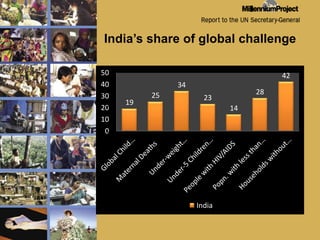
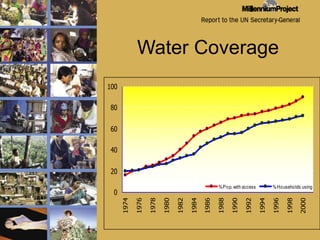
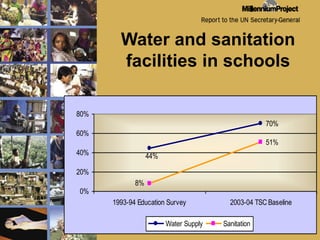
The document discusses MDG 7, which aims to ensure environmental sustainability. It focuses on India's progress and challenges in achieving the targets of MDG 7 related to access to safe drinking water, basic sanitation, and improving the lives of slum dwellers. While India has made progress in areas like water coverage in rural areas, it faces major challenges in sanitation access and quality. UNICEF supports the government's efforts in areas like hygiene education, school sanitation programs, and scaling up access to water and sanitation facilities.