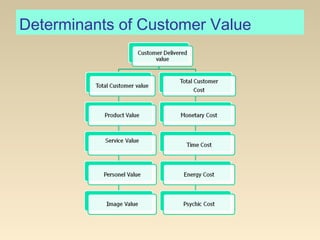
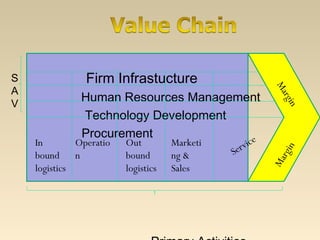
This document discusses customer value, satisfaction, and relationship management. It defines customer perceived value as the difference between total customer value and total customer cost. Total customer value is the benefits customers expect, while total customer cost is what they expect to pay. Customer satisfaction depends on performance meeting or exceeding expectations. Companies can increase value by improving benefits, lowering costs, and managing the customer relationship through collecting detailed customer data and ensuring positive touchpoints across departments. The goal is to maximize customer loyalty and equity.