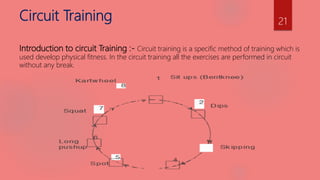
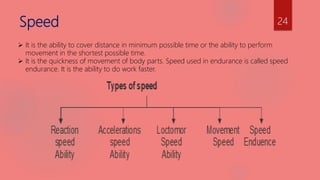
The document discusses various components of sports training including strength, endurance, speed, flexibility, and coordinative abilities. It defines each component and describes different types. For strength, it outlines isometric, isotonic, and isokinetic exercises and their advantages and disadvantages. For endurance, it discusses continuous training, interval training, fartlek training, and circuit training methods. For speed, it covers pace runs and acceleration runs. For flexibility, it explains active, passive, and static flexibility as well as stretching techniques. Finally, it lists types of coordinative abilities such as reaction, balance, and adaptation.