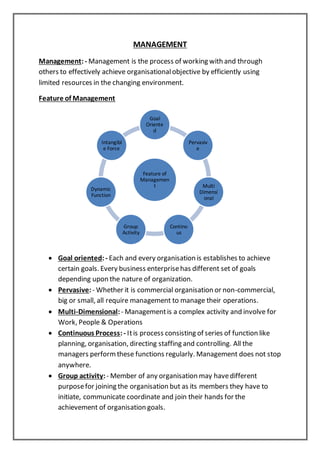
Management involves working with others to achieve organizational objectives efficiently. It is a continuous process that includes planning, organizing, staffing, directing, and controlling. Management has several key features - it is goal oriented, pervasive, multidimensional, dynamic, and an intangible force. The objectives of management include organizational objectives to maximize profits, social objectives to benefit society, and personal objectives to satisfy employee needs. Management can be viewed as an art that requires skills and creativity, a science with systematic principles, and a profession with defined roles and ethics. Management occurs at multiple levels, including top management that sets strategy, middle management that implements plans, and supervisory management that oversees operations.