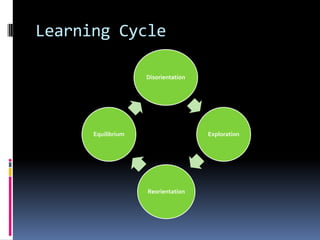
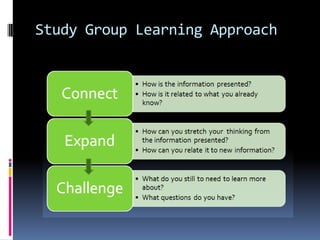
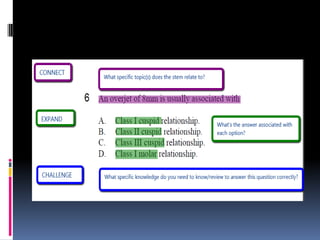
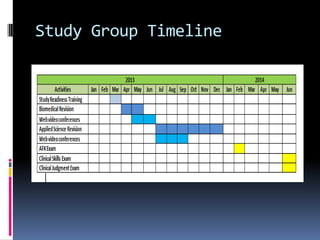
This document discusses different approaches to learning and effective study skills. It describes high and low context communication styles and explains that learning is an active process where individuals construct knowledge based on their experiences. The document then provides examples of how International English-Taught Dentists (IETDs) can apply their clinical experience to new learning. Some key active learning strategies discussed include linking prior knowledge to new concepts, evaluating important information, and explaining topics that are not fully understood. The document concludes by outlining various study skills and systems like managing time, setting goals, developing a study plan, and self-evaluating progress.