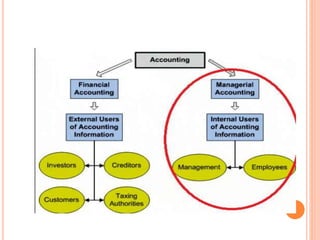
Managerial accounting involves identifying, measuring, analyzing, interpreting, and communicating financial and non-financial information to help an organization achieve its goals. It provides information to managers within an organization to help with planning, operating, and controlling decisions. Managerial accounting focuses on providing internal reporting, cost allocation, planning and control, and performance measurement to assist management decision making. It differs from financial accounting in that it provides internal reporting, focuses on specific areas and future planning rather than external reporting of past financial performance. Managerial accounting uses both monetary and non-monetary information to aid decisions, while financial accounting focuses on monetary reporting and the organization as a whole.