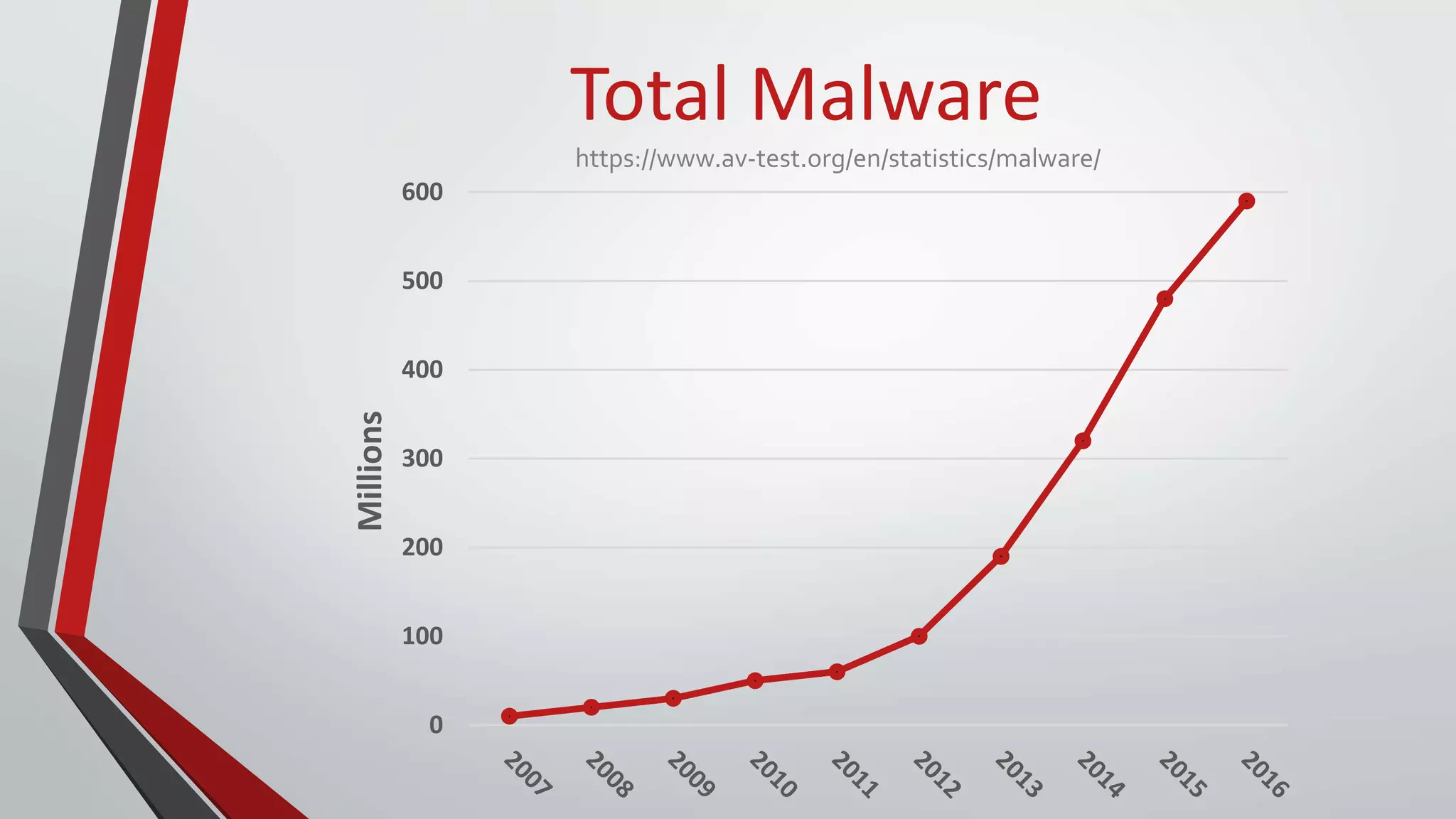
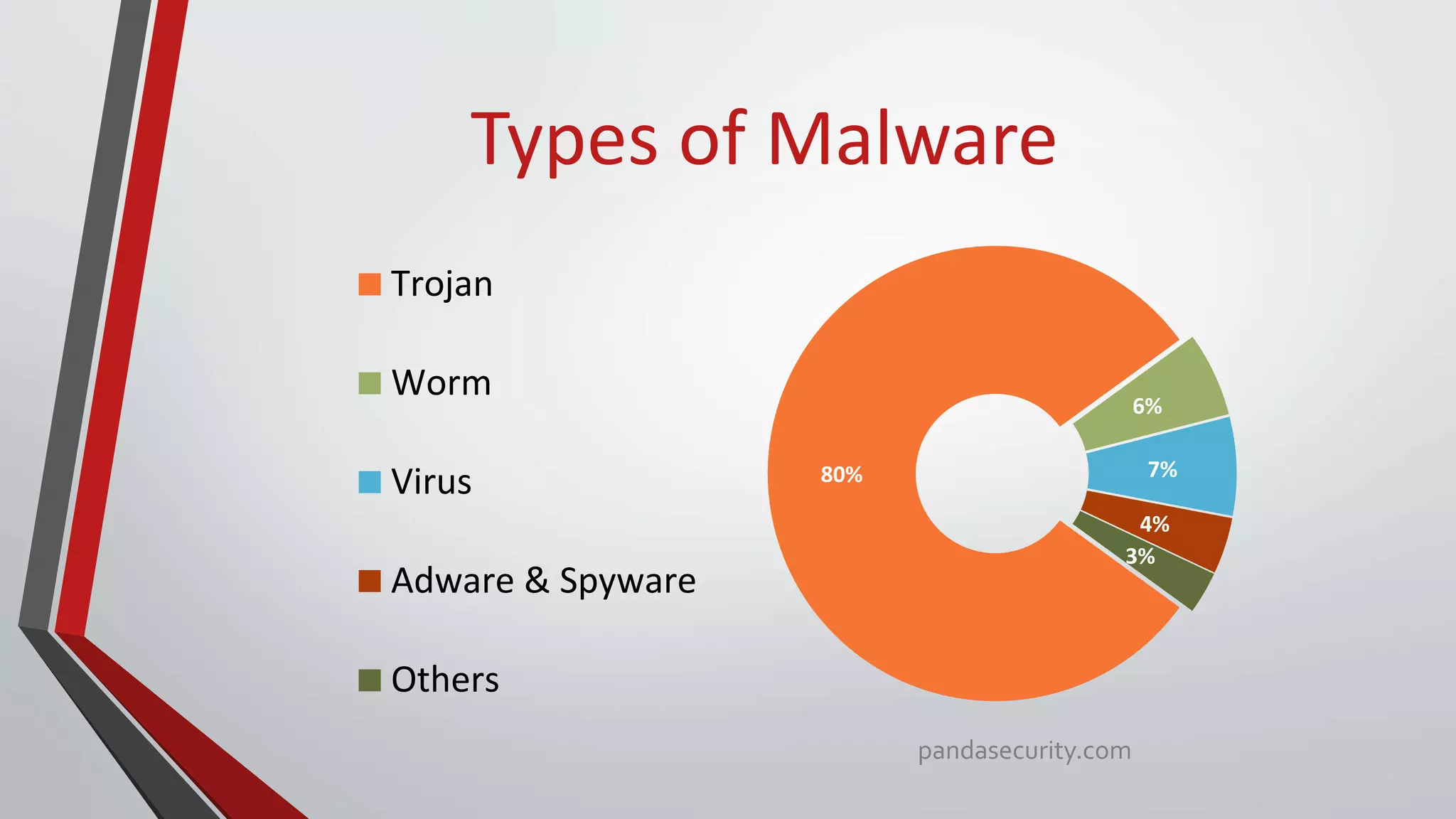
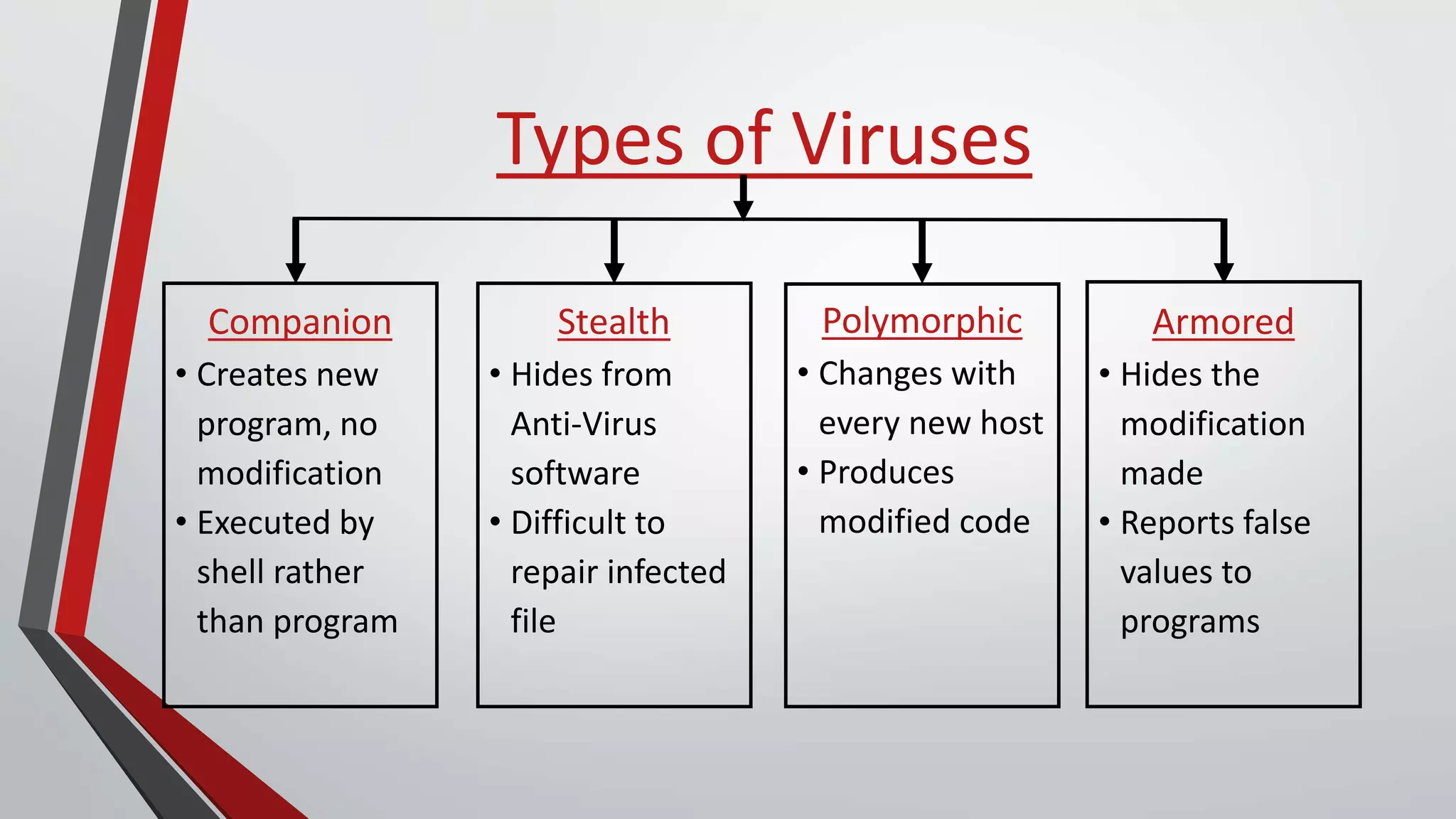
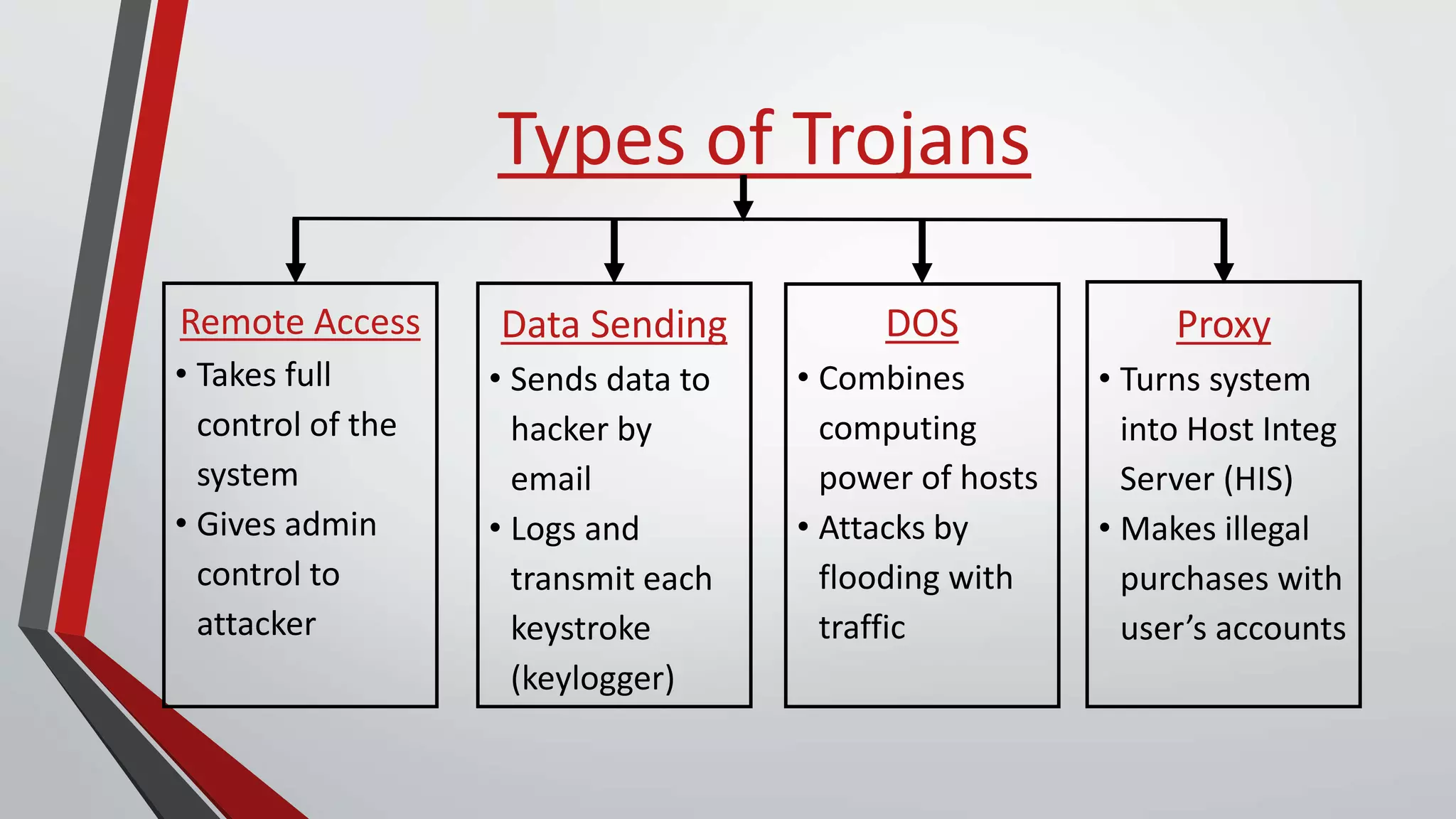
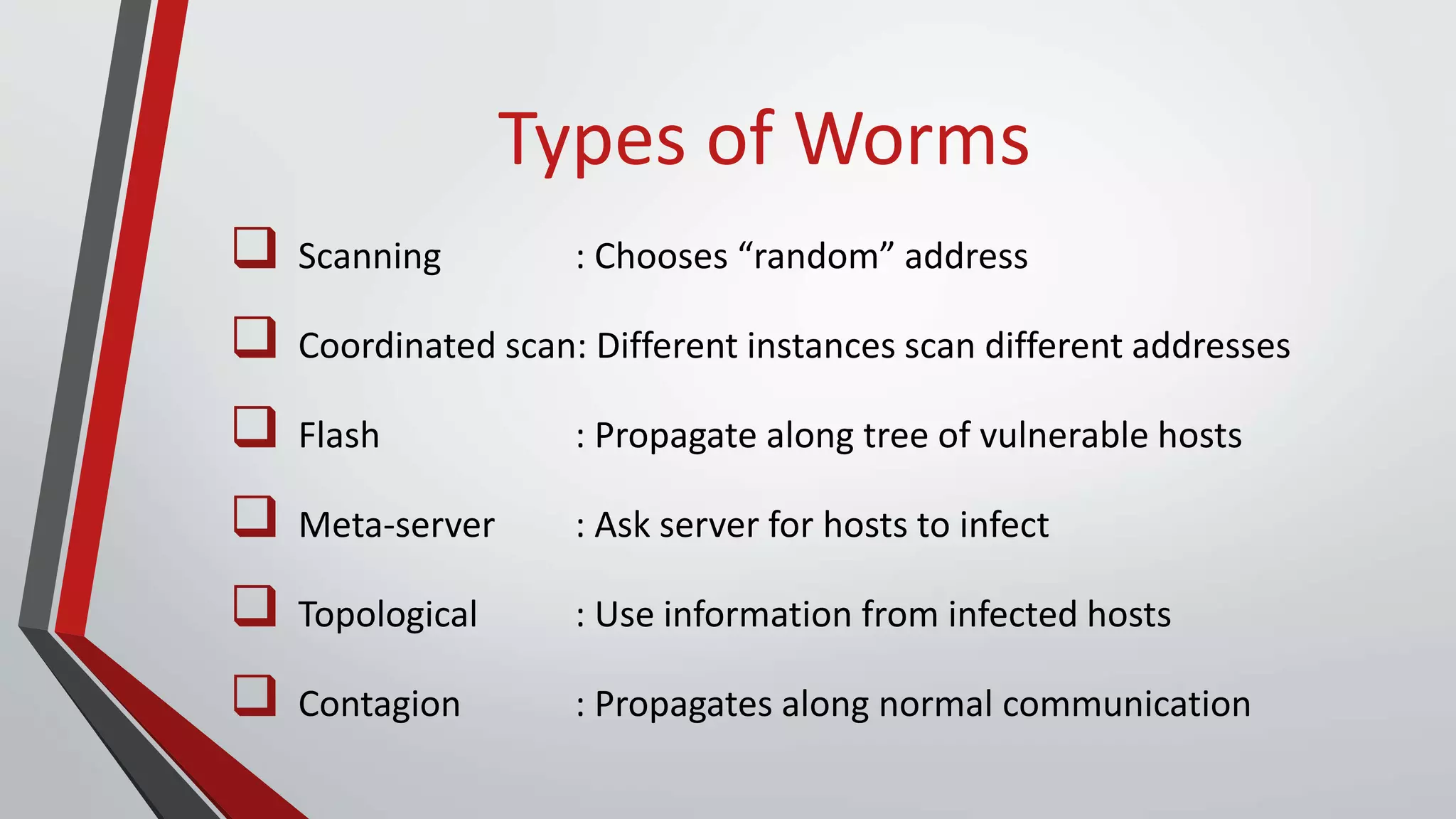
The document provides a comprehensive overview of malicious software (malware), including its history, types, and methods of spread. It details various malware types such as viruses, trojans, and worms, along with their functions and impacts on systems. The document also lists recent threats and offers security measures to protect against malware attacks.