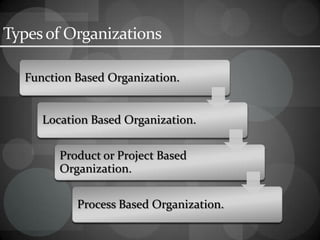
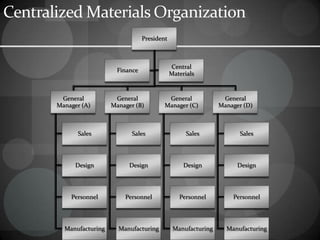
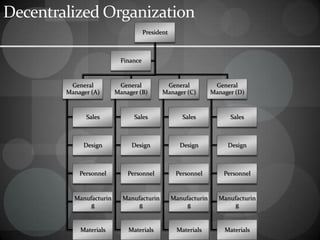
The document discusses materials management in organizations. It provides definitions of key terms like "material" and describes the various subsections that make up materials departments, like purchasing, receiving, stores, and dispatching. The objectives of materials management are outlined as well as the relationships between the materials department and other departments. Different types of organizational structures for materials management are described, including function-based, location-based, and process-based models. The roles and functions of materials managers are also summarized.