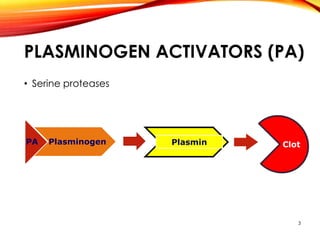
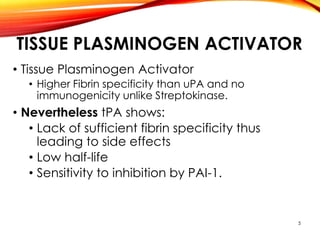
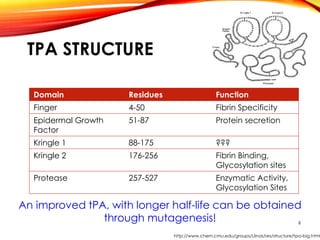
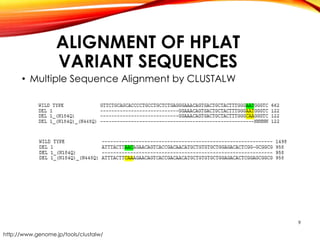
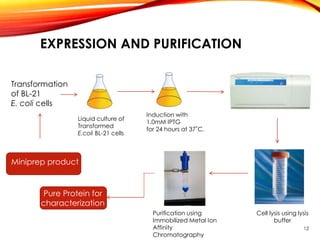
This document outlines a research project to clone and express variants of human plasminogen activator (HPLAT) in E. coli in order to develop an improved tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) with a longer half-life. The researchers designed mutations to the glycosylation sites of tPA and will clone the mutant HPLAT genes into E. coli, induce expression, purify the proteins, and analyze their fibrin specificity, half-life, and inhibition by PAI-1 compared to wild type tPA. The goal is to develop an improved tPA through mutagenesis for treatments of cardiovascular diseases.