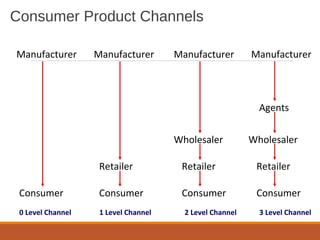
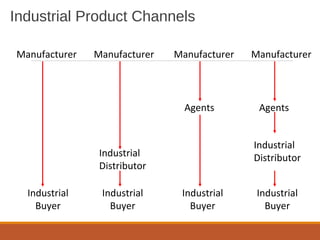
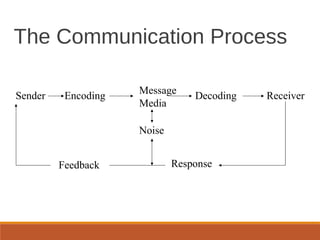
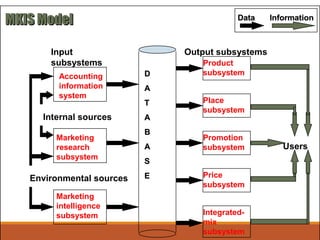
The document outlines the key concepts of marketing channels, including their nature, roles, and communication processes. It discusses various promotional tools such as advertising, sales promotions, personal selling, and public relations, along with factors that impact the selection of distribution channels. It also emphasizes the importance of marketing communication, research, and the marketing information system in making informed marketing decisions.