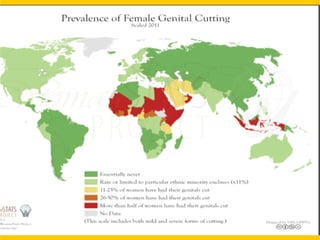
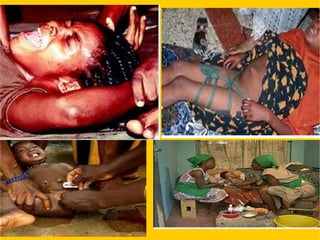
The document discusses female genital mutilation (FGM), defining it as the partial or complete removal of external female genitalia for non-medical reasons, primarily rooted in cultural and religious traditions. In Nigeria, approximately 20 million women have undergone FGM, making it a prevalent practice; despite being illegal, it persists due to various societal factors and beliefs. The document outlines the health complications associated with FGM, the psychological impact on women, and the importance of education and legal measures in its prevention.