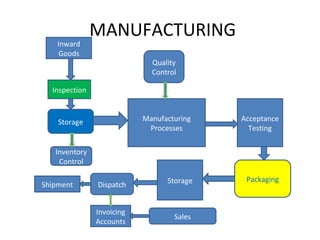
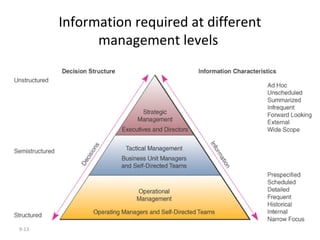
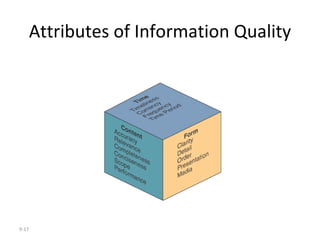
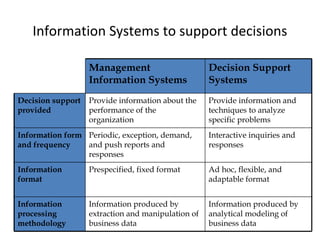
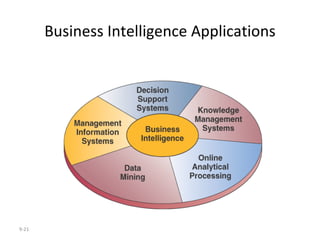
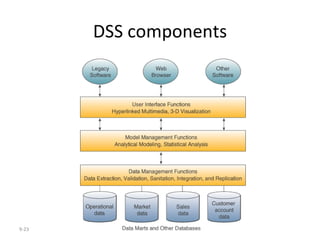
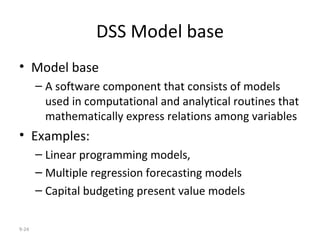
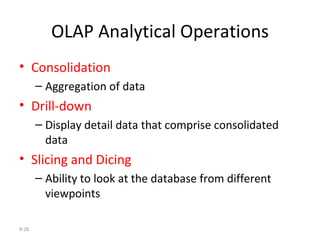
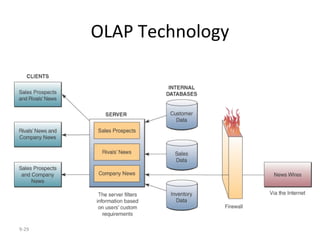
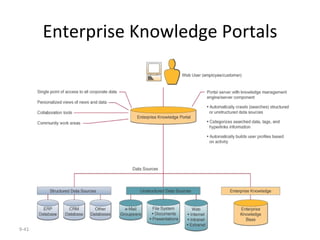
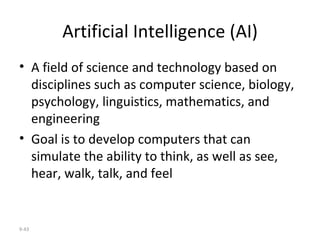
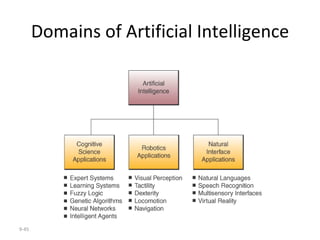
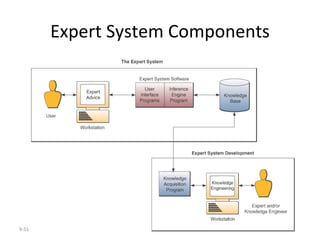
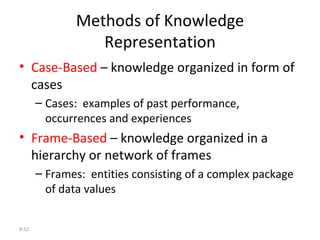
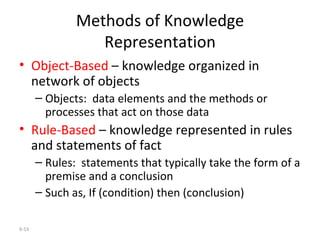
The document outlines extensive processes and systems involved in manufacturing, including goods inspection, inventory control, quality assurance, and data management. It also discusses various levels of management decision-making, information quality attributes, and different types of information systems such as Management Information Systems (MIS), Decision Support Systems (DSS), and Business Intelligence applications. Additionally, it covers artificial intelligence concepts, expert systems, neural networks, and intelligent agents that enhance decision-making and operational efficiency within organizations.