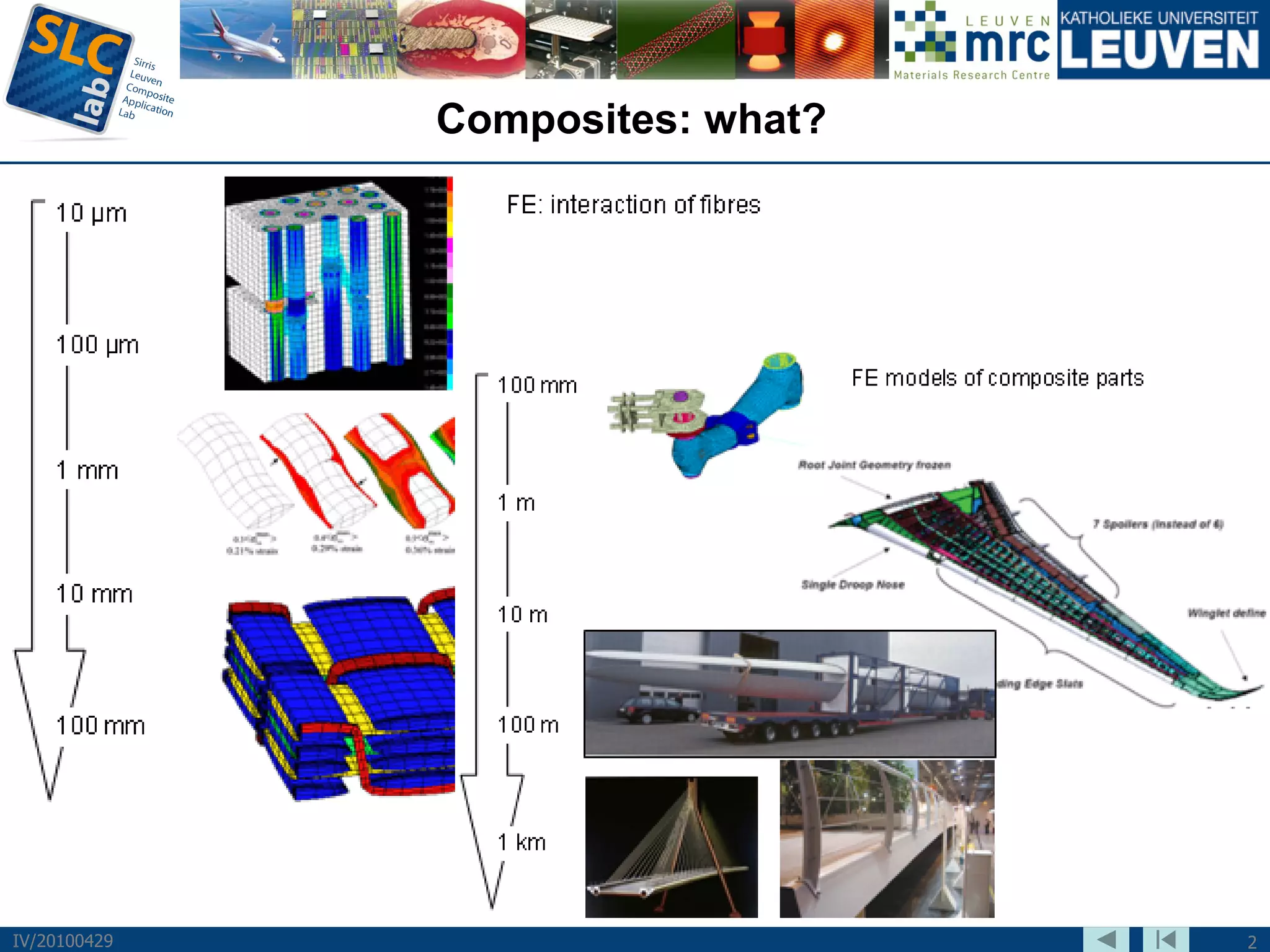
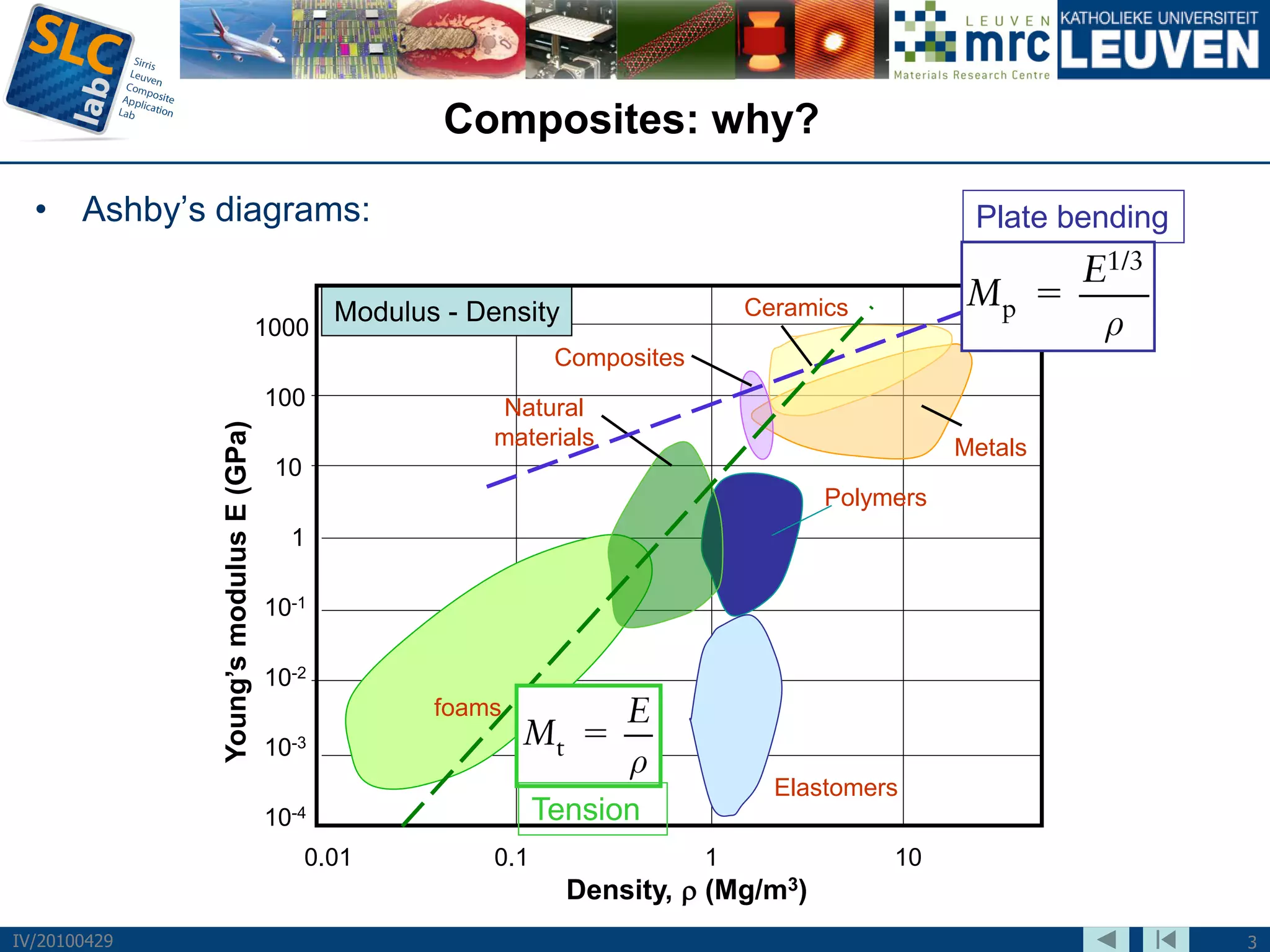
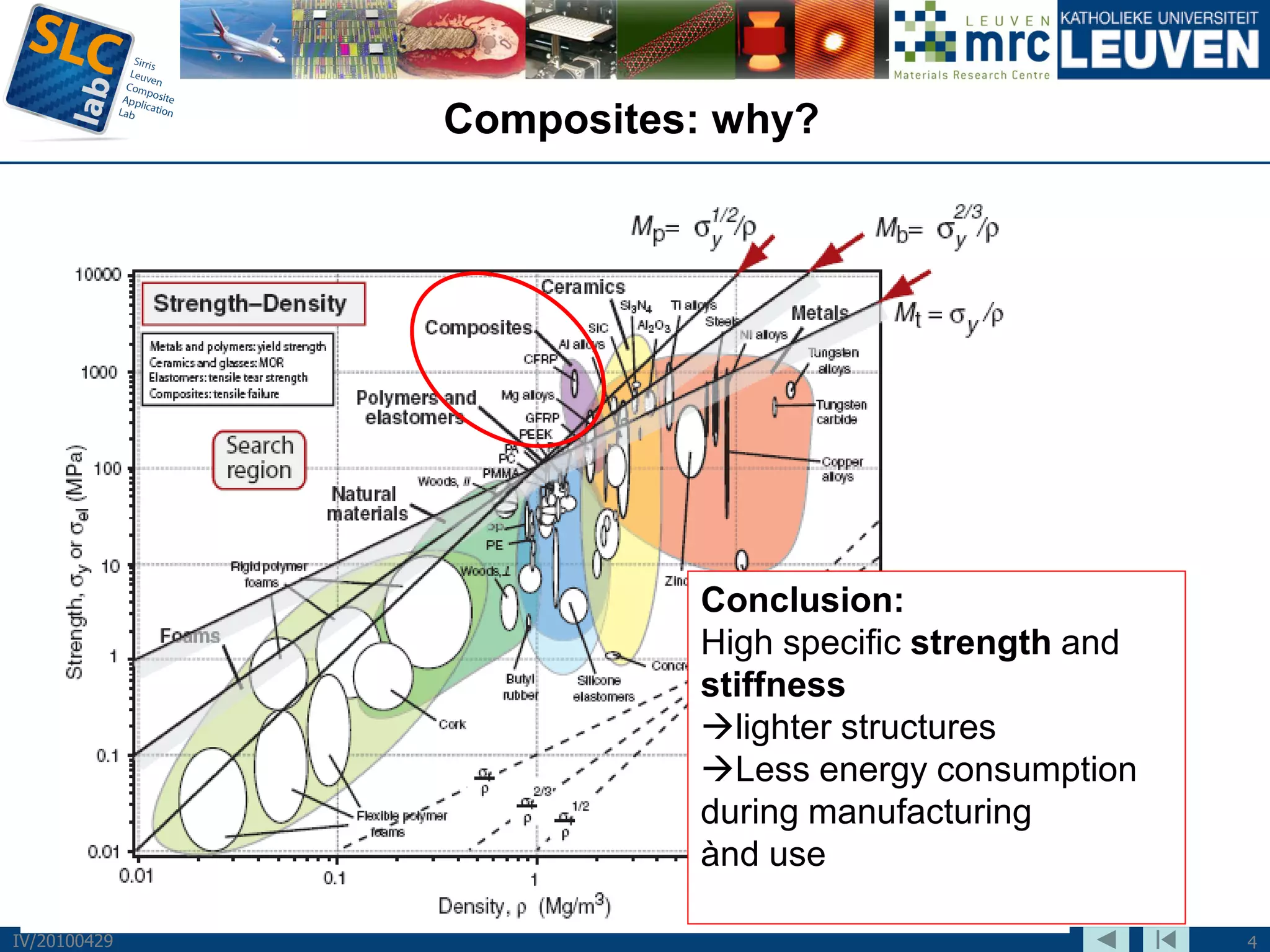
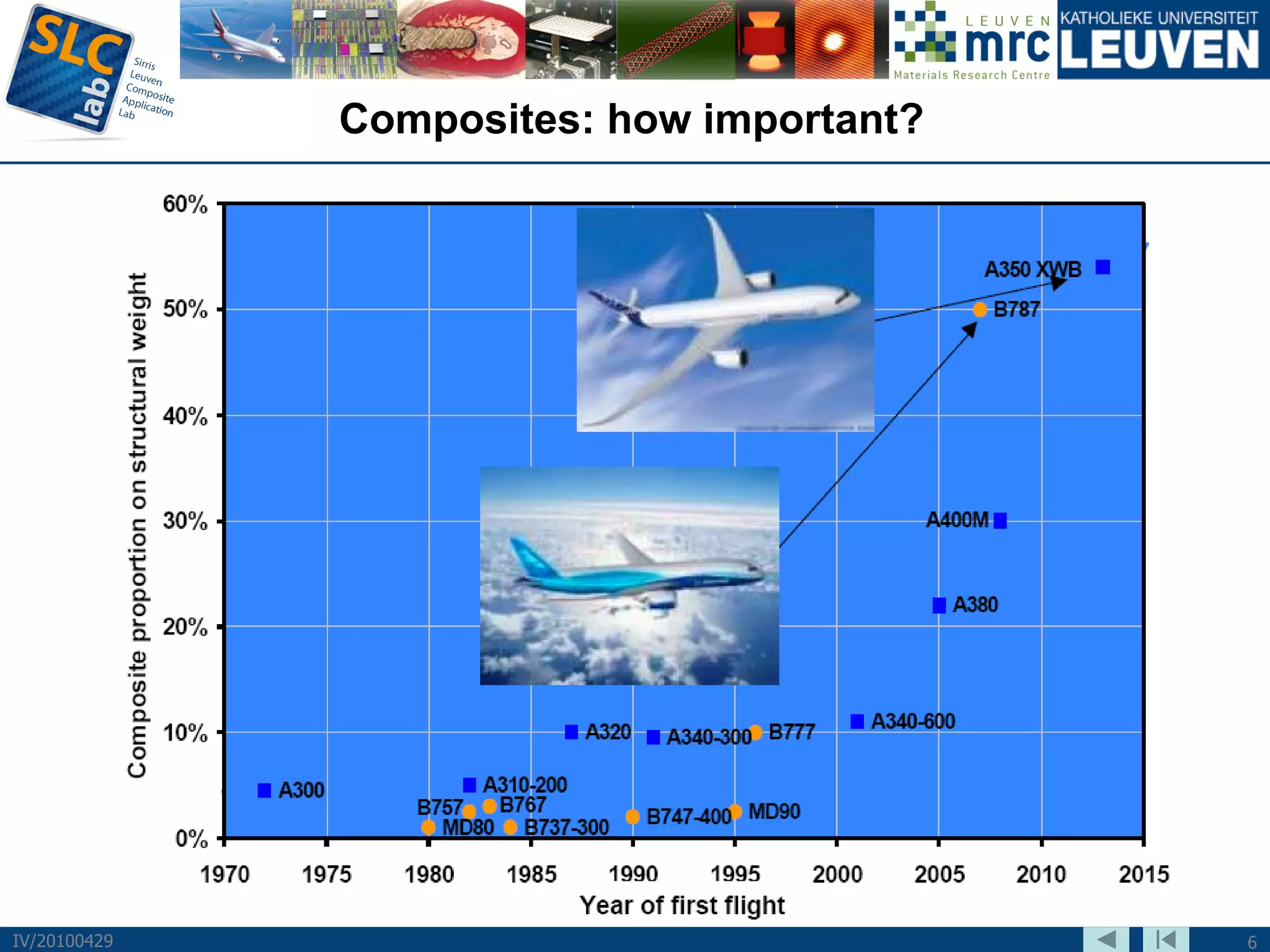
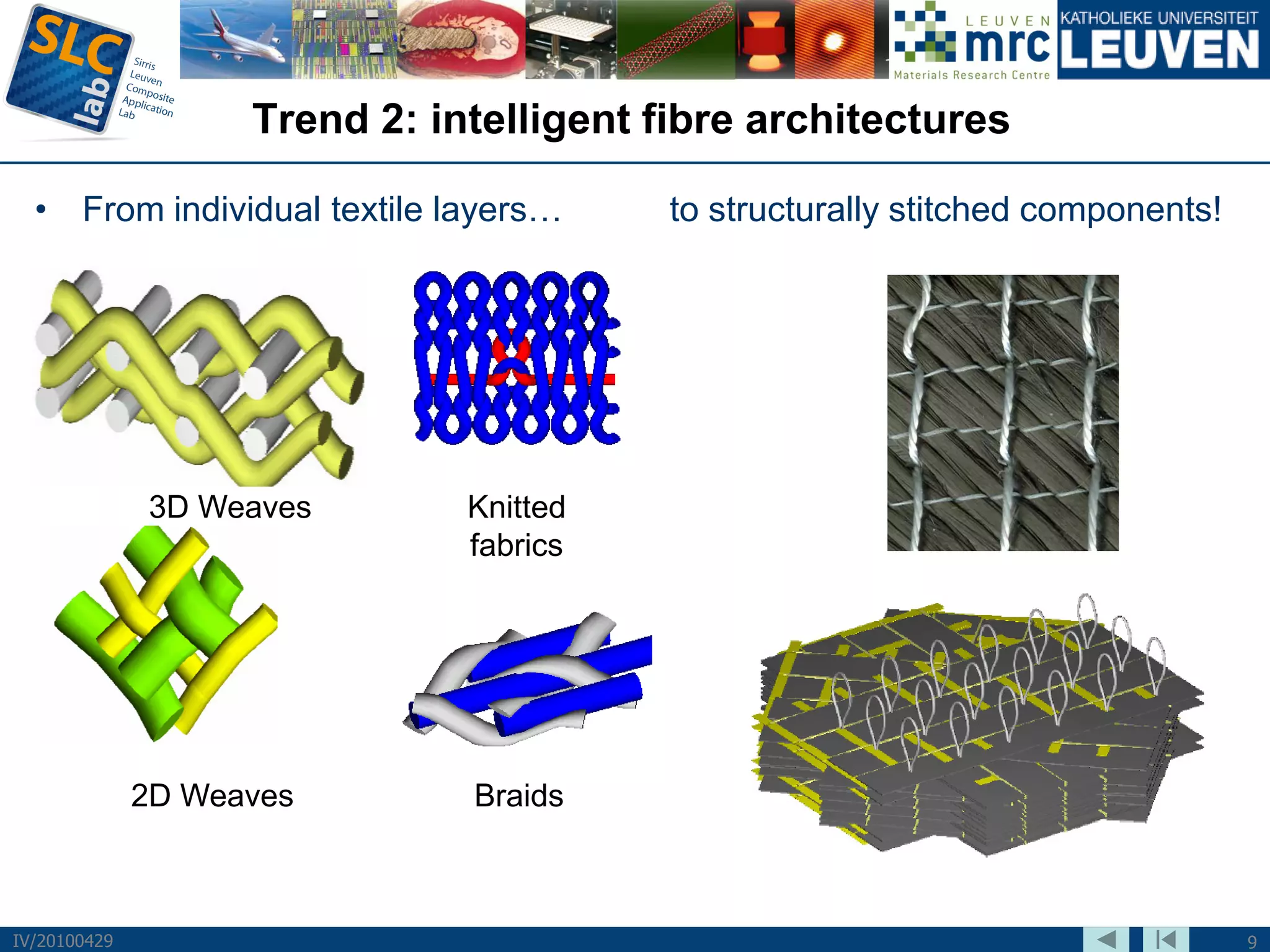
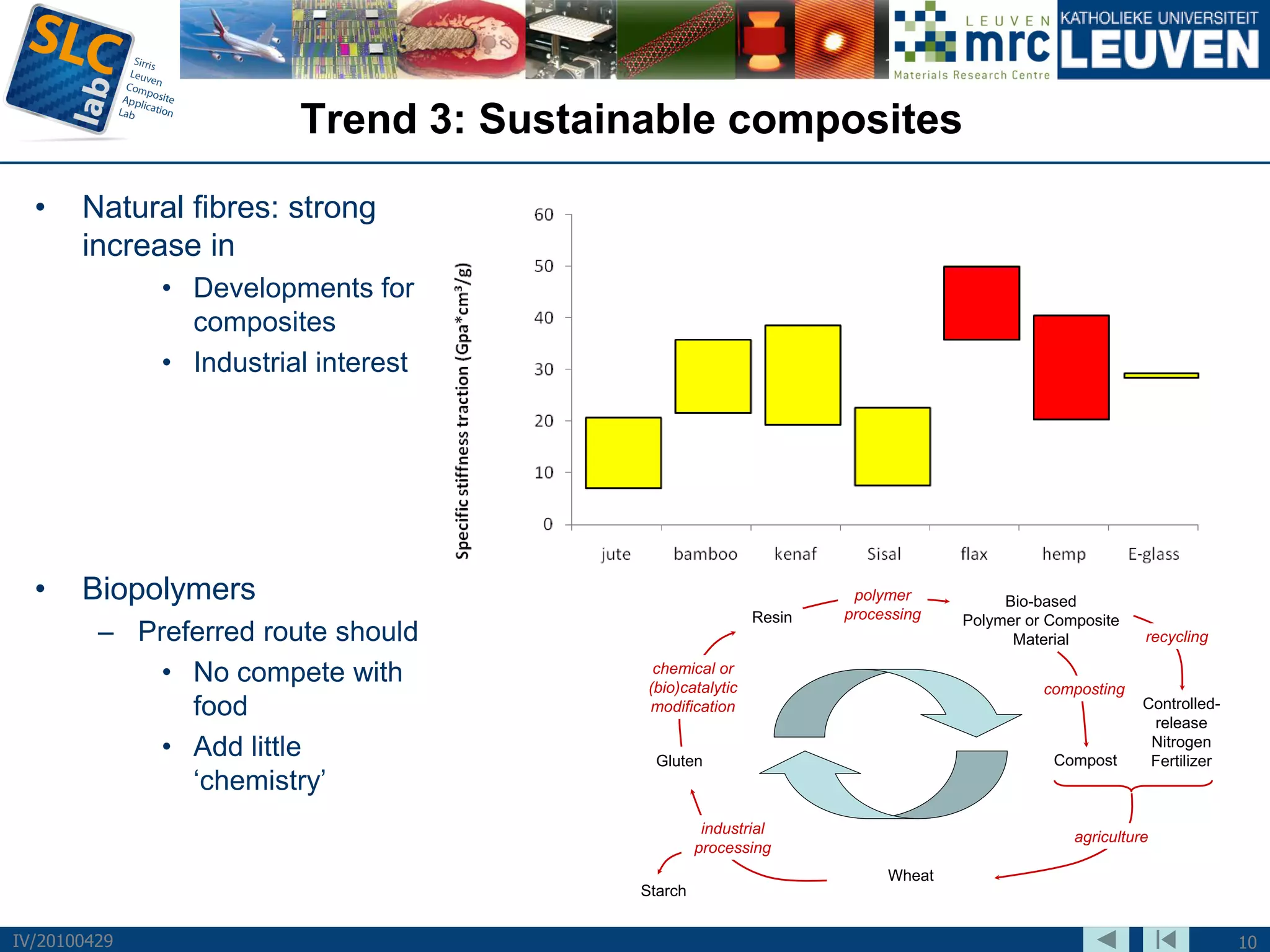
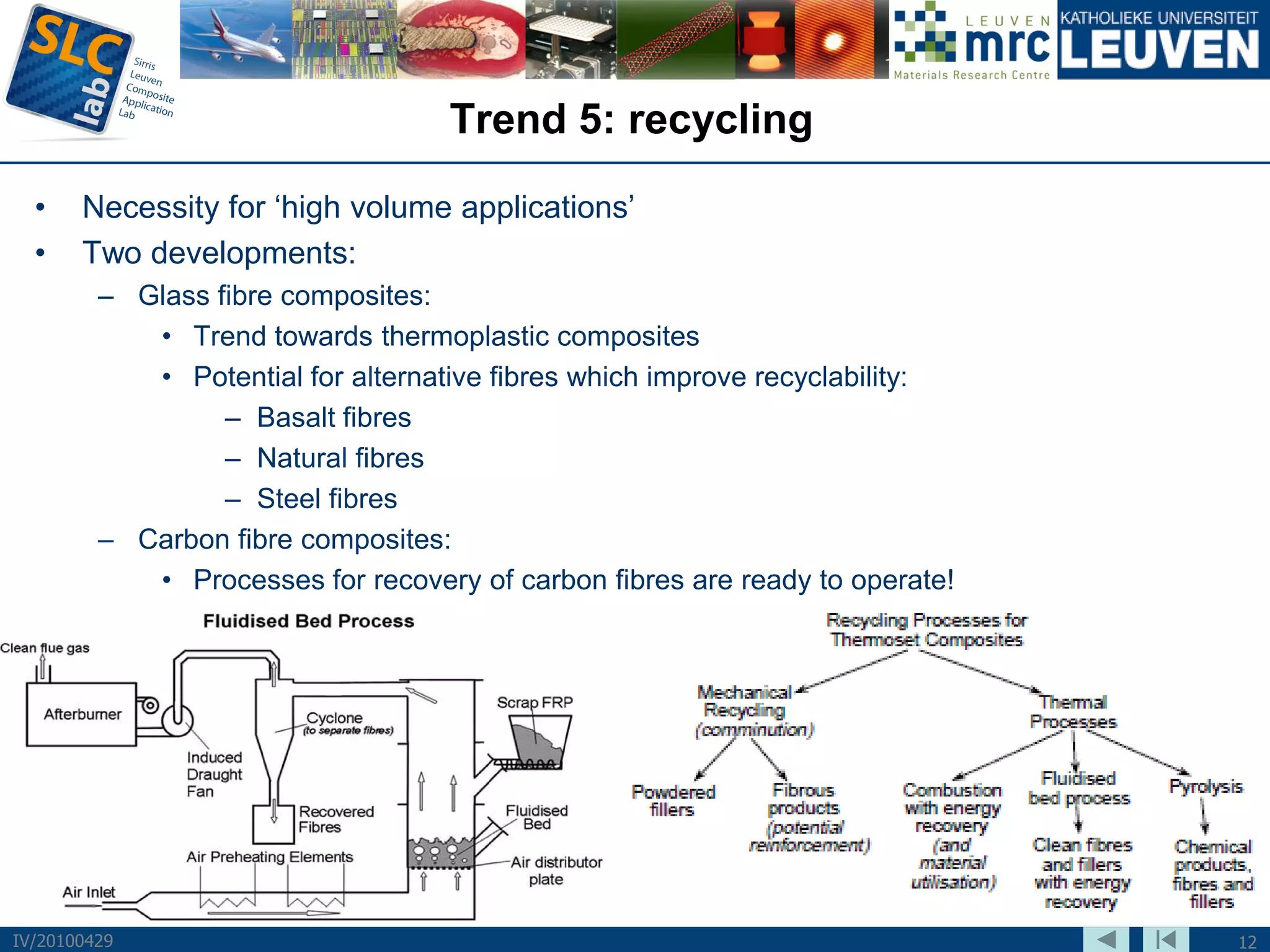
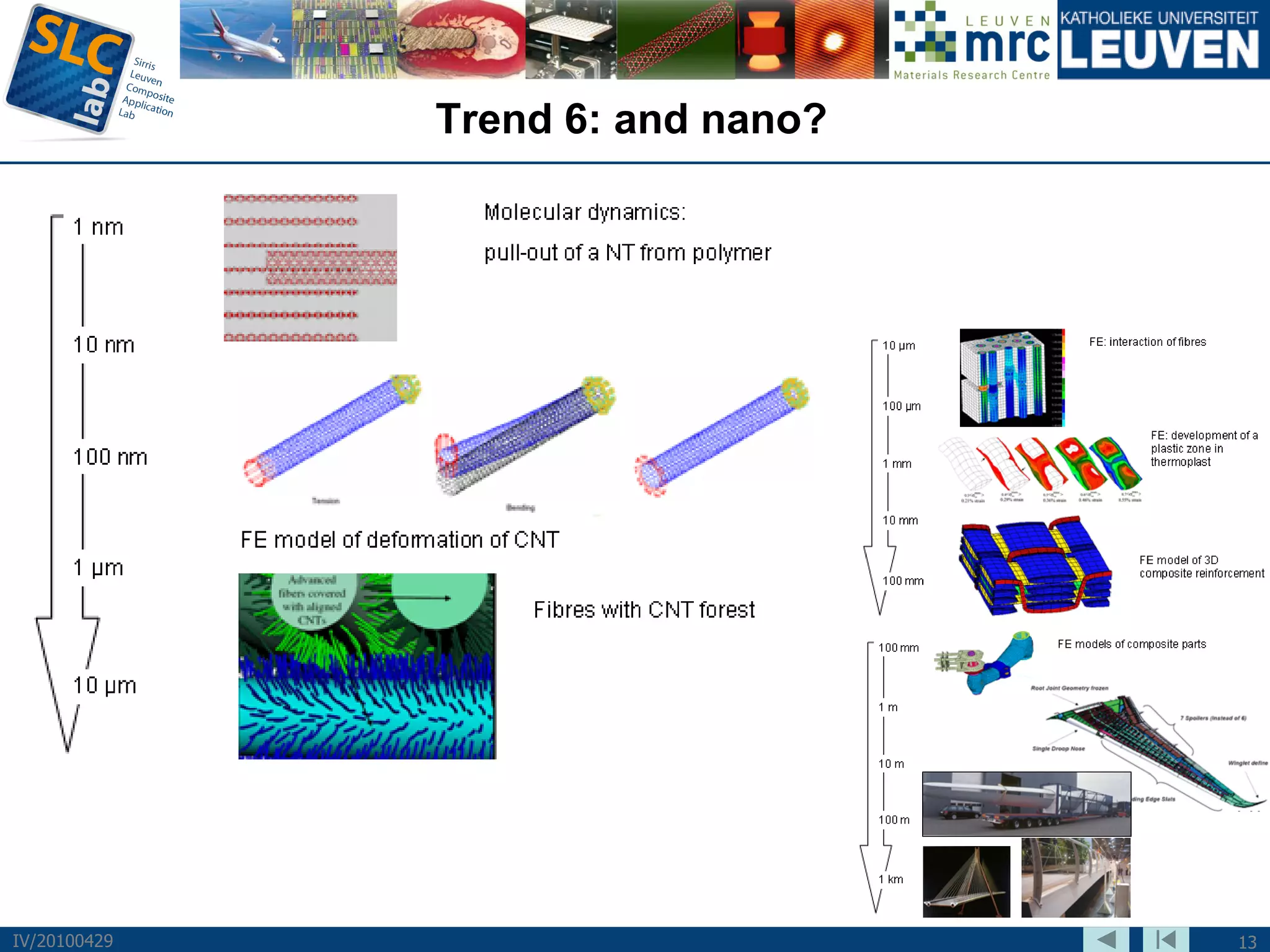
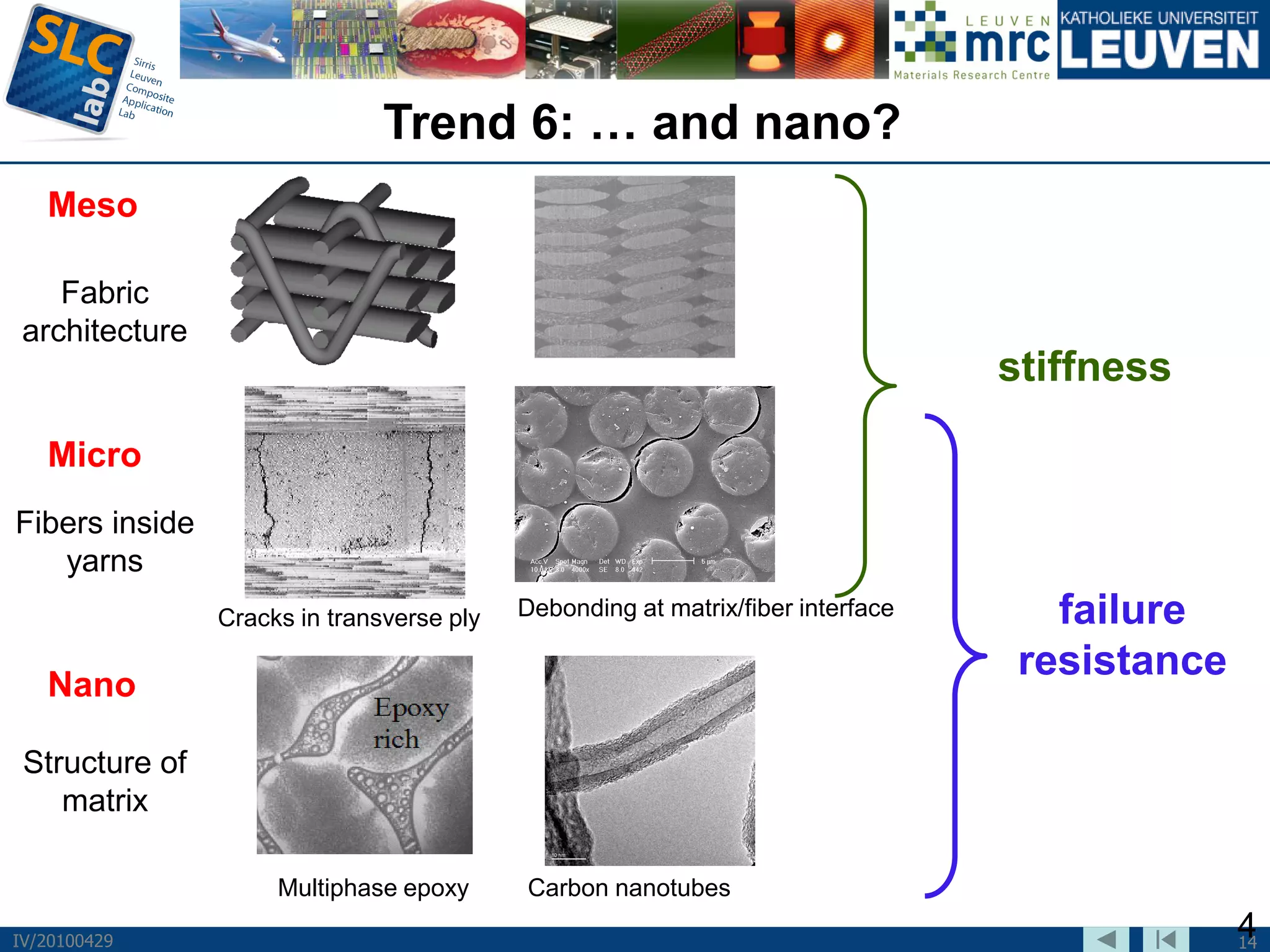
The document discusses trends and challenges in composite materials. It outlines 6 major trends: 1) Proliferation of carbon fibers for high-volume applications. 2) Intelligent fiber architectures like 3D weaves. 3) Development of sustainable composites using natural fibers and biopolymers. 4) Automation driven by demand for high-volume production. 5) Recycling of glass and carbon fiber composites. 6) Use of nano-scale materials and structures to improve properties. The trends are driving wider composite usage but new recycling and sustainable approaches are needed to meet challenges of high-volume applications.