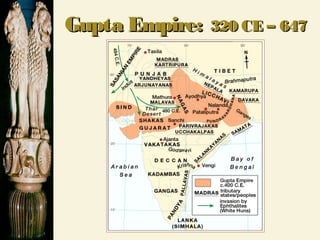
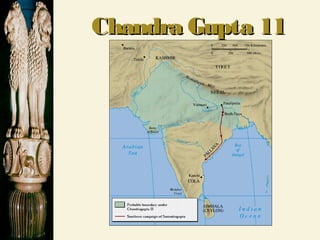
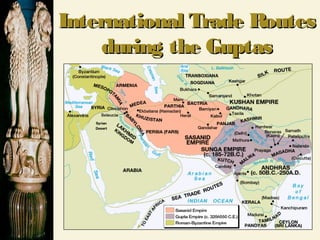
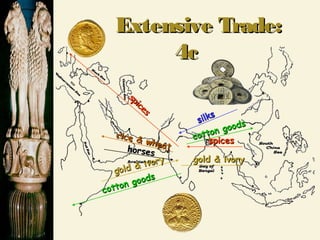
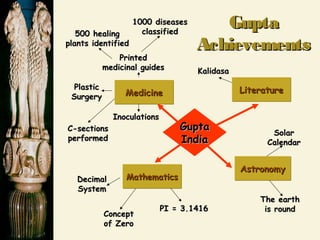
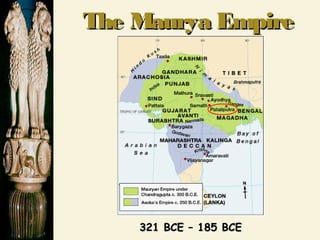
Chandragupta unified northern India in the 4th century BCE and defeated the Persian general Seleucus. He divided his empire into provinces and districts for administration and law enforcement. Chandragupta's advisor Kautilya wrote the Arthashastra, a guide for kings that supported strong central authority. In the 3rd century BCE, Emperor Asoka converted to Buddhism after a bloody battle and promoted Buddhist principles through edicts scattered across South Asia. The powerful Gupta Empire arose in the 4th century CE and saw economic prosperity through trade, as well as cultural and scientific achievements, but declined due to invasions starting in the 5th century CE, leaving India politically fragmented.

![ChandraguptaChandragupta:: 321 BCE-298321 BCE-298
BCEBCE
Unified northern India.Unified northern India.
Defeated the PersianDefeated the Persian
generalgeneral SeleucusSeleucus..
Divided his empire intoDivided his empire into
provinces, then districtsprovinces, then districts
for tax assessments and lawfor tax assessments and law
enforcement.enforcement.
He feared assassination [like SaddamHe feared assassination [like Saddam
Hussein]Hussein] food tasters, slept in differentfood tasters, slept in different
rooms, etc.rooms, etc.
301 BCE301 BCE gave up his throne & becamegave up his throne & became
a Jain.a Jain.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maurya-guptaempires-150518081530-lva1-app6892/85/Maurya-gupta-empires-2-320.jpg)



![Asoka’s law codeAsoka’s law code
Edicts scattered inEdicts scattered in
more than 30 placesmore than 30 places
in India, Nepal,in India, Nepal,
Pakistan, & Afghanistan.Pakistan, & Afghanistan.
Written mostly inWritten mostly in
Sanskrit, but one was inSanskrit, but one was in
Greek and Aramaic.Greek and Aramaic.
10 rock edicts.10 rock edicts.
Each pillar [Each pillar [stupastupa] is 40’-50’ high.] is 40’-50’ high.
Buddhist principles dominate his laws.Buddhist principles dominate his laws.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maurya-guptaempires-150518081530-lva1-app6892/85/Maurya-gupta-empires-7-320.jpg)