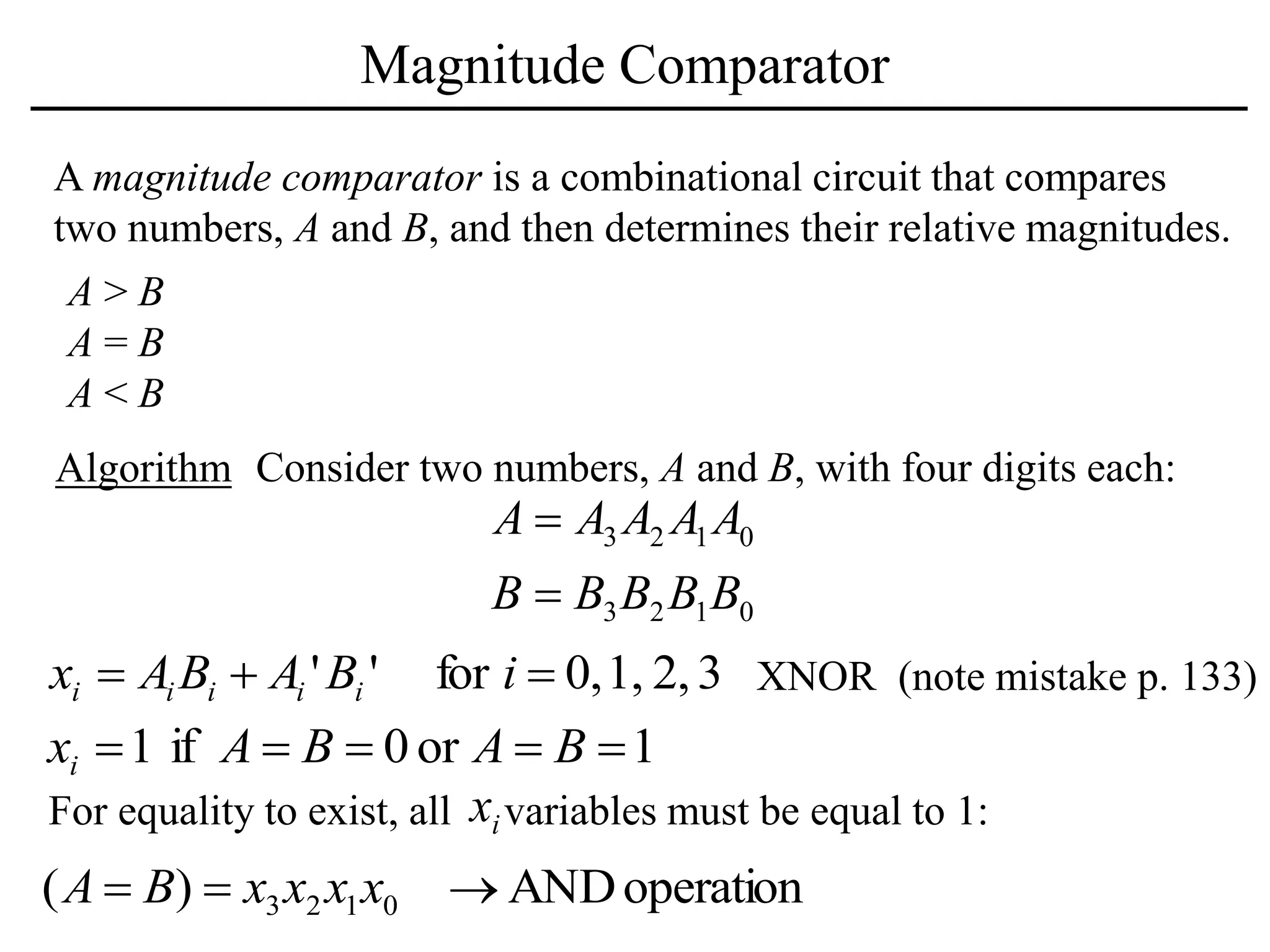
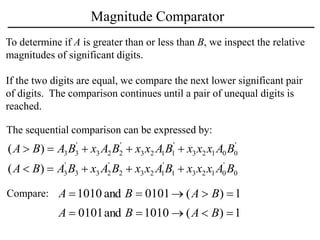
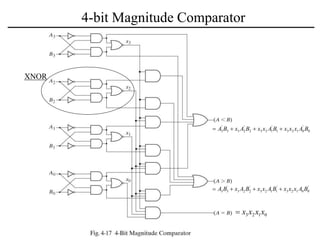
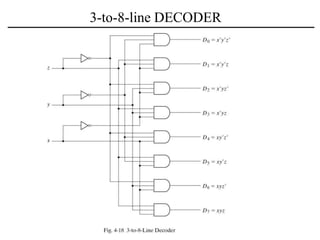
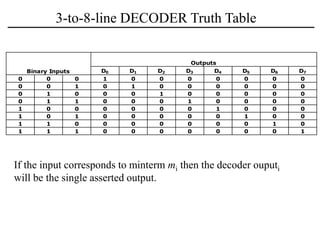
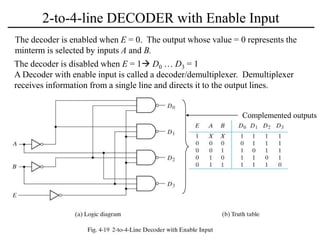
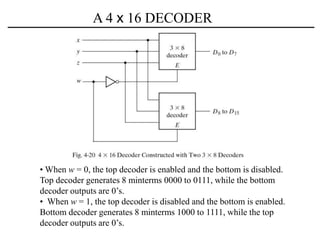
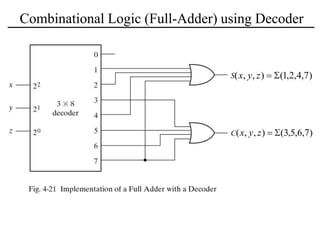
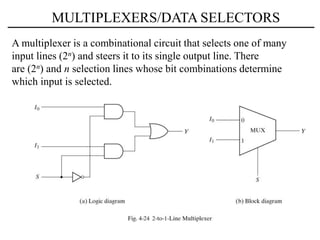
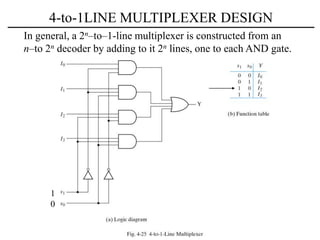
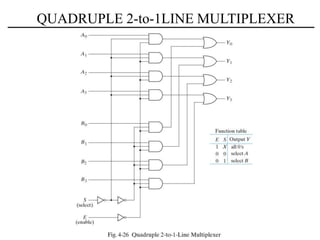
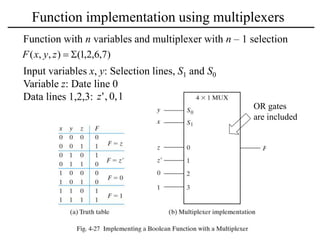
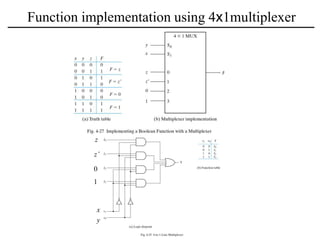
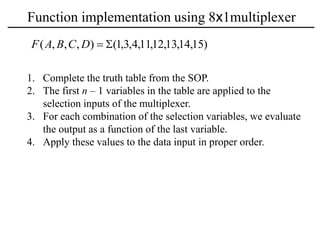
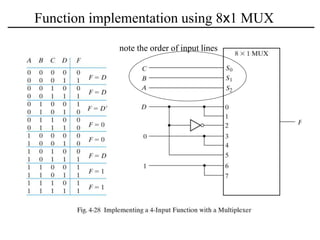
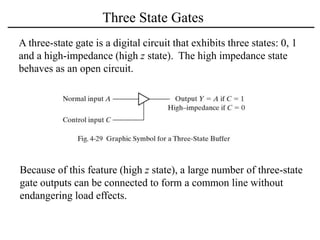
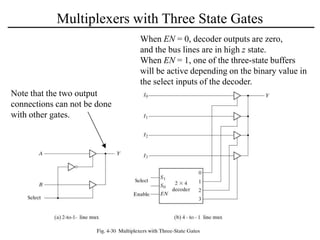
The document discusses a magnitude comparator, which is a combinational circuit that compares two numbers and determines if the first number is greater than, less than, or equal to the second number. It explains how the comparator works by sequentially comparing pairs of digits from the most significant to the least significant. The document also discusses decoders, which convert binary inputs to unique outputs, and multiplexers, which select one of several inputs and output it. Three-state gates are introduced, which can output 0, 1, or a high-impedance state, allowing multiple outputs to be connected without interference.