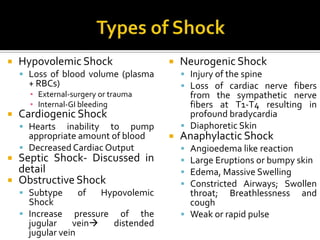
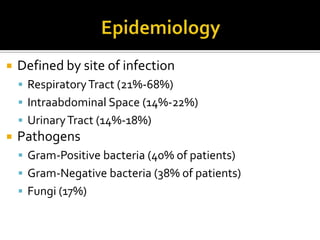
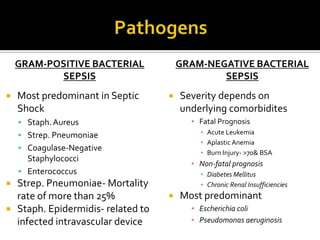
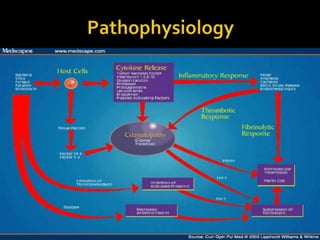
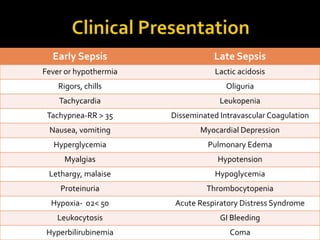
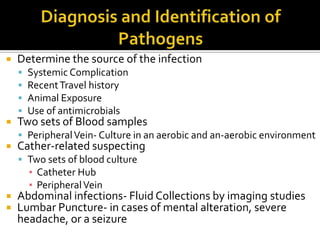
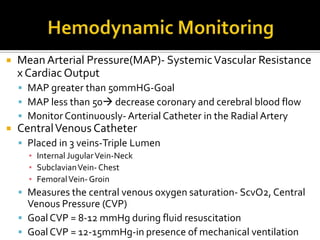
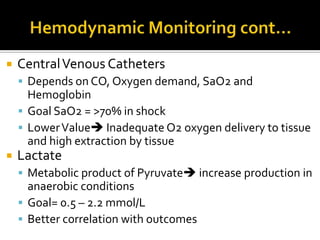
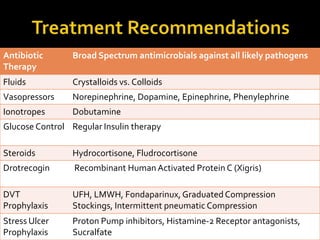
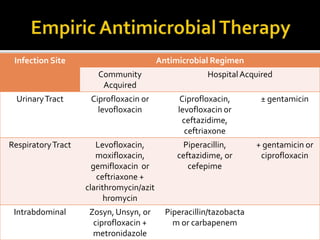
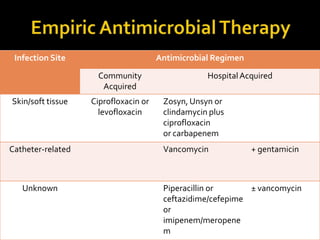
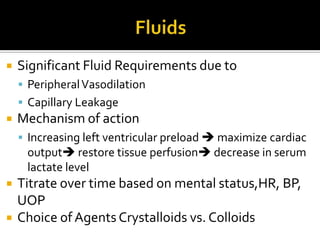
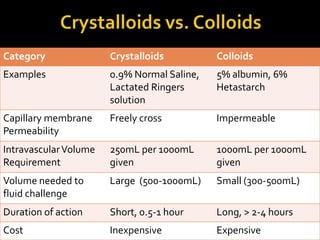
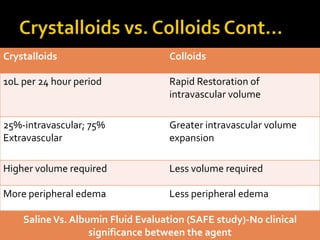
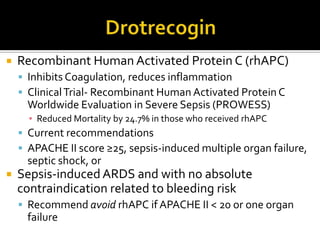
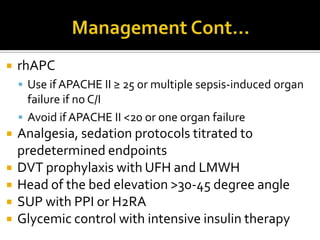
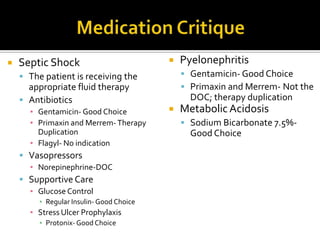
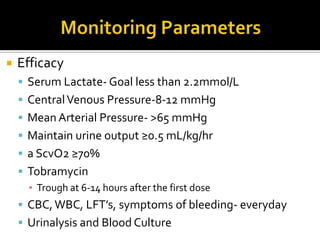
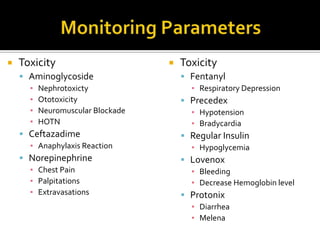
This document discusses the pharmacotherapy of septic shock. It begins with a case presentation of a 59-year-old female admitted with septic shock secondary to pyelonephritis. It then covers the epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, goals of treatment which include identifying the infection source and providing hemodynamic support. Therapeutic alternatives discussed in detail include antimicrobial therapy, hemodynamic monitoring, fluids, inotropes and vasopressors.