Embed presentation
Download to read offline








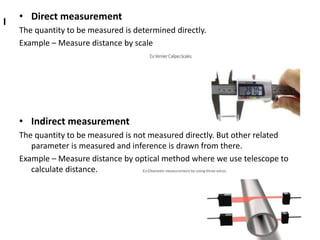
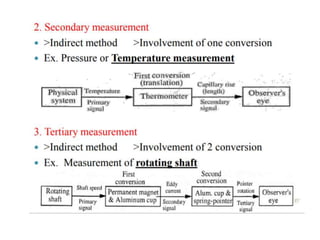


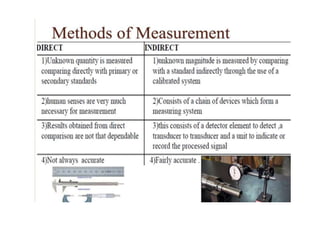
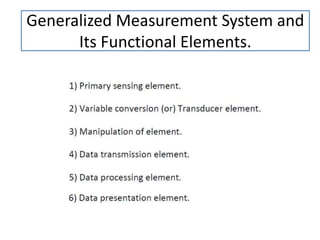
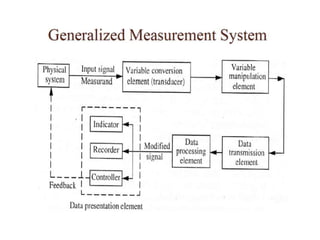
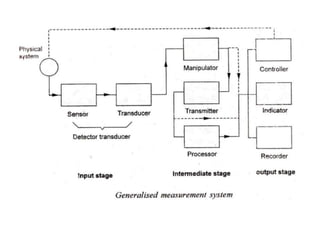
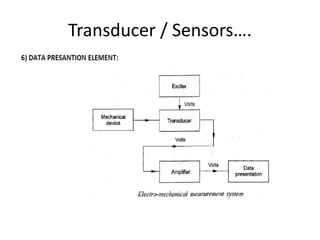

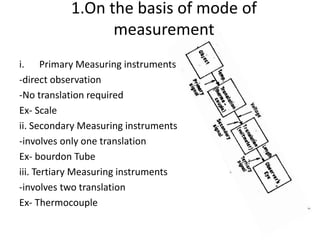

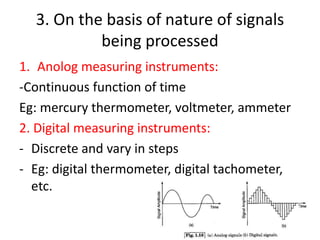
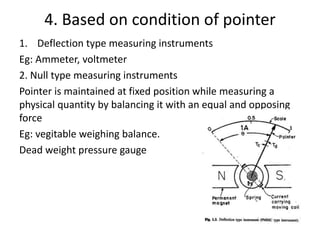



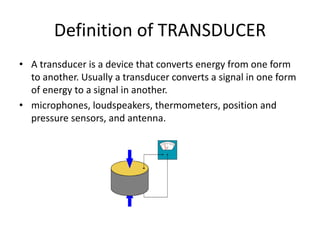
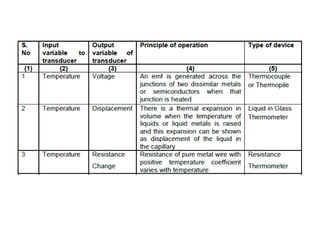


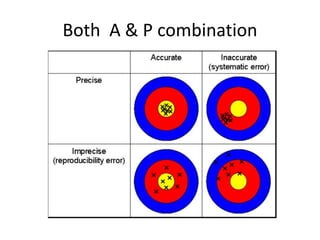
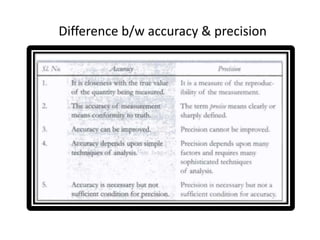
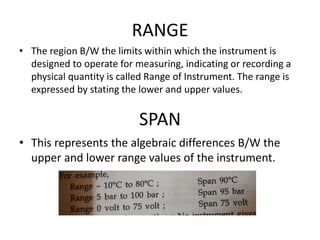

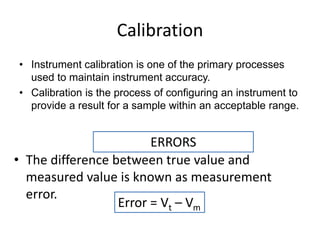



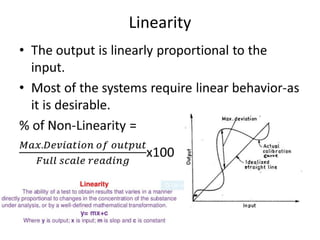
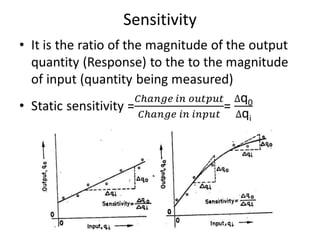














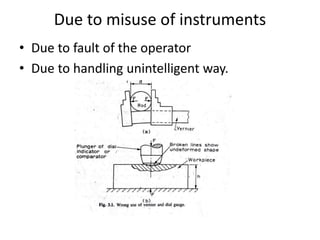


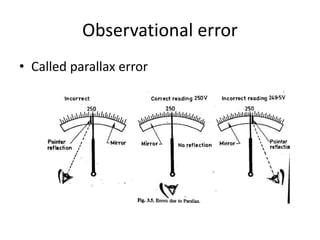







This document provides an introduction to instrumentation and measurement. It discusses key parameters that are continuously monitored in process plants like pressure, flow, temperature, and level. It defines instrumentation as the division of engineering that deals with measuring techniques, devices, and associated problems. The document outlines different types of instruments used to measure pressure, flow, temperature, and level. It also discusses concepts like transducers, calibration, accuracy, precision, range, and errors in instrumentation.













































































