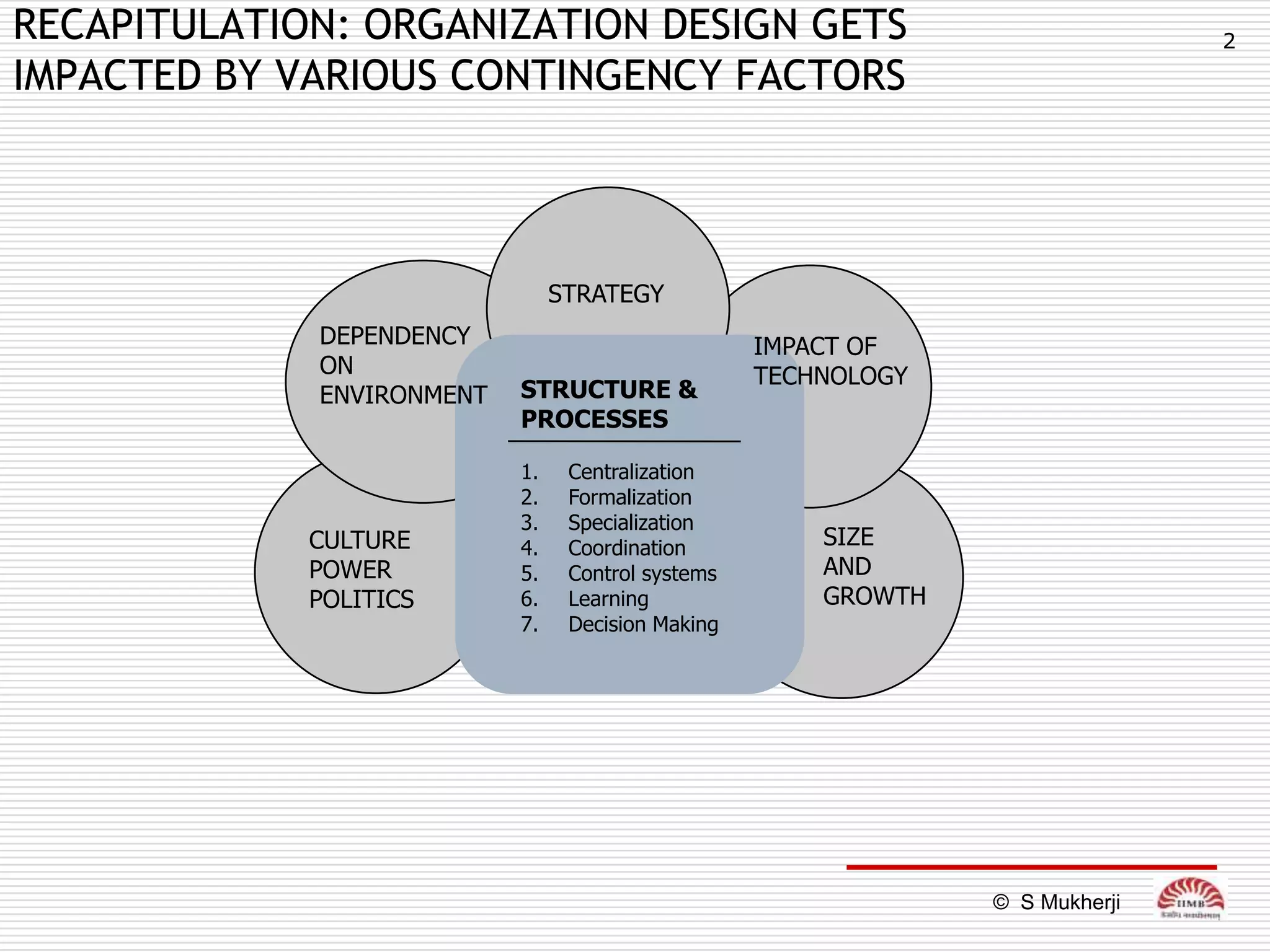
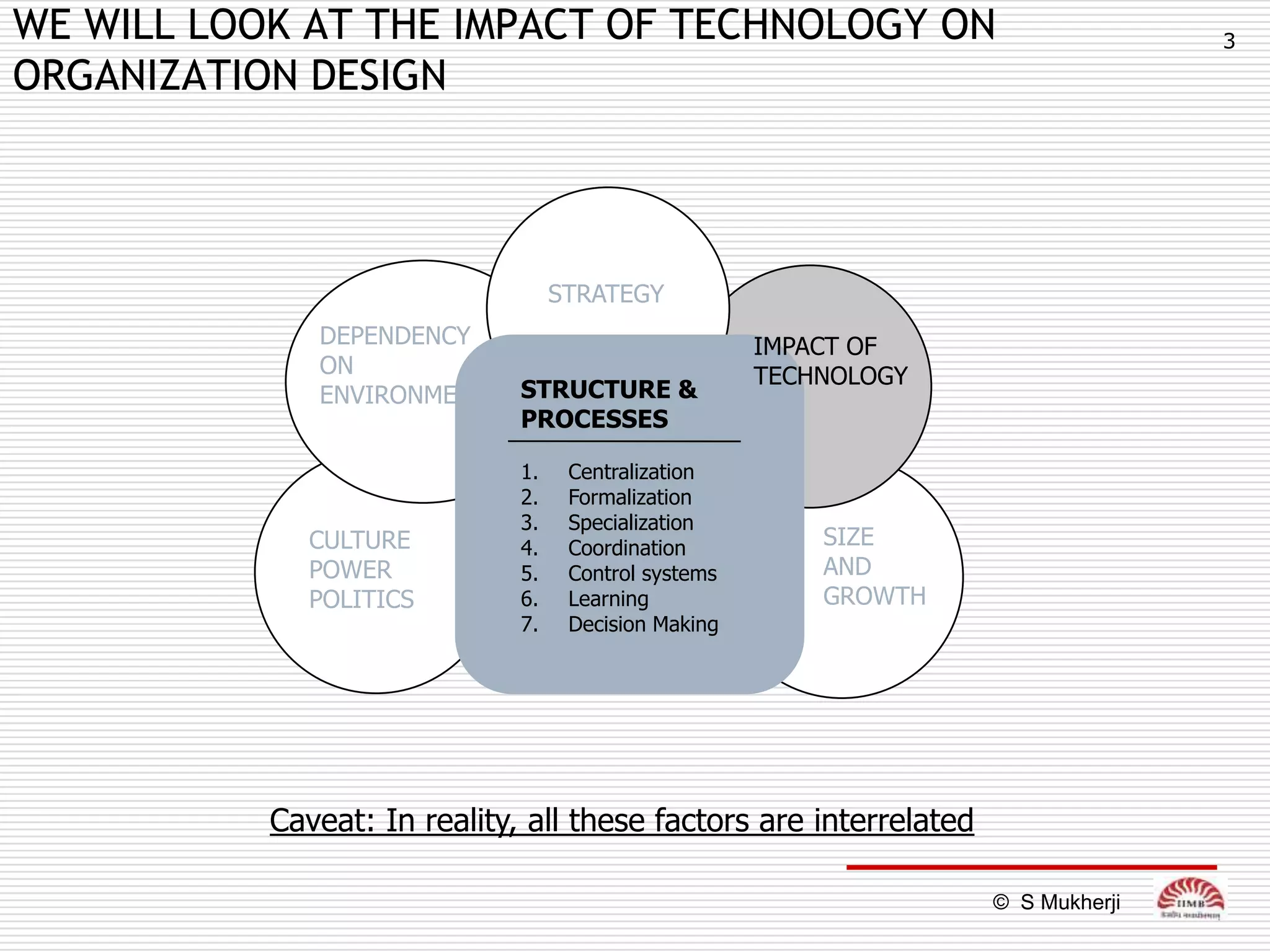
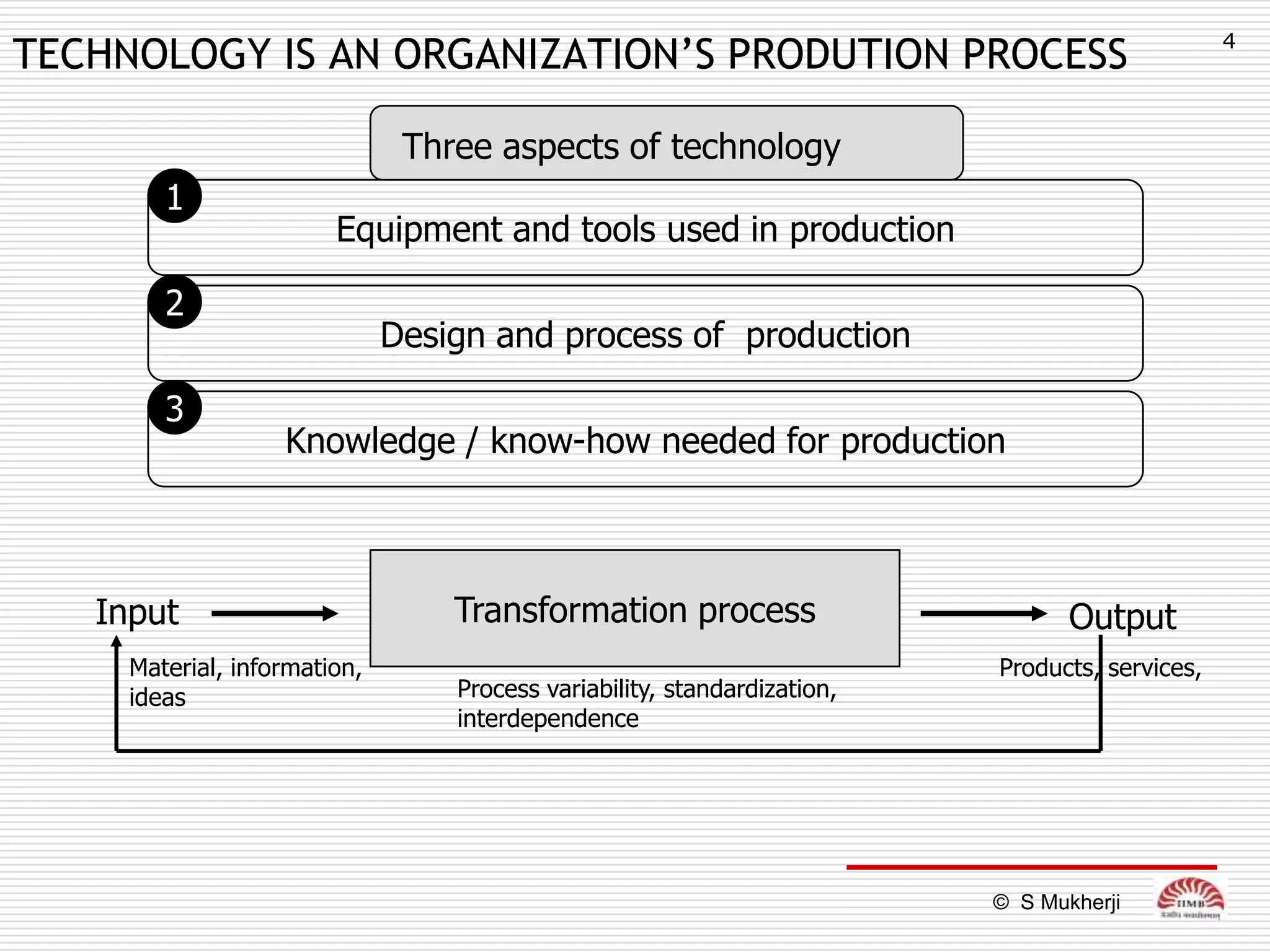
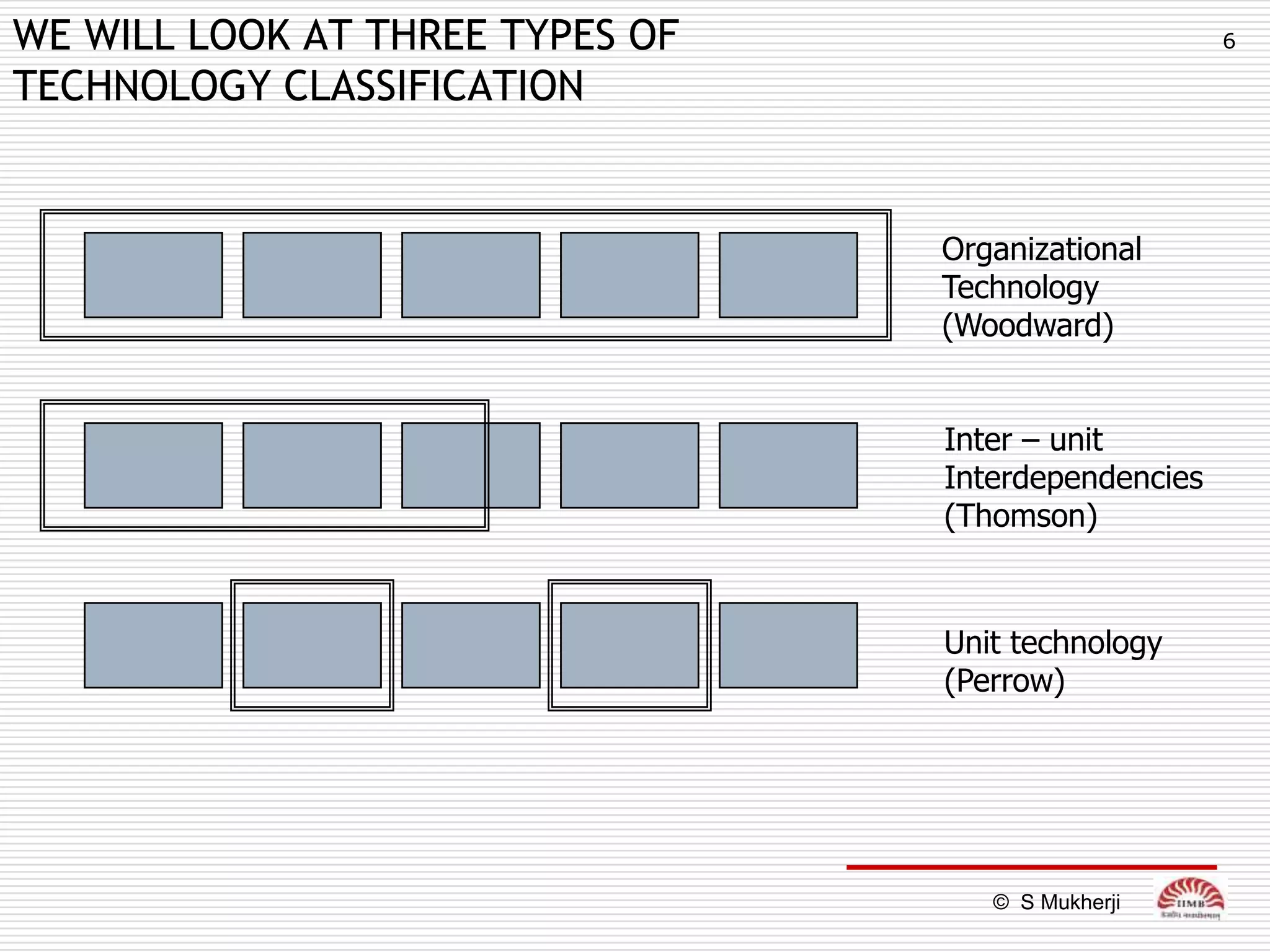
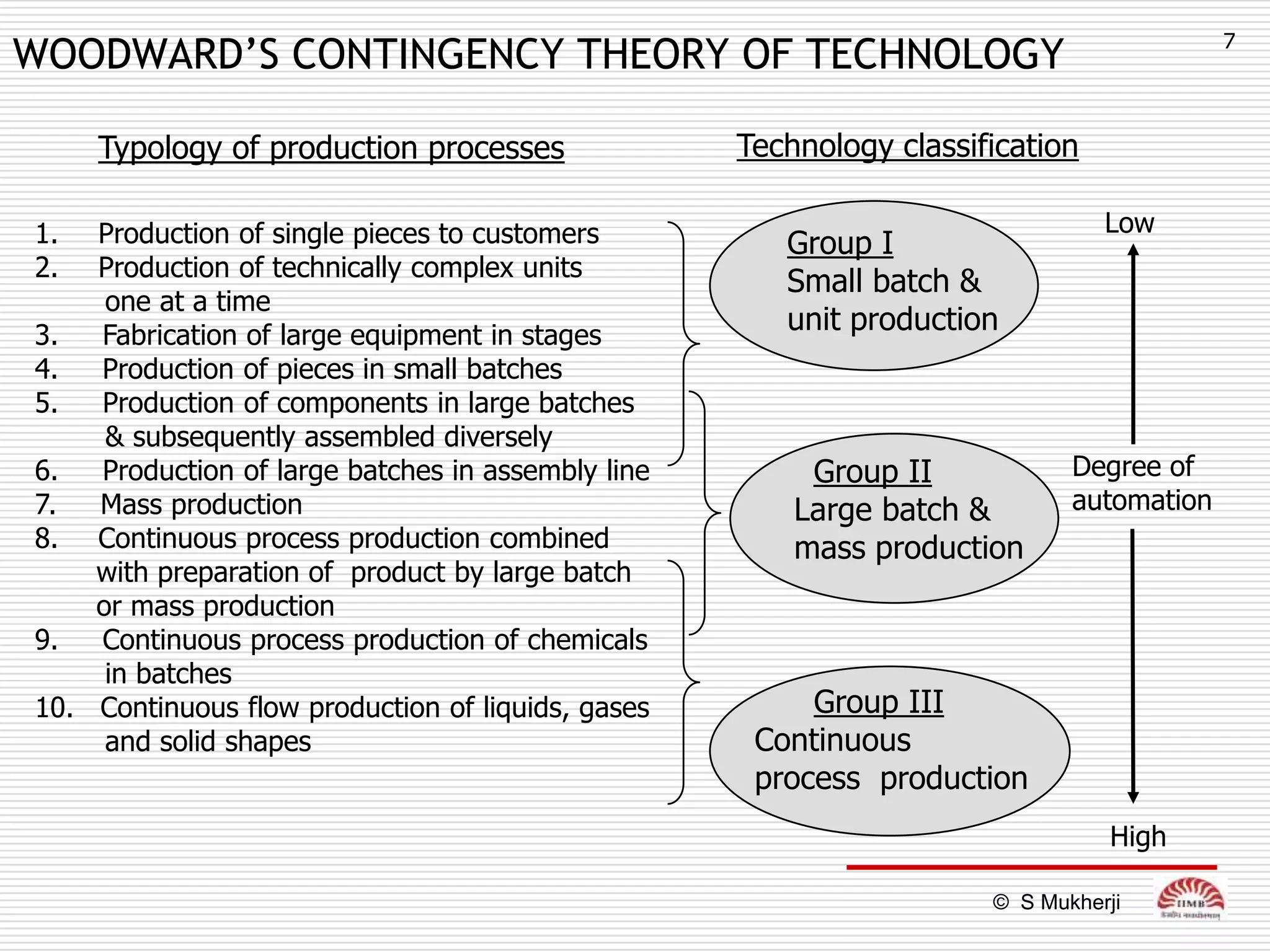
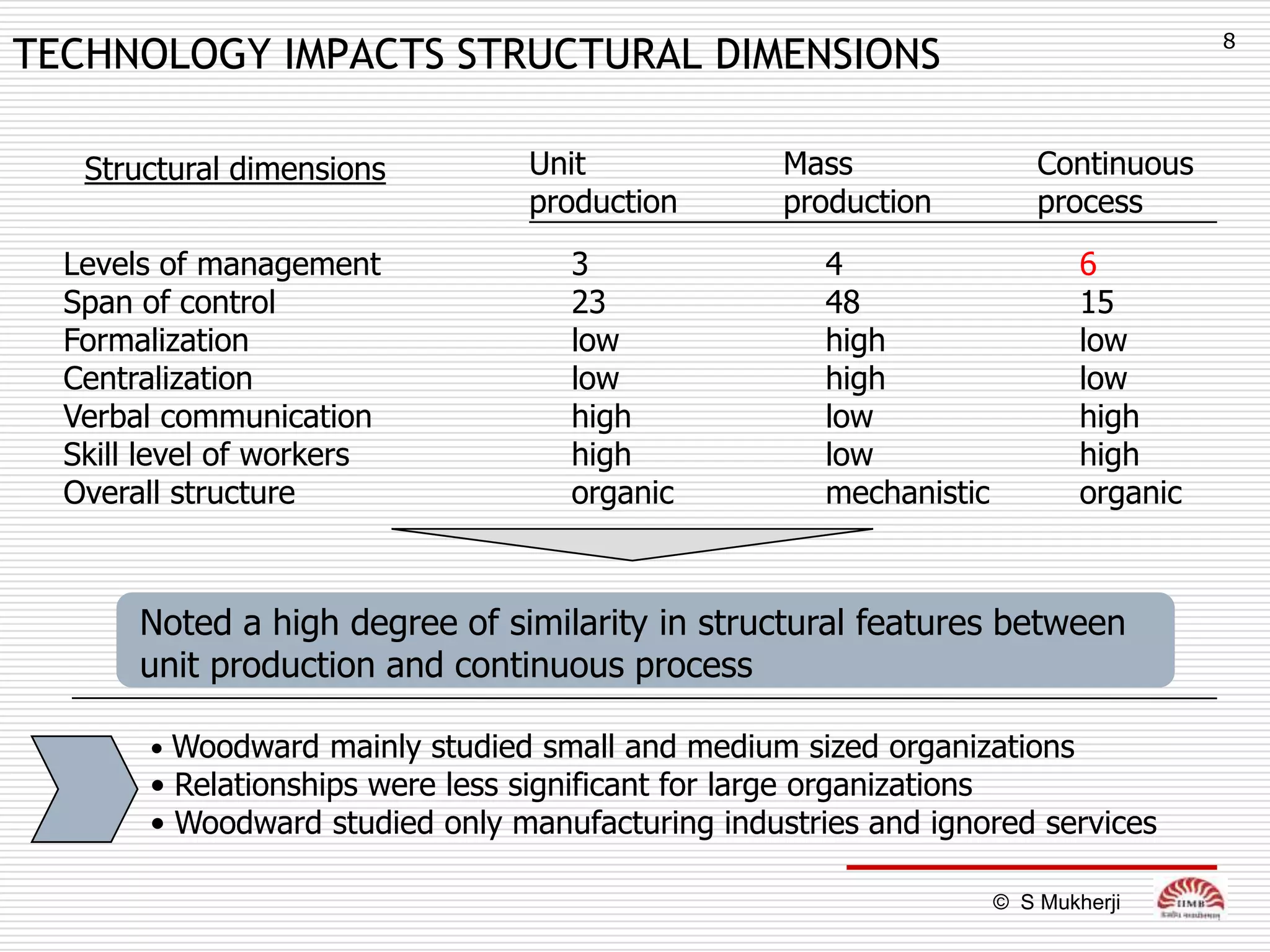
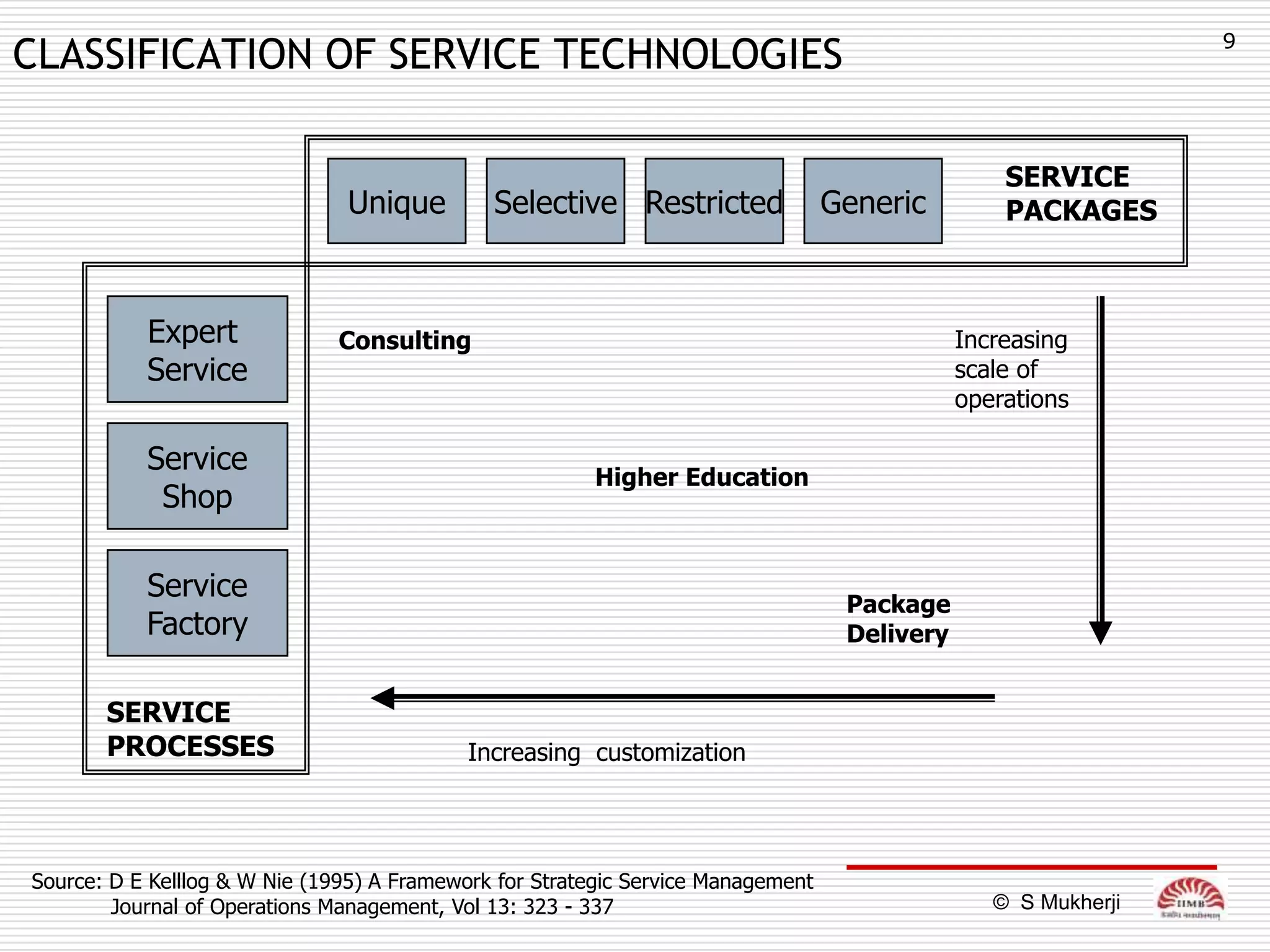
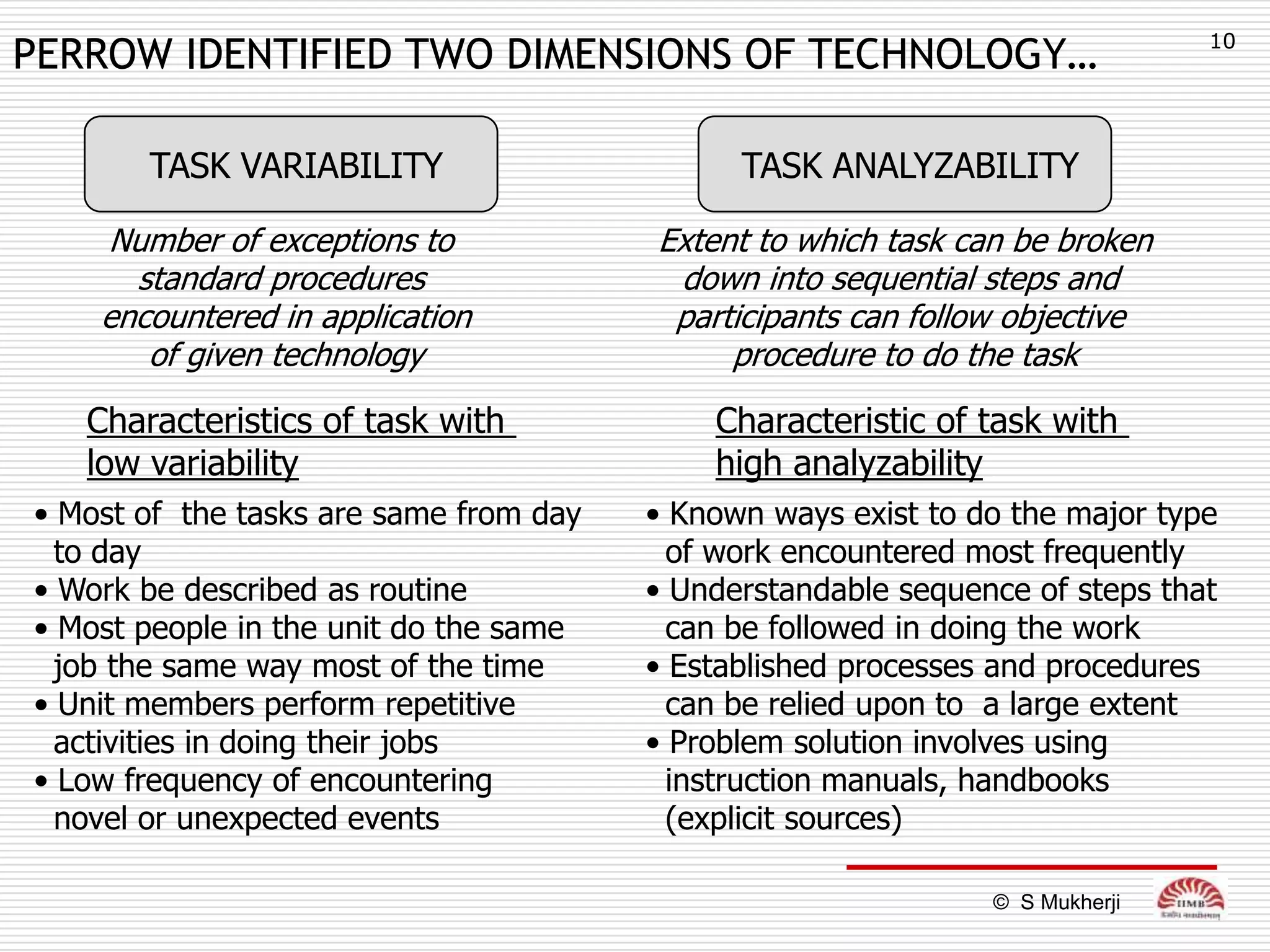
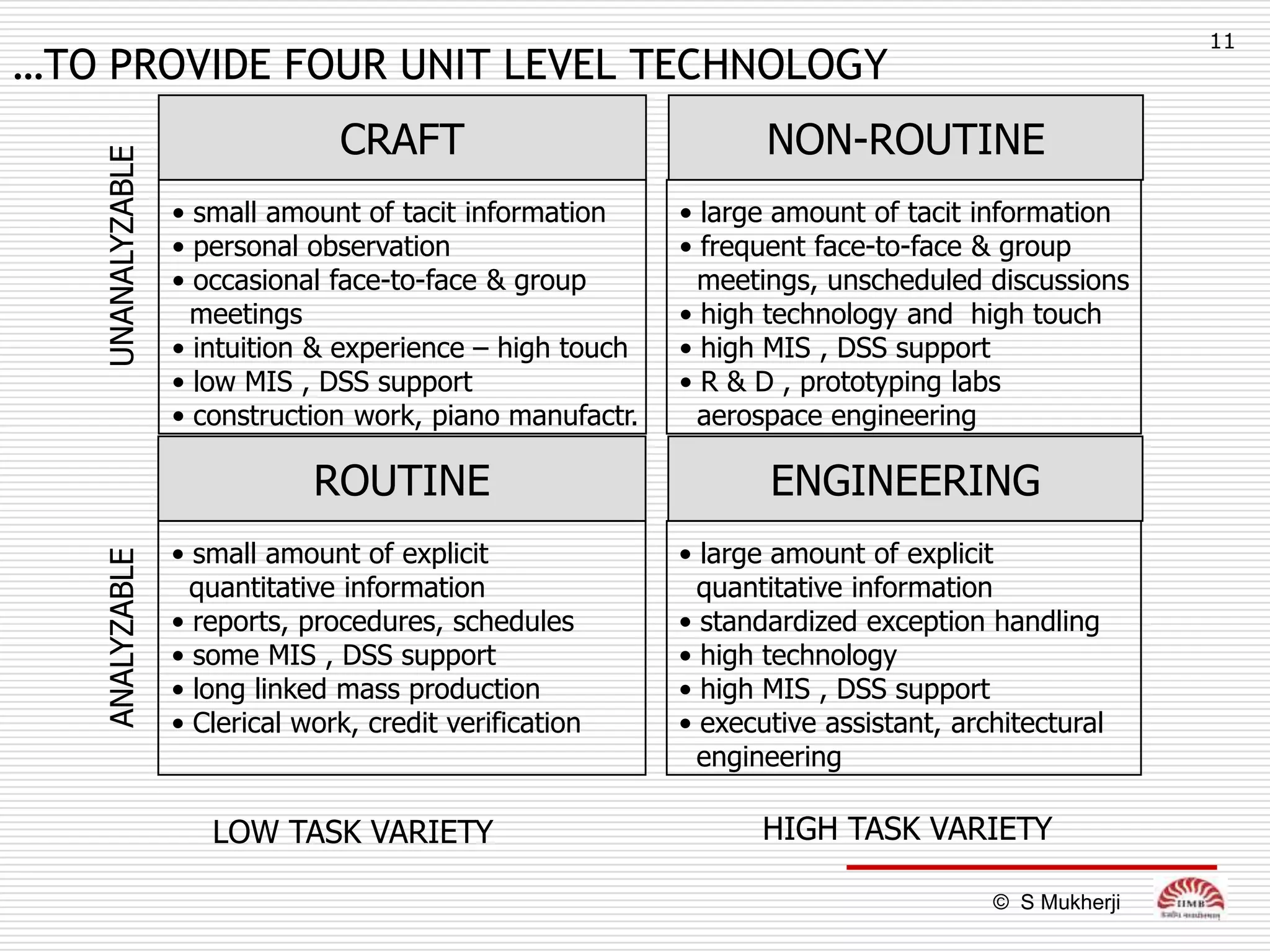
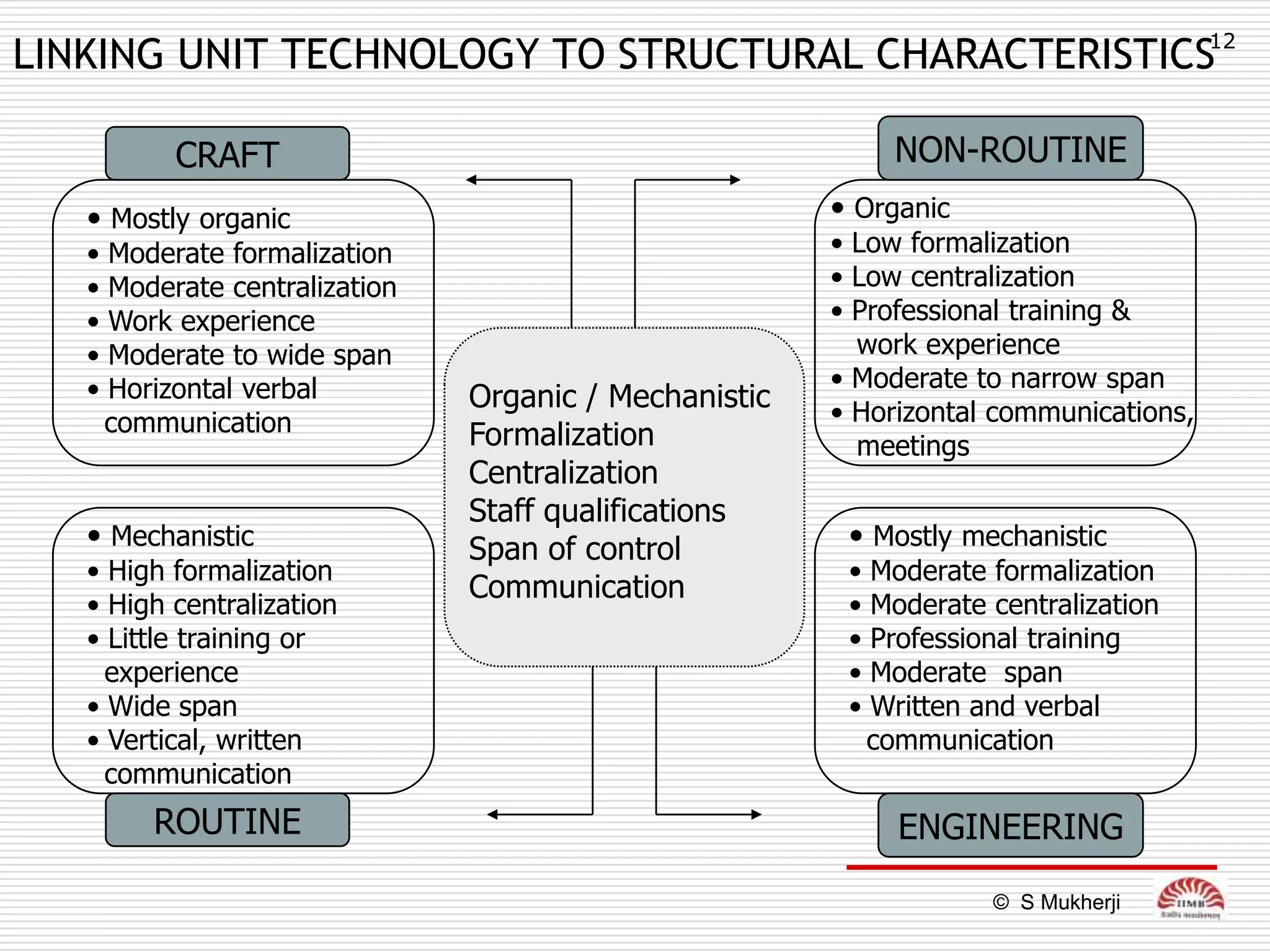
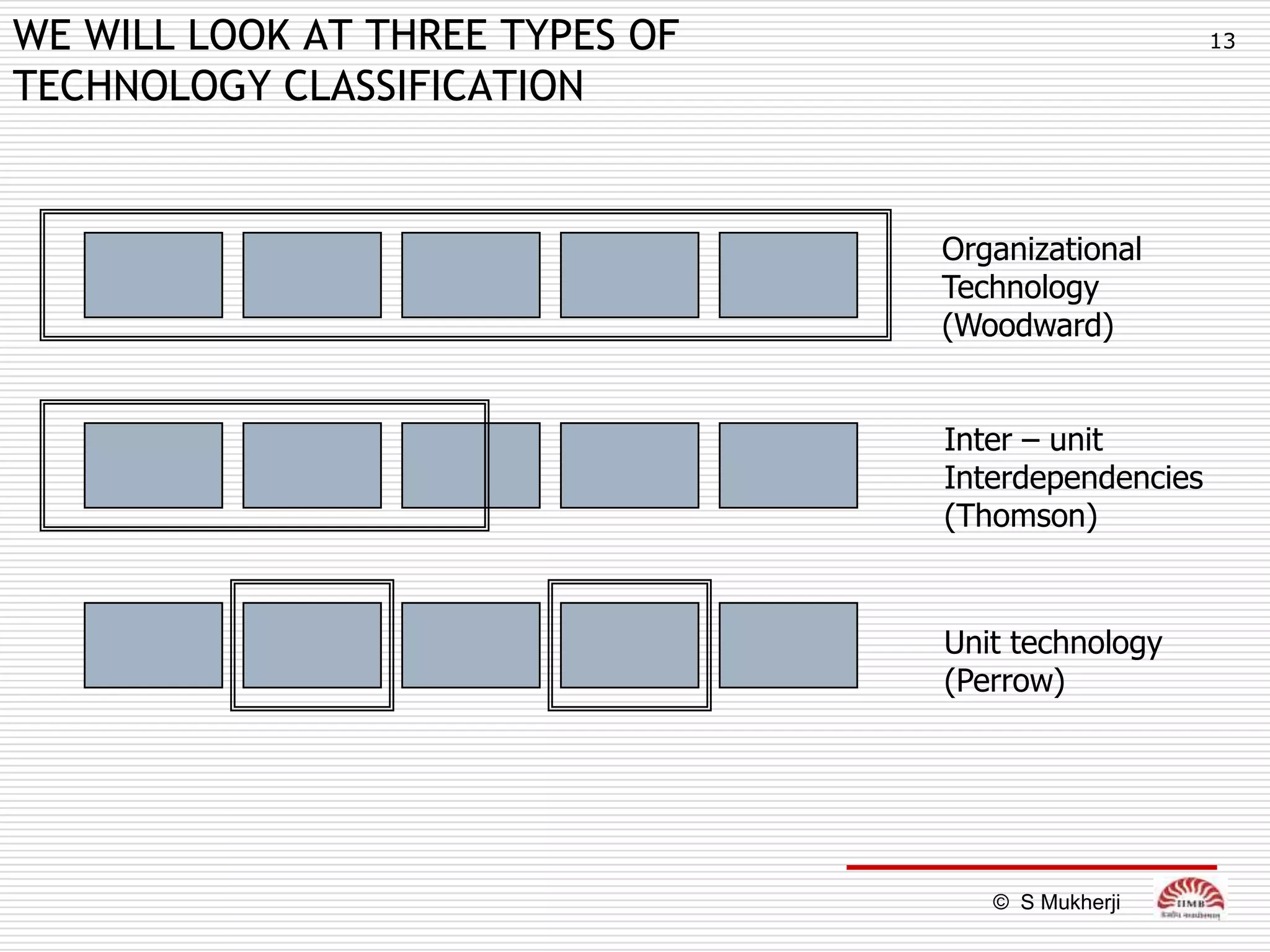
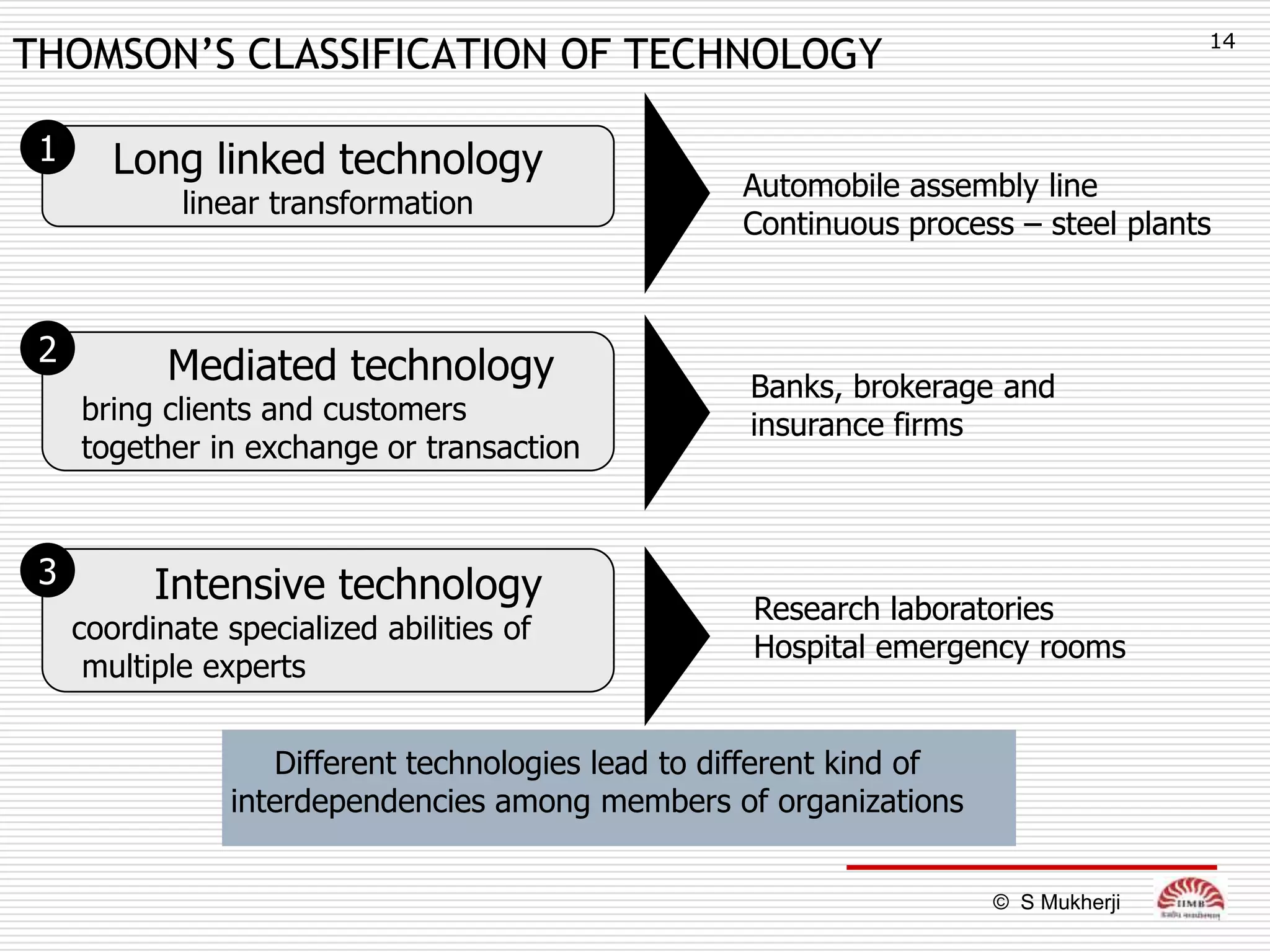
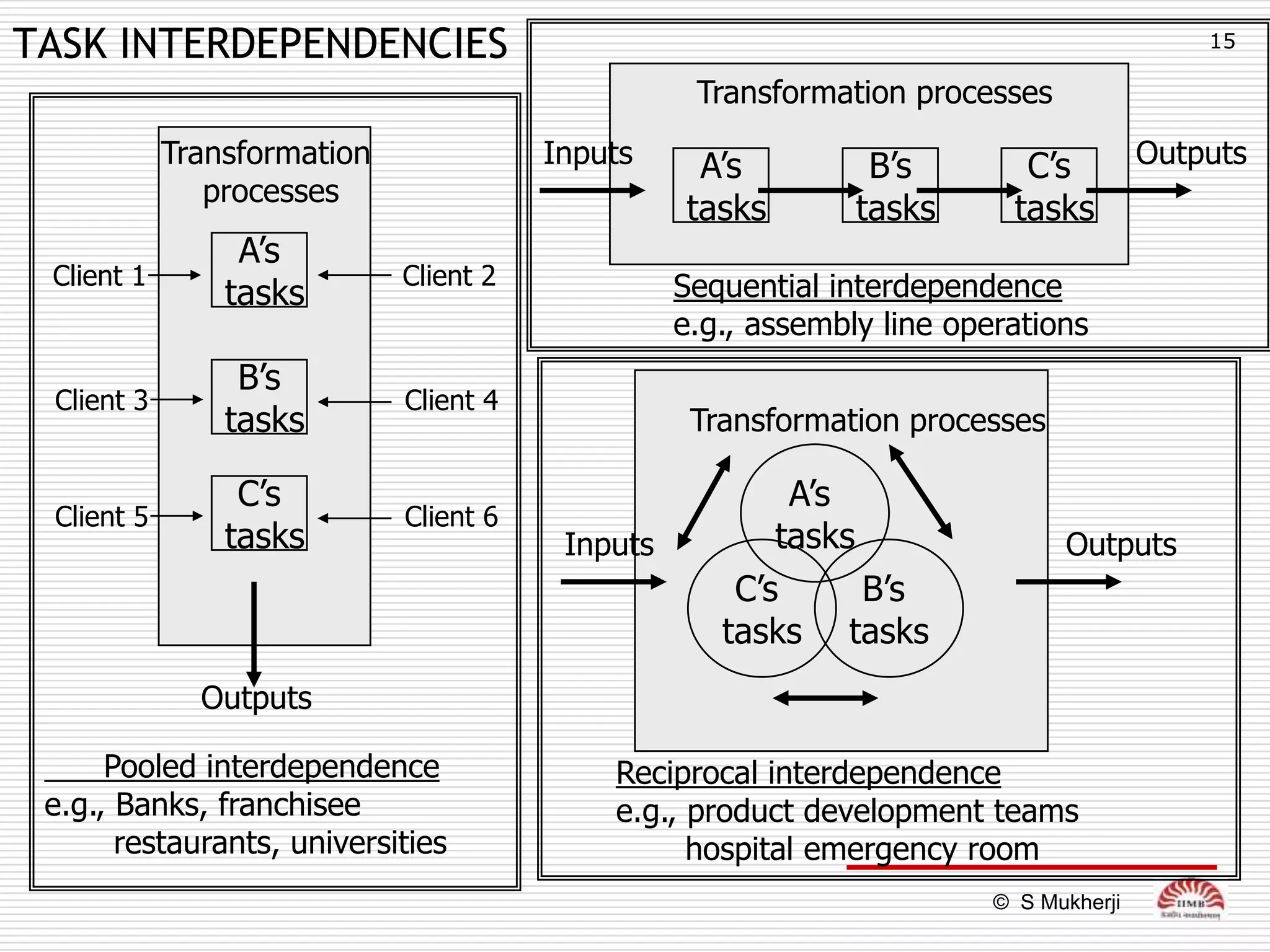
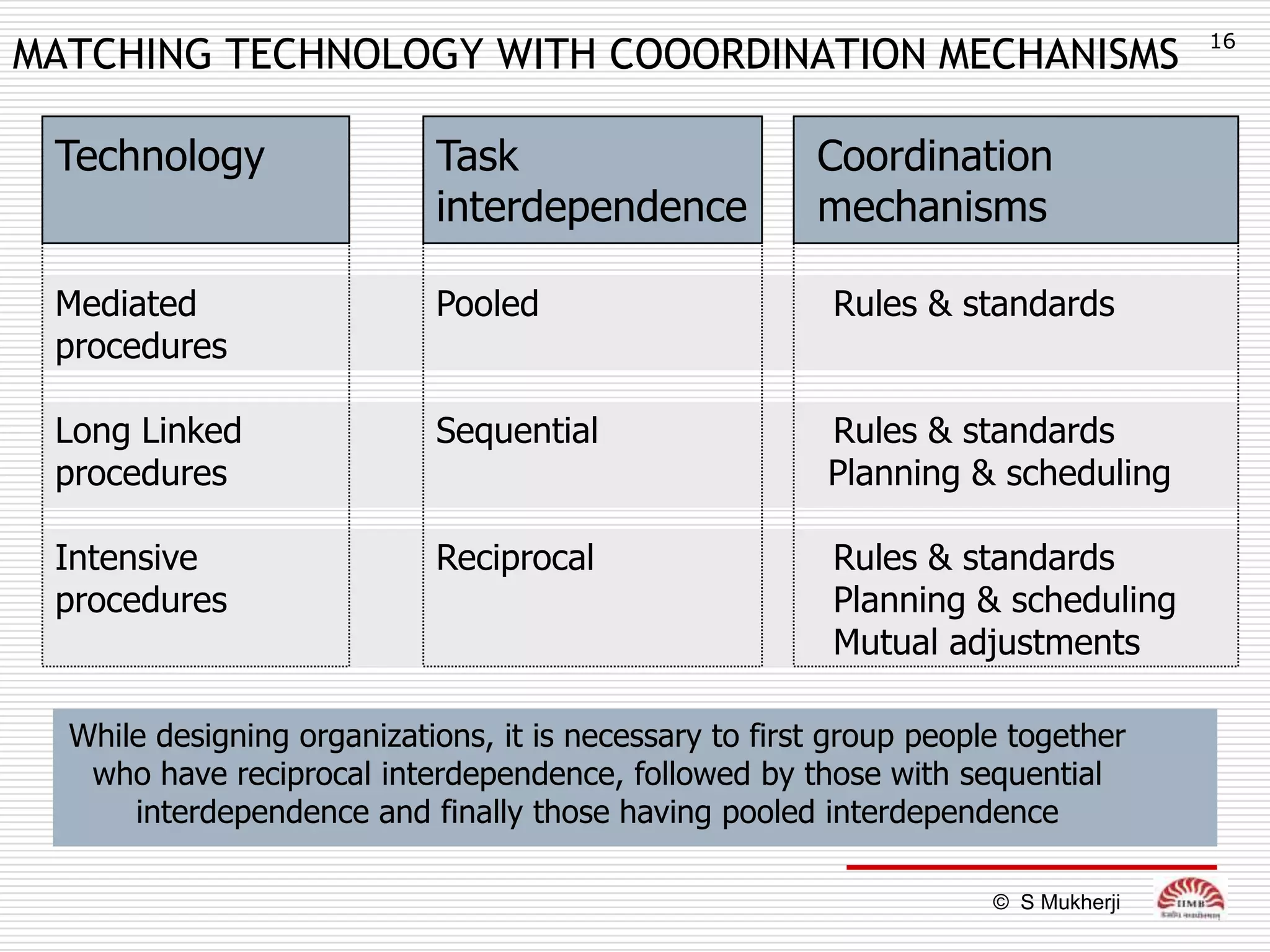
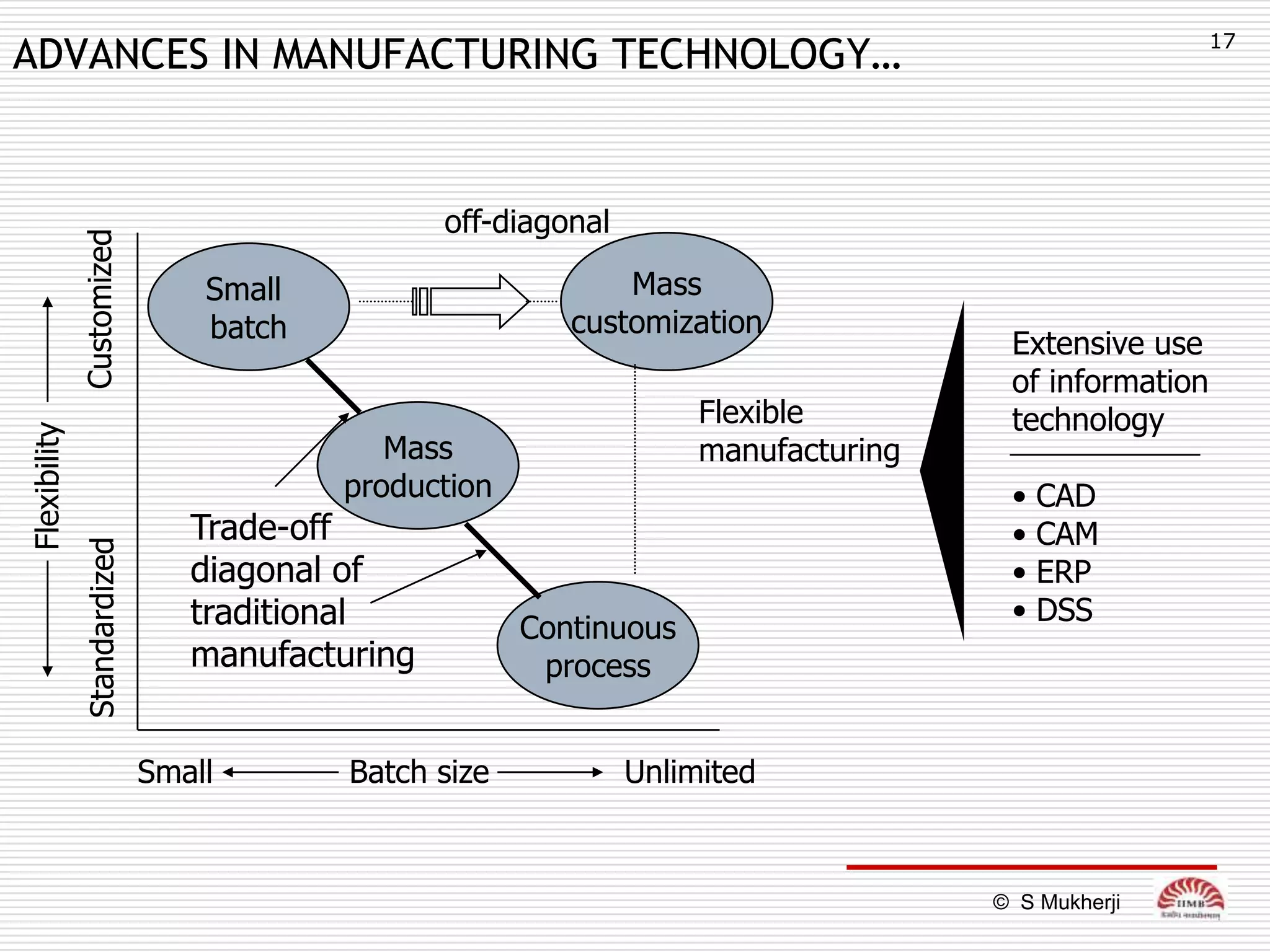
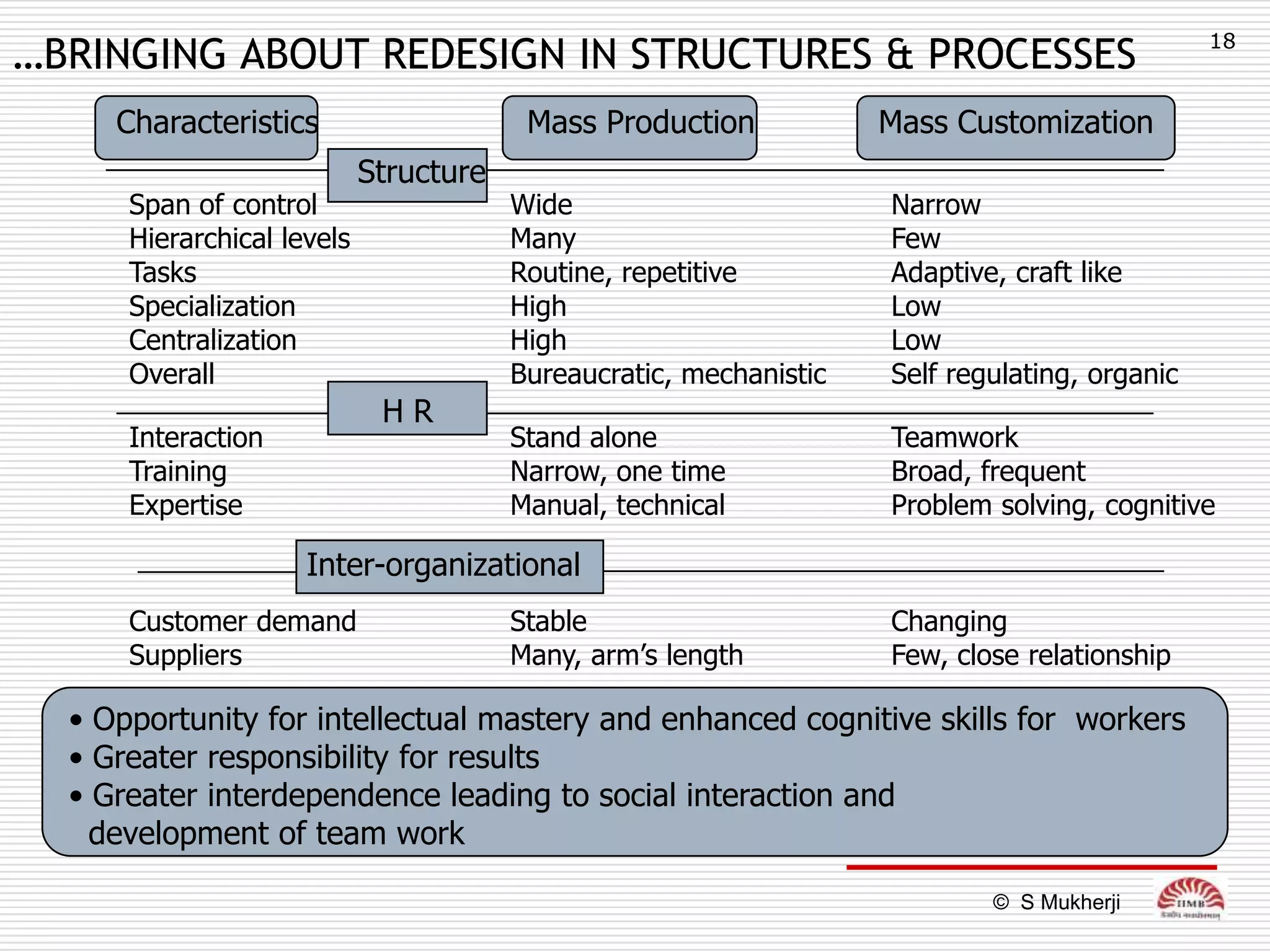
The document discusses how technology impacts organizational structure. It presents three frameworks for classifying technology: Woodward's organizational technology framework classifies production processes based on degree of automation; Thomson's framework looks at inter-unit interdependencies based on production linkages; and Perrow's framework categorizes technologies based on task analyzability and variability. The frameworks are then used to examine how different technologies require different structural designs and coordination mechanisms within organizations. Advances in manufacturing technology like customization and flexibility are also discussed in terms of their impact on redesigning organizational structures and processes.