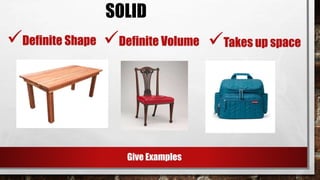
The document discusses the nature of matter, defining it as anything that occupies space and has mass, and categorizes it into solids, liquids, gases, and plasma. It describes the properties and states of matter, including characteristics such as mass, volume, weight, and density. Additionally, it highlights various changes materials undergo due to temperature, including melting, freezing, evaporation, condensation, and sublimation.