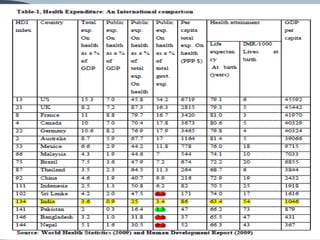
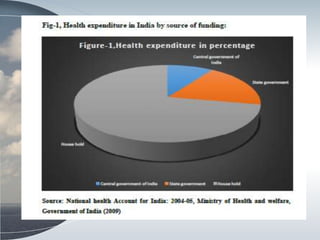
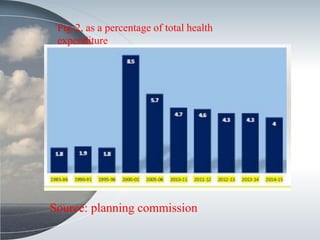
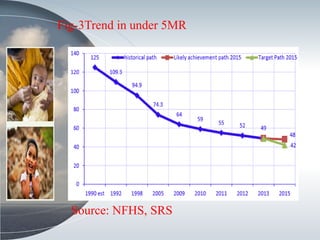
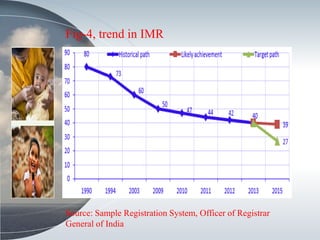
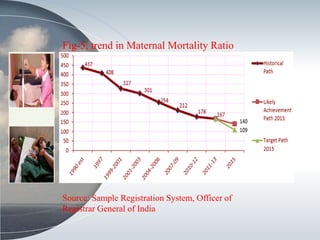
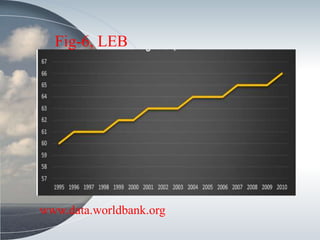
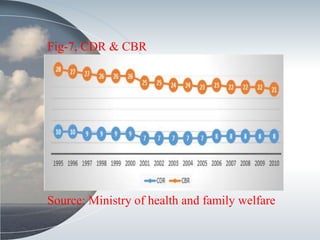
This document discusses the relationship between health expenditure and development. It notes that public health expenditure is important for both fighting diseases and promoting economic development. Health is considered a form of human capital. The document then examines several indicators of development in India, such as life expectancy, infant mortality rate, and maternal mortality rate, finding that they have generally improved but some targets have not yet been met. It analyzes trends in these health outcomes over time and relationships to factors like health expenditure. The conclusion is that greater investment in efficient, equitable health services can lead to better health status, human capital, reduced poverty, and improved economic development.