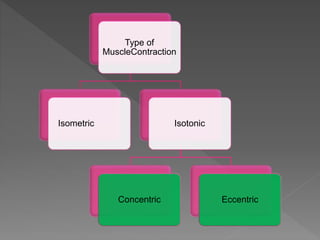
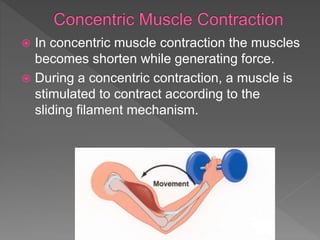
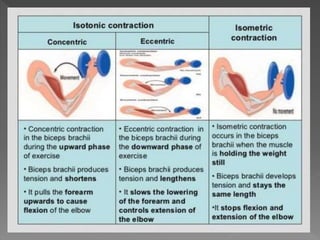
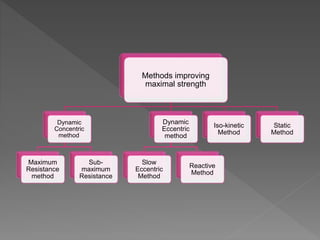
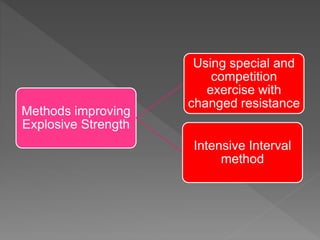
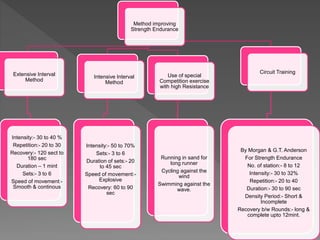
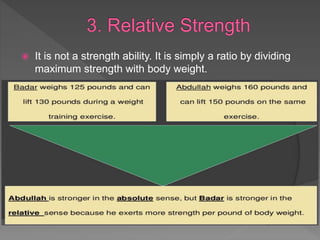
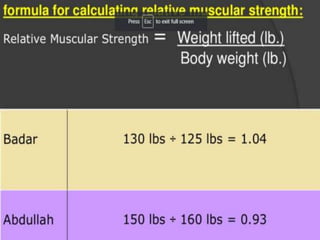
Strength is the ability to exert force or overcome resistance. It can be categorized as maximal strength, explosive strength, or strength endurance. Maximal strength refers to the highest force produced in a single effort, while explosive strength involves producing force as fast as possible. Strength endurance is the ability to exert force against resistance while fatigued. Various training methods like weightlifting, interval training, or circuit training can be used to improve different types of strength. Muscle contractions can be isometric, which does not involve joint movement; or isotonic, which involves movement and can be concentric or eccentric.