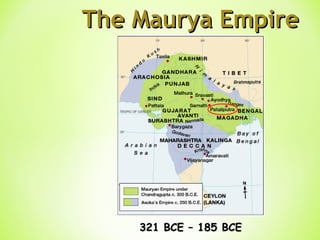
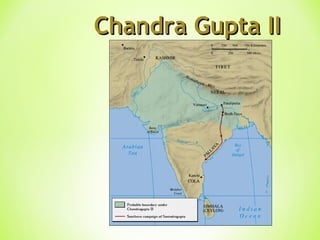
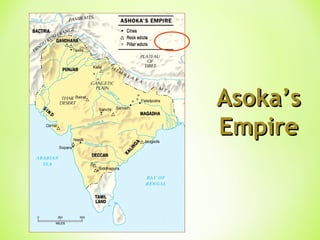
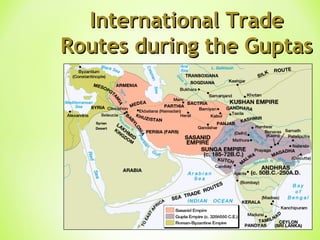
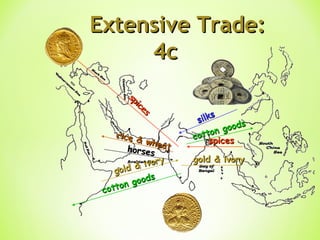
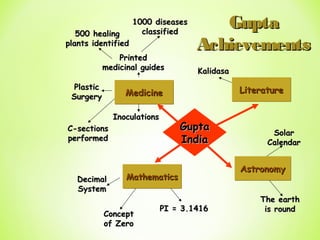
The Golden Age in India from 320-550 CE saw the rise of the powerful Gupta Empire. Key events included Chandragupta unifying northern India in the 4th century BCE and the conversion of Emperor Ashoka to Buddhism in the 3rd century BCE after a bloody battle, leading him to dedicate his life to nonviolence and spreading Buddhist teachings. The Gupta Empire reached its peak under Emperor Chandragupta II in the 4th-5th centuries CE, when it saw advances in areas like mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and literature alongside extensive trade networks and beautiful art flourishing under the religious tolerance of the Guptas.