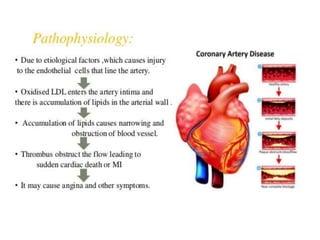
The document presents a case study of a 58-year-old male patient diagnosed with coronary artery disease (CAD) after experiencing symptoms such as shortness of breath, palpitations, and angina. Key findings from lab and diagnostic tests indicate risk factors like hypertension, diabetes, and obesity, and emphasize treatment options including pharmacological therapies and lifestyle modifications. The document also outlines drug interactions and patient counseling on managing CAD and prescribed medications.