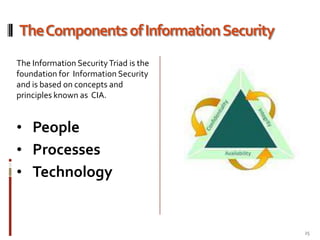
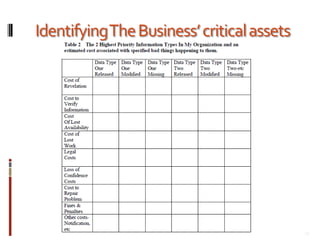
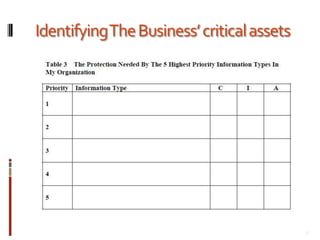
This document provides an overview of information security best practices for small businesses. It discusses the importance of information security for small businesses, common threats such as cybercrime and malicious software. It outlines the key components of information security as people, processes, and technology. It provides recommendations for security policies, backups, access controls, firewalls, software updates, and secure practices for email, wireless networks, and online activities. The document emphasizes establishing security as a foundational part of running a successful small business.