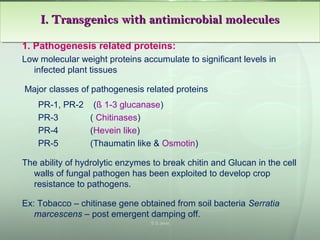
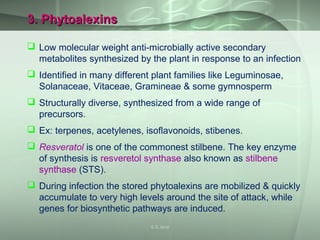
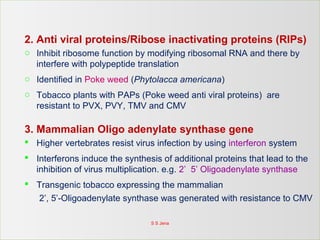
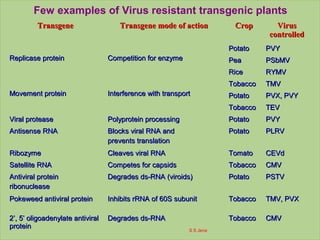
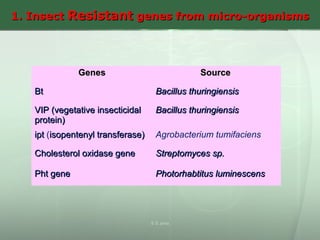
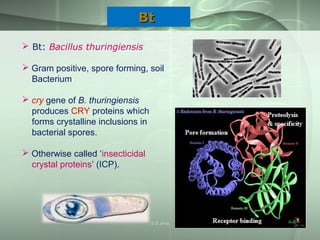
This document discusses molecular breeding methods for developing plant resistance. It outlines several approaches including using transgenics with antimicrobial molecules like pathogenesis related (PR) proteins from microbes, manipulating disease resistance genes, and using genes from Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) to develop insect resistance. The molecular approaches described include using coat protein-mediated resistance, movement protein-mediated resistance, and ribozymes to develop virus resistance in transgenic plants. Examples are provided of transgenic crops developed with resistance to various fungal, bacterial, viral, and insect pests.