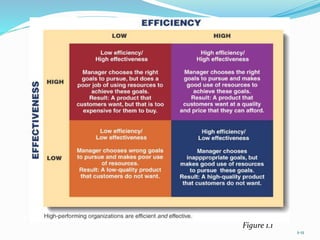
This document discusses managers and management. It defines management as coordinating the actions of people in an organization to achieve goals. Managers are responsible for supervising the use of resources, including people, equipment, and finances. The main functions of management are planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. Managers spend differing amounts of time on each function. An organization's structure and a manager's skills can impact its performance.