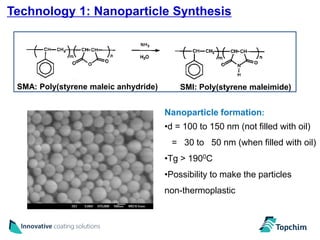
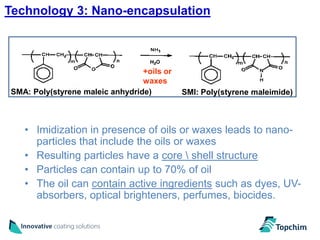
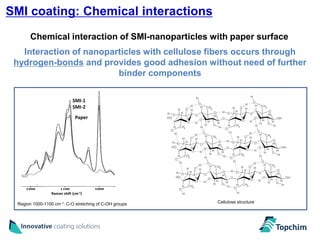
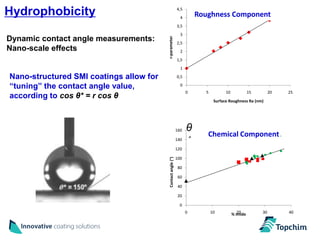
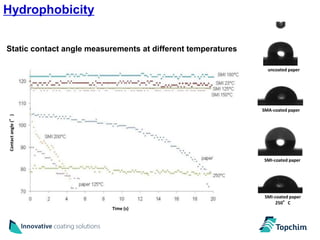
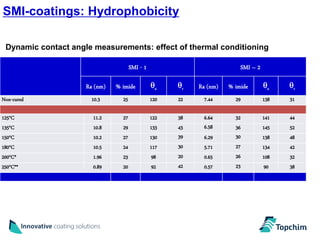
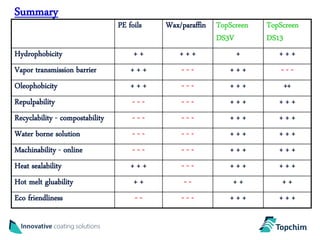
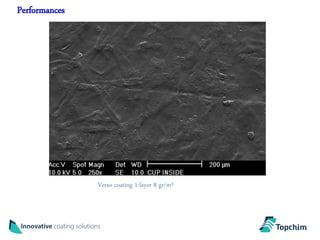
Topchim produces organic nanoparticles from poly(styrene-maleic anhydride) (SMA) using various techniques, including imidization of SMA in the presence of oils or waxes to create core-shell nanoparticles, and applies these nanoparticles in coatings for applications like paper, packaging, textiles, and inks to provide properties such as hydrophobicity, barrier properties, and encapsulation of active ingredients. The nanoparticles can be tuned based on the raw materials and processing used to suit different market needs.