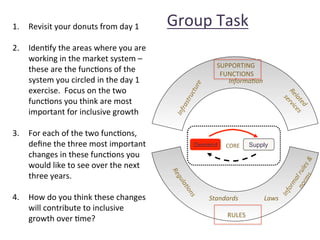
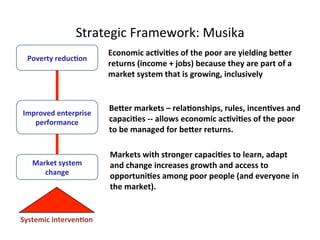
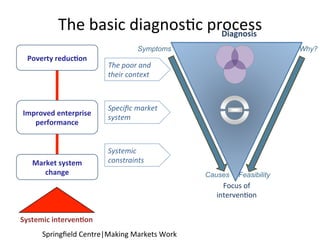
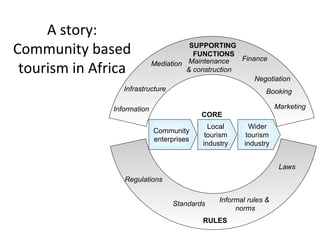
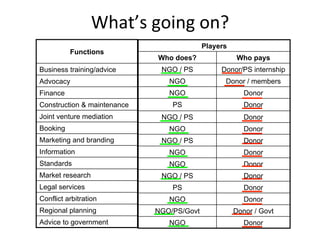
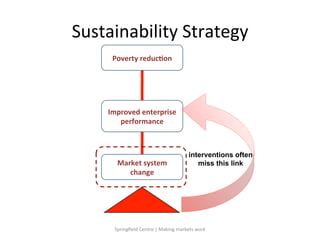
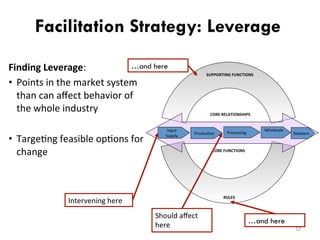
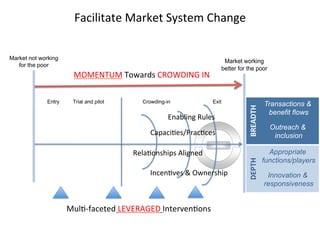
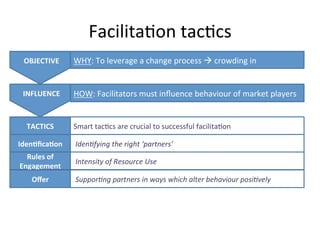
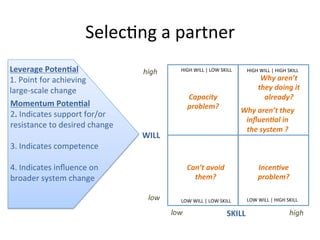
This document details a session focused on utilizing a market systems approach to foster inclusive growth through strategic interventions in market functions. Participants are encouraged to identify key areas for improvement within the market system, define desired changes over three years, and discuss leveraging partnerships to facilitate behavior changes among market players. The session emphasizes the importance of understanding systemic constraints, partner selection, and implementing effective market relationships to achieve better economic outcomes for the poor.