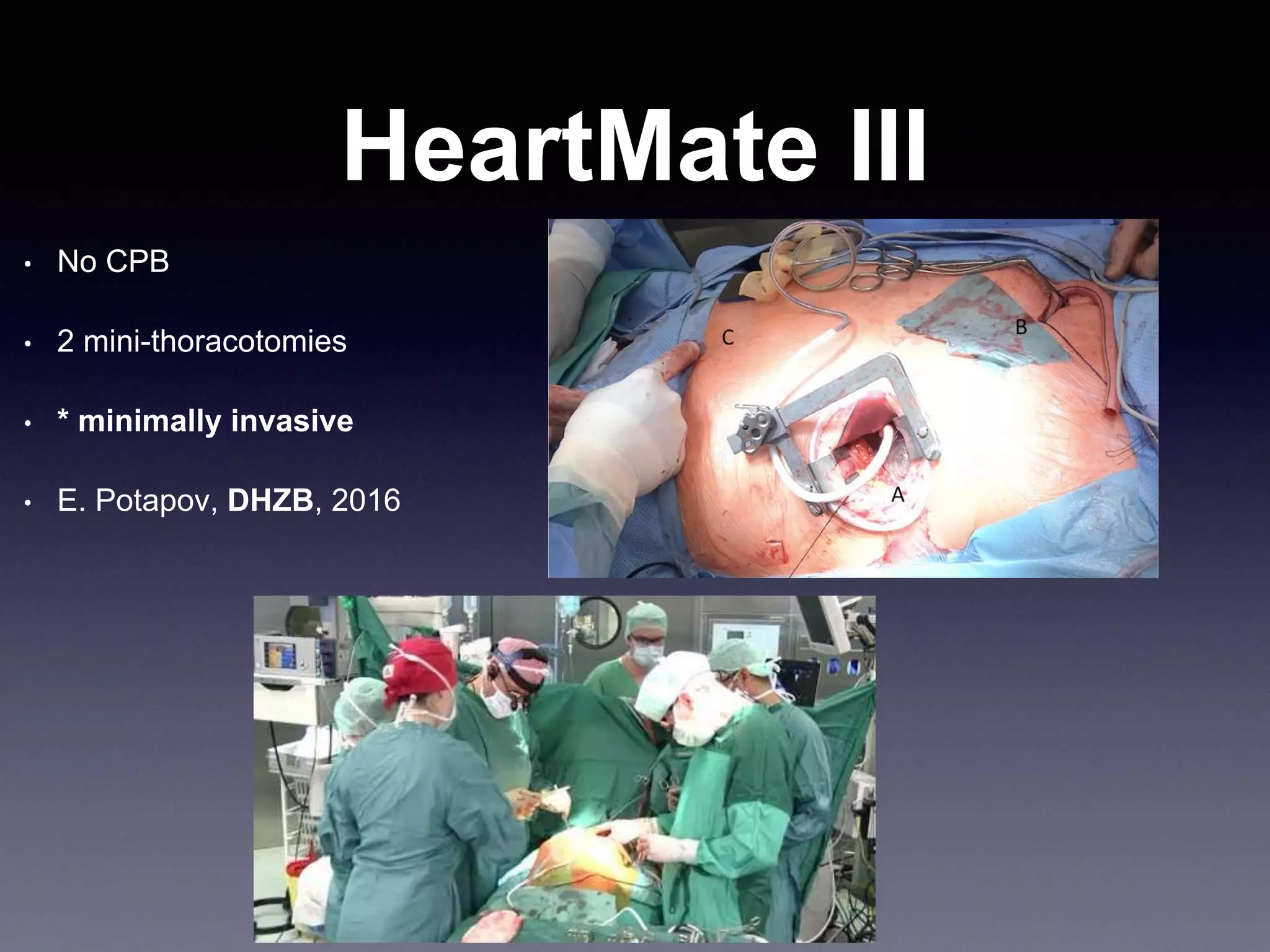
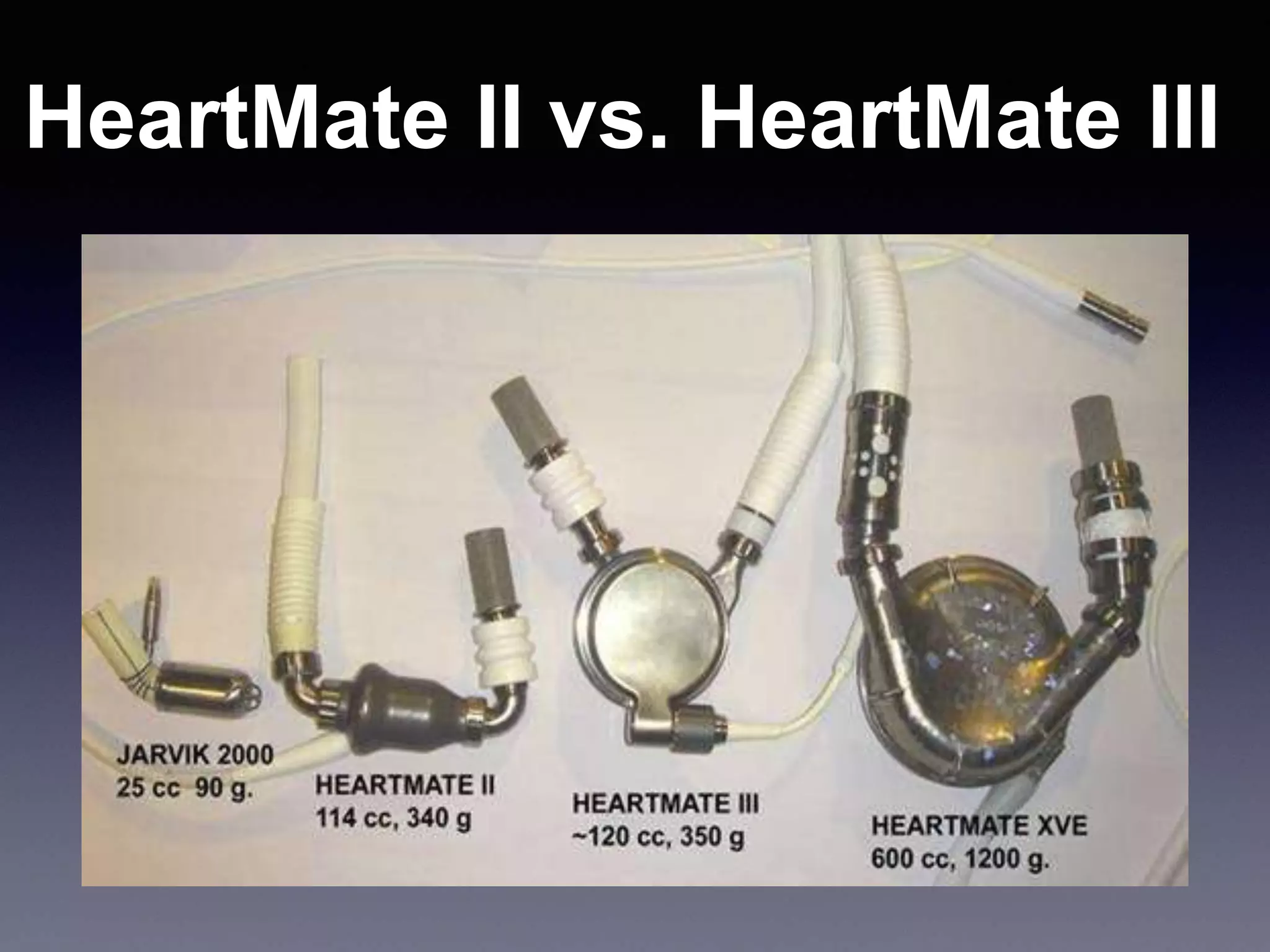
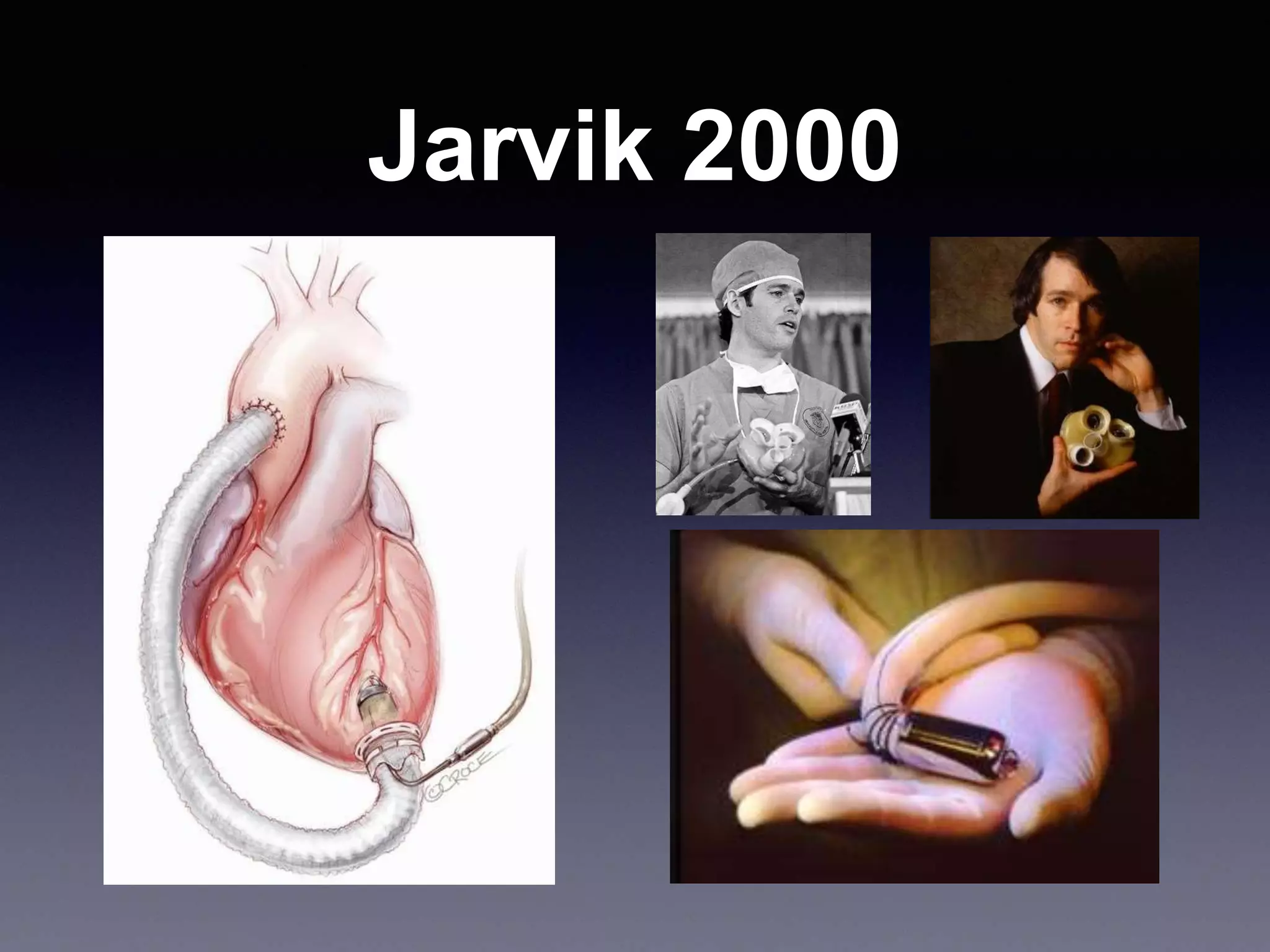
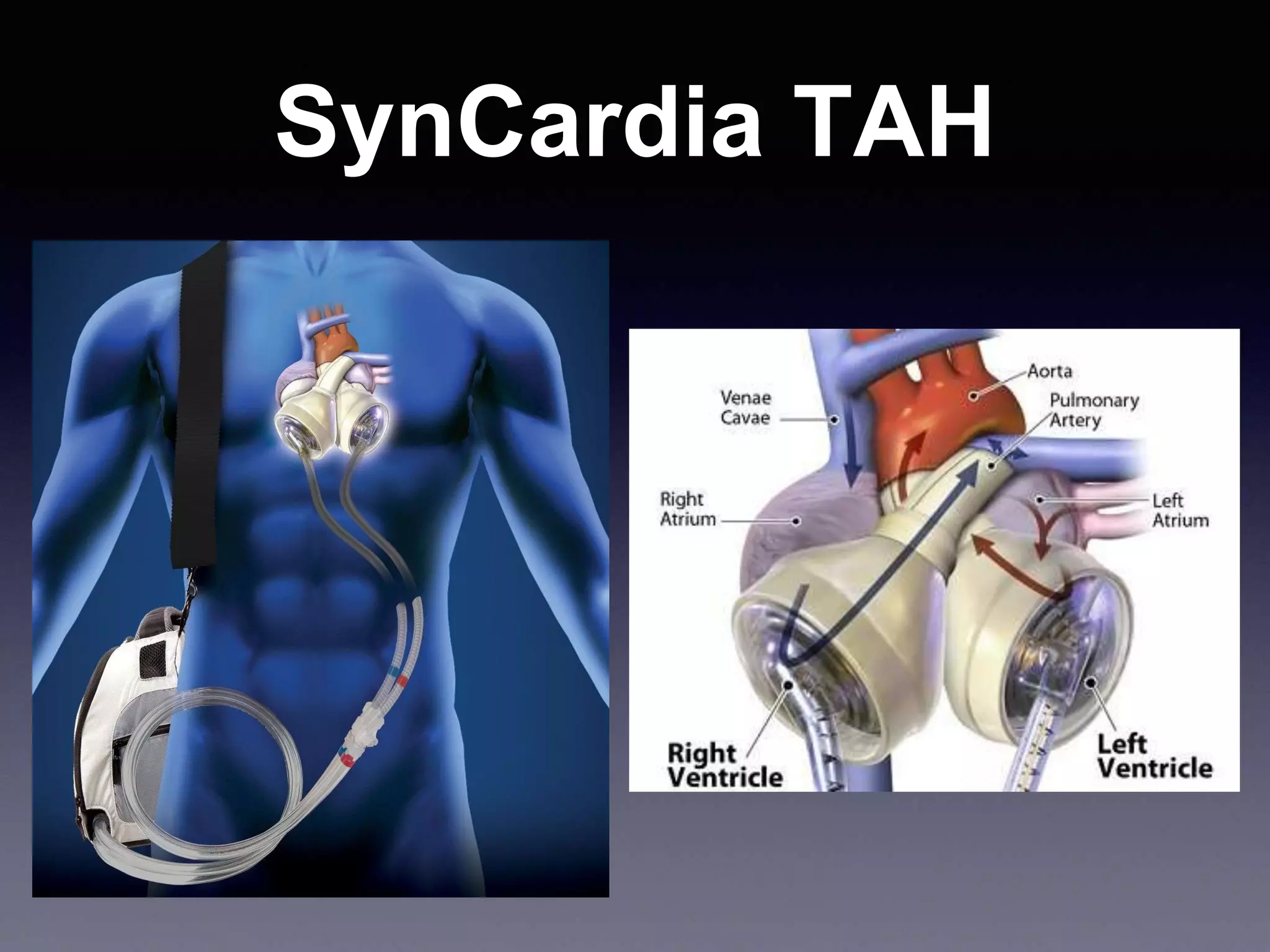
This document discusses mechanical circulatory support devices (MCSDs) and artificial hearts. It begins by explaining heart failure and its stages. It then describes various types of temporary and permanent MCSDs, including their goals, energy sources, blood flow characteristics, and implantation methods. Examples of specific MCSDs are provided like the IABP, ECMO, Impella, TandemHeart, HeartMate XVE, HeartMate II, HeartWare, Jarvik 2000, and total artificial hearts from SynCardia and Carmat. Major complications of MCSDs and artificial hearts discussed are bleeding, infection, and thrombosis.