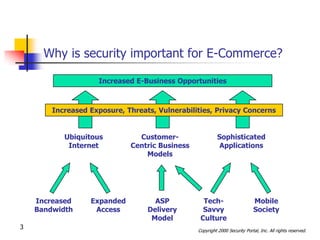
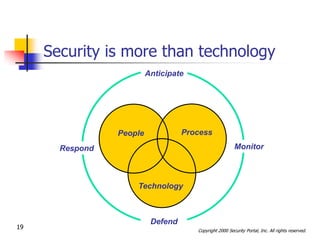
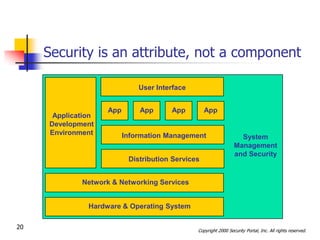
This document discusses security issues related to international e-commerce. It defines key security concepts like confidentiality, integrity, availability and accountability. It outlines general security threats to e-commerce like denial of service attacks, theft of customer data and intellectual property. The document also examines international security issues such as varying regulations, cultural differences, and mobile access challenges. It recommends taking a holistic approach to security that considers people, processes, and technology.